17 March 2025
Threat landscape for industrial automation systems. Regions, Q4 2024
Q4 overview
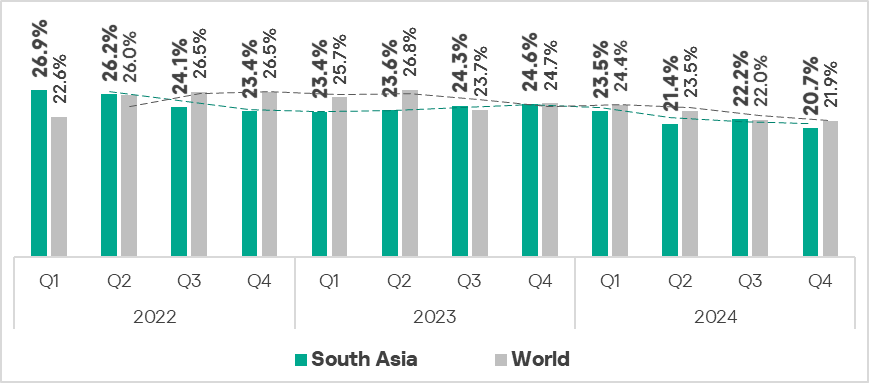
Percentage of ICS computers
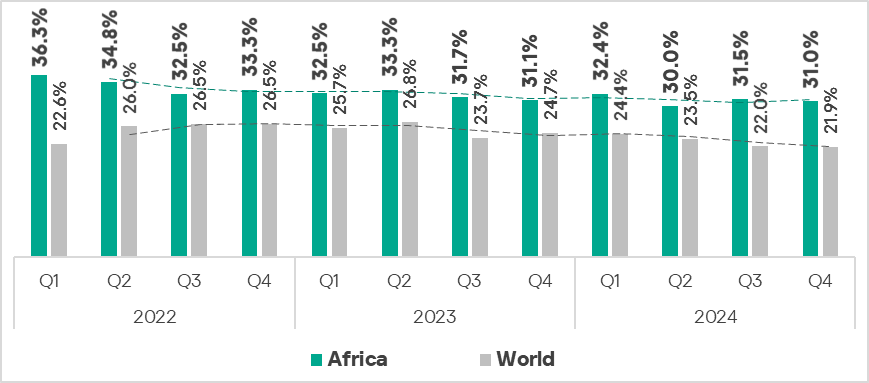
In the fourth quarter of 2024, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked decreased by 0.1 pp from the previous quarter to 21.9%.
Regionally, the percentage of ICS computers that blocked malicious objects during the quarter ranged from 10.6% in Northern Europe to 31% in Africa.
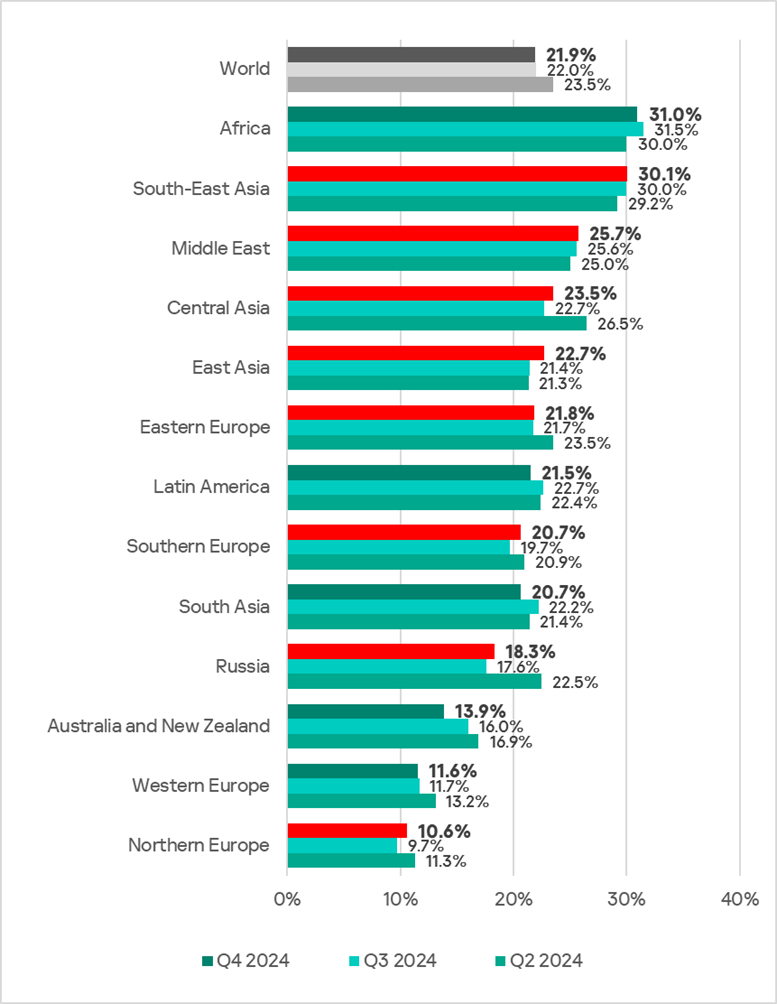
All regions ranked by percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked in the fourth quarter can be divided into three groups:
|
Over 25%
|
In the regions within this group, OT computers are generally overexposed to cyberthreats. There is underinvestment in cybersecurity, both in terms of tools and measures, as well as in addressing the shortage of experts, fostering a strong cybersecurity culture, and raising awareness. |
|
20–25%
|
The regions within this group may face specific challenges in isolating their OT infrastructure from potential cyberthreats. |
|
Up to 20%
|
The third group consists of regions that are the safest in terms of keeping their OT infrastructure isolated from cyberthreats. |
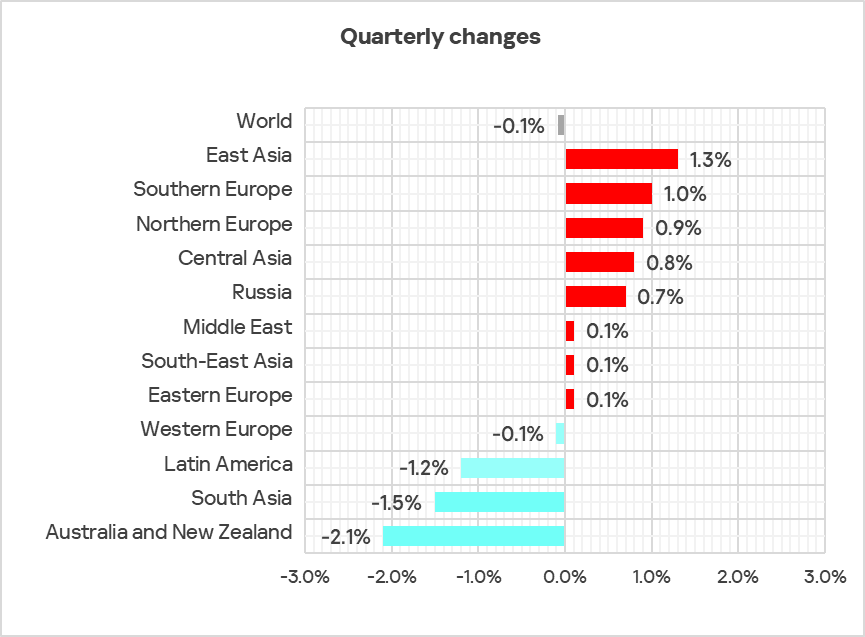
Compared to the third quarter, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked during the fourth quarter has increased in eight regions.
Malicious object categories
Malicious objects used for initial infection
Malicious objects that are used for initial infection of ICS computers include dangerous internet resources that are added to denylists, malicious scripts and phishing pages, and malicious documents.
By the logic of cybercriminals, these malicious objects can spread easily. As a result, they are blocked by security solutions more often than anything else. This is reflected in our statistics.
Typical attacks blocked within an OT network are a multi-stage process, where each subsequent step of the attackers is aimed at increasing privileges and gaining access to other systems by exploiting vulnerabilities in OT systems and networks.
It is worth noting that during the attack, intruders often repeat the same steps (TTP), especially when they use malicious scripts and established communication channels with the management and control infrastructure (C2) to move horizontally within the network and advance the attack.
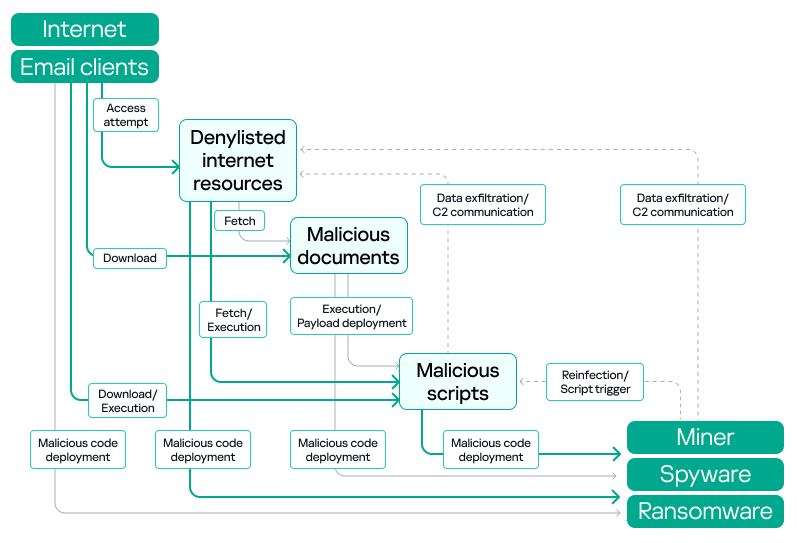
Globally and in almost all regions, denylisted internet resources and malicious scripts and phishing pages are the top categories of malicious objects in terms of the percentage of ICS computers on which these objects were blocked.
The sources of the majority of malicious objects used for initial infection are the internet and email.
In Q4 2024, Africa, South-East Asia, and the Middle East ranked as the top three regions by the percentage of ICS computers on which threats from the internet were blocked.
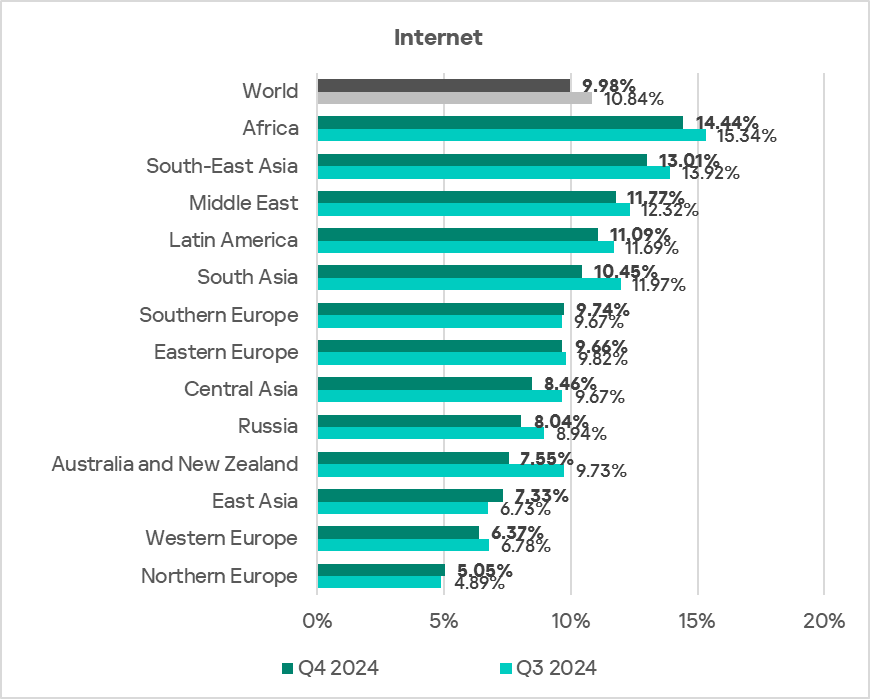
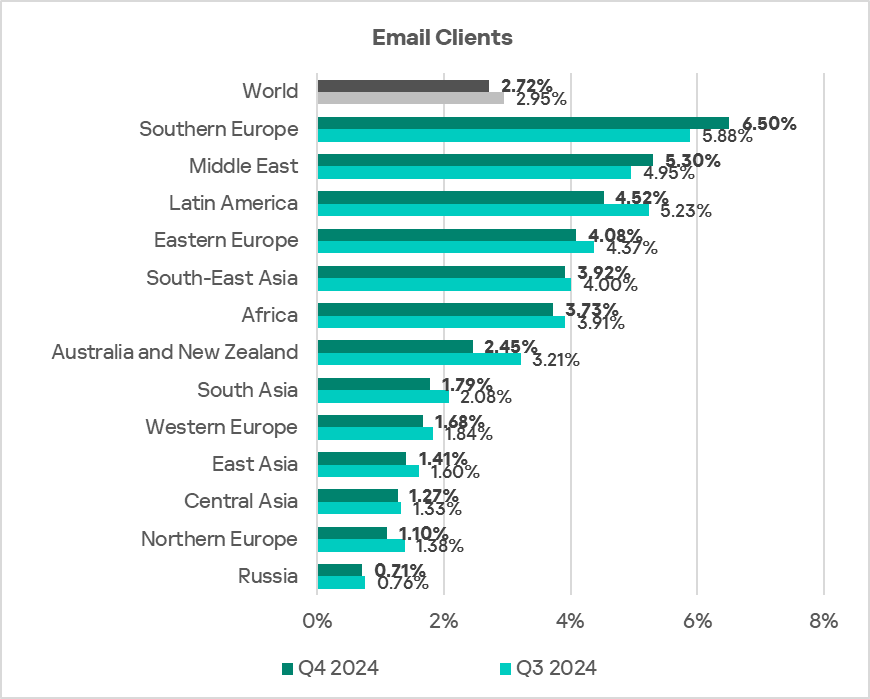
The top three regions with the highest email threat rates were Southern Europe, the Middle East, and Latin America.
Denylisted internet resources
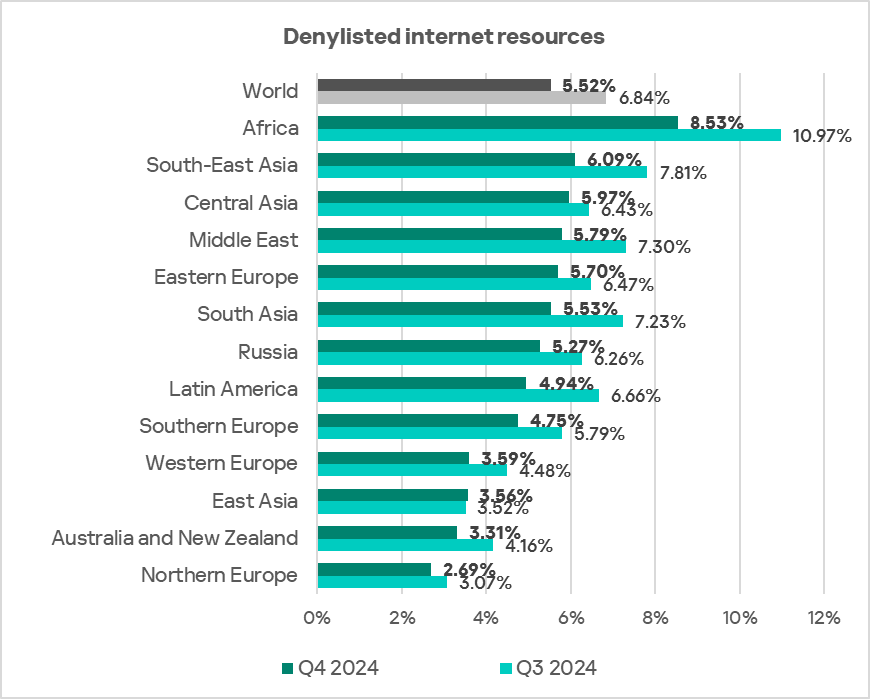
Africa, South-East Asia, and Central Asia ranked as the top three regions by the percentage of ICS computers on which denylisted internet resources were blocked.
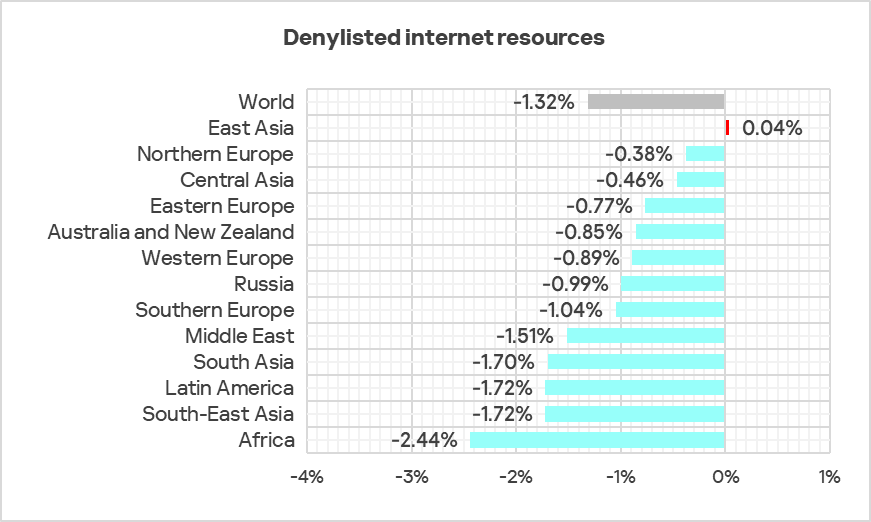
All regions, except East Asia, saw a decrease in the percentage of ICS computers on which denylisted internet resources were blocked.
As previously noted in the Q3 2024 report, the increase in blocked denylisted internet resources was primarily driven by an increase in the number of newly created domain names and IP addresses used by cybercriminals as command and control (C2) infrastructure for distributing malware and phishing attacks.
The decline in the percentage of denylisted internet resources in November-December 2024 was likely influenced not only by proactive threat mitigation measures at various levels – from resource owners and hosting providers to ISPs and law enforcement agencies. Another contributing factor was the tendency of attackers to frequently change domains and IP addresses to evade detection in the initial stages, based on lists of known malicious resources.
In practice, this means that until a malicious web resource is identified and added to a denylist, it may not immediately appear in threat statistics, leading to an apparent decrease in the percentage of ICS computers on which such resources were blocked.
However, in Q4, we also saw a rise in the percentage of the next steps in the attack chain – malicious scripts and phishing pages, spyware, and ransomware.
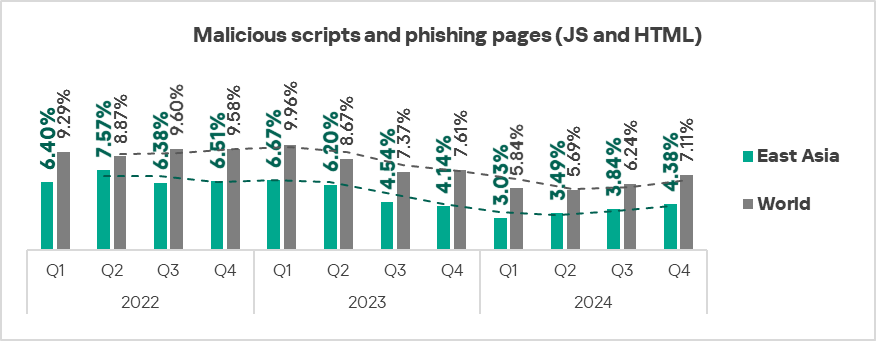
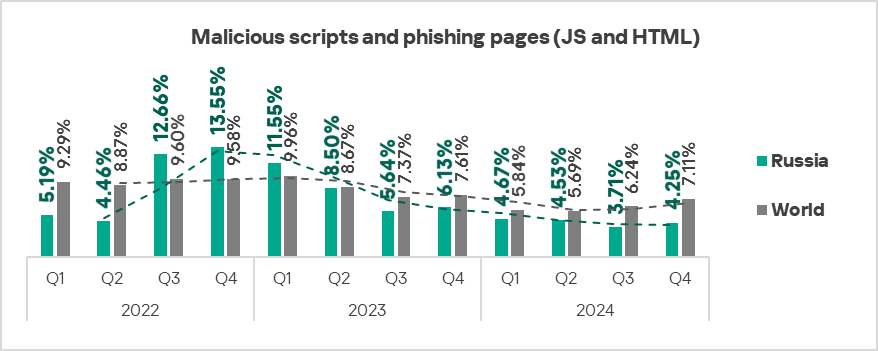
Malicious scripts and phishing pages
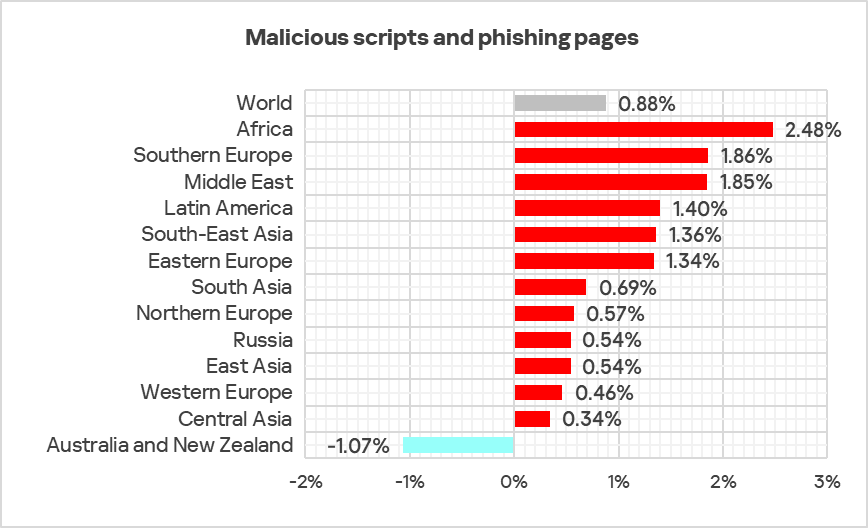
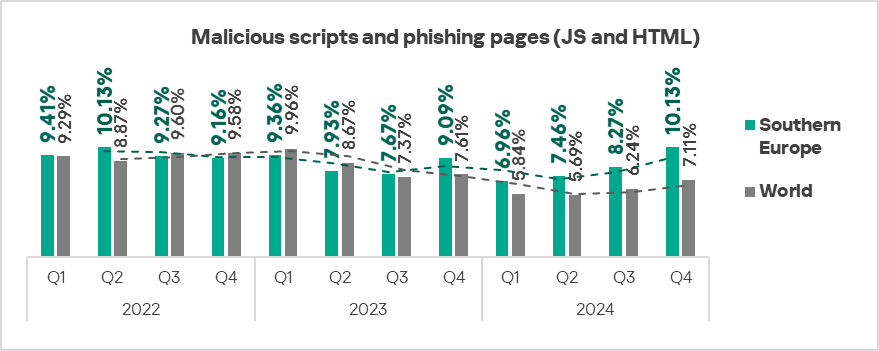
The top three regions by percentage of ICS computers on which malicious scripts and phishing pages were blocked were Africa, Southern Europe, and Latin America.
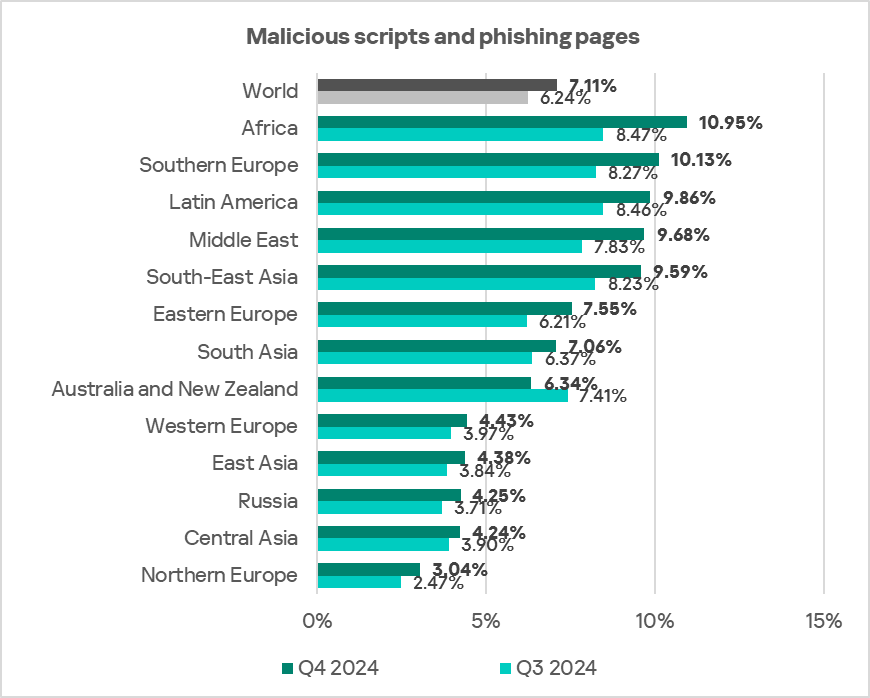
The top three regions in terms of growth in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious scripts and phishing pages were blocked were Africa, Southern Europe, and the Middle East.
Malicious documents
Southern Europe, Latin America, and the Middle East ranked as the top three regions by the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious documents were blocked.
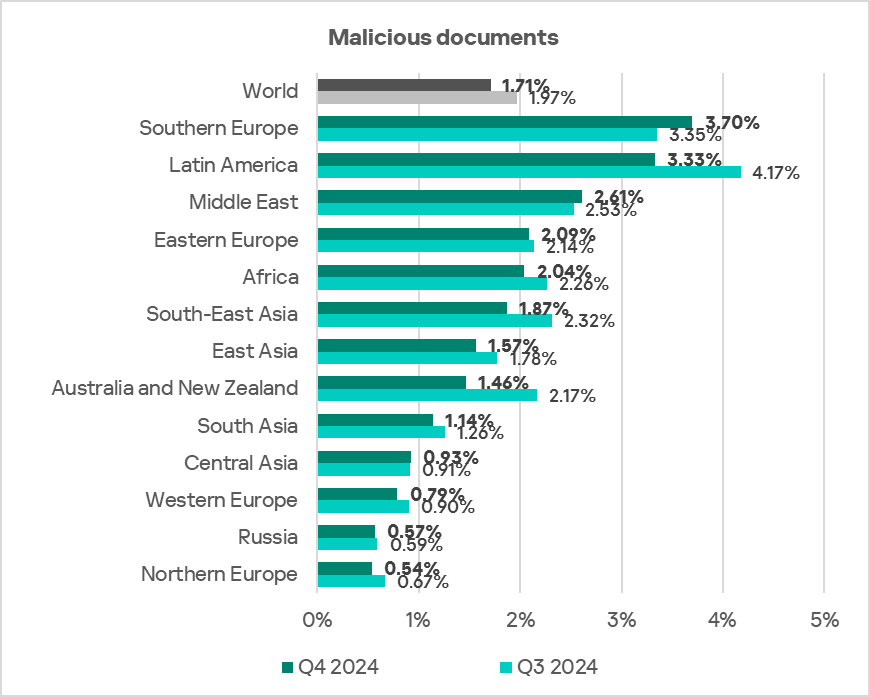
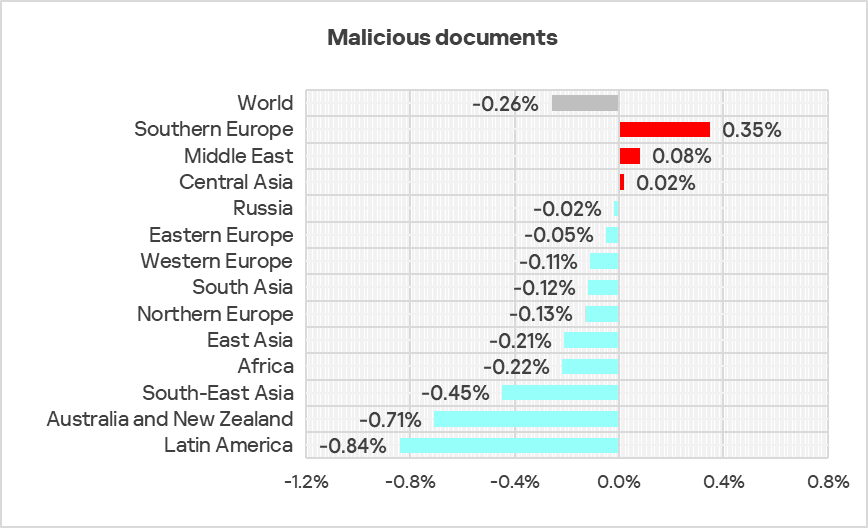
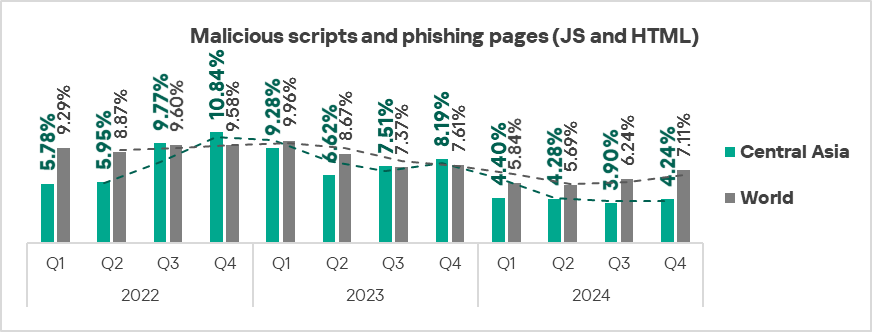
The only three regions in terms of growth in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious documents were blocked were Southern Europe, the Middle East, and Central Asia.
Next-stage malware
Malicious objects used to initially infect computers deliver next-stage malware – spyware, ransomware, and miners – to victims’ computers.
As a rule, the higher the percentage of ICS computers on which the initial infection malware is blocked, the higher the percentage for next-stage malware.
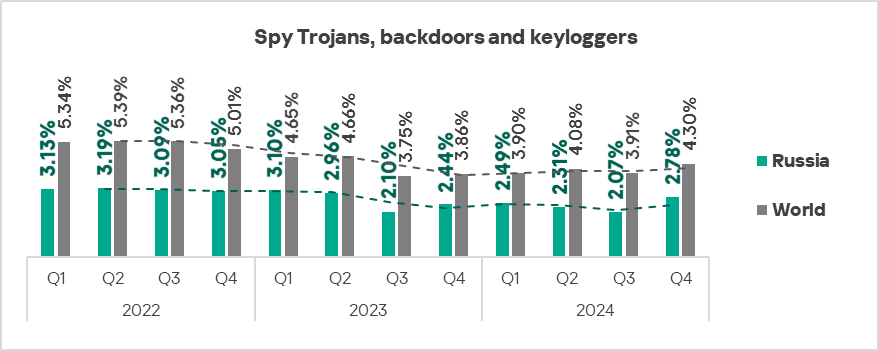
Spyware
Spyware (including Trojans, backdoors, and keyloggers) is typically the most frequently detected type of next-stage malware. It is either used as a toolset for intermediate steps in the kill chain (such as reconnaissance and lateral movement) or as a final-stage tool for stealing and exfiltrating confidential data.
When spyware is detected on an OT computer, it usually indicates that the initial infection vector was not prevented – whether through a user clicking on a malicious link, opening an attachment from a phishing email, or plugging in an infected USB drive. This suggests that OT perimeter protection measures (such as network security and enforcement of removable device policies) were either absent or ineffective.
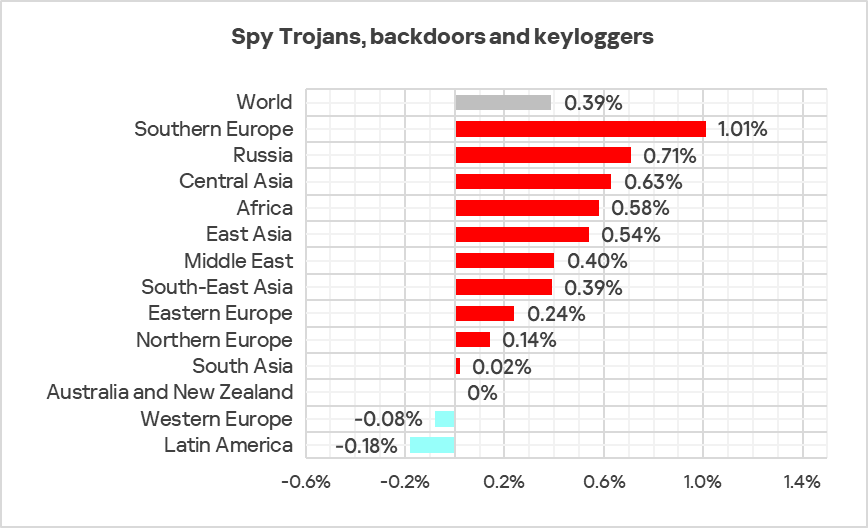
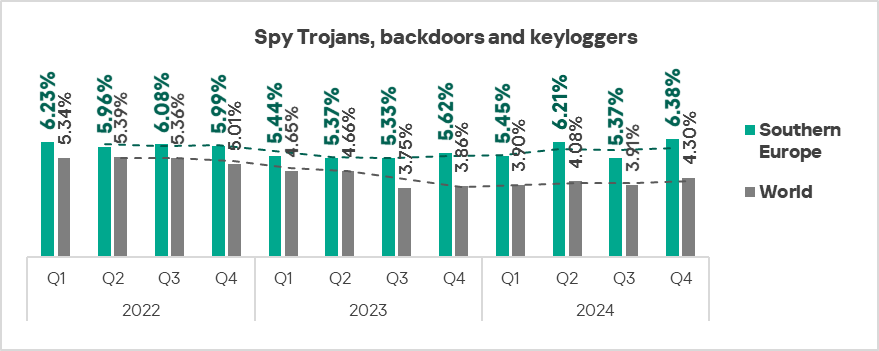
In Q4 2024, Africa, the Middle East, and Southern Europe ranked as the top three regions by the percentage of ICS computers on which spyware was blocked.
These regions also ranked among the highest for one or more types of initial infection threats.
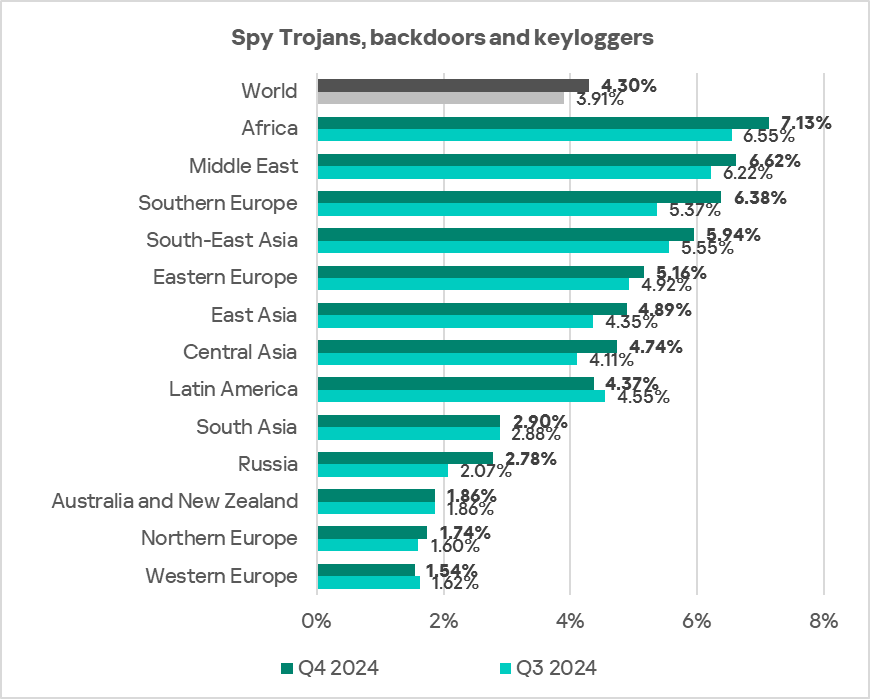
In almost all regions, spyware does not rank higher than third in the threat category rankings by percentage of ICS computers on which it was blocked, except in the following regions:
- East Asia: in this region, spyware is the number one malware category in terms of the percentage of ICS computers on which it was blocked.
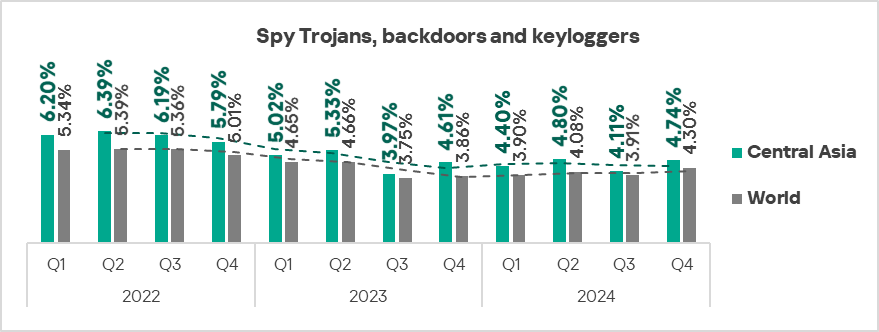
- The Middle East, Southern Europe, and Central Asia: spyware is the second most prevalent threat in these regions.
The top three regions in terms of growth in the percentage of ICS computers on which spyware was blocked were Southern Europe, Russia, and Central Asia.
Covert cryptomining programs
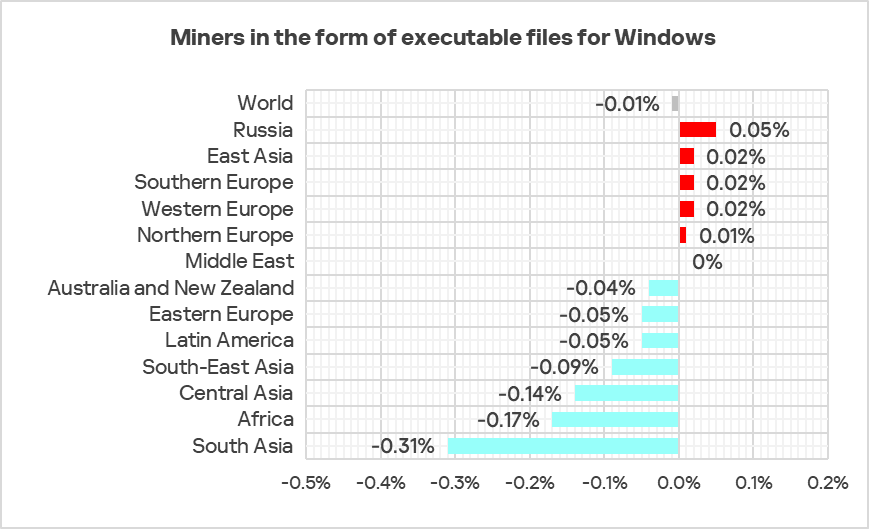
Miners in the form of executable files for Windows
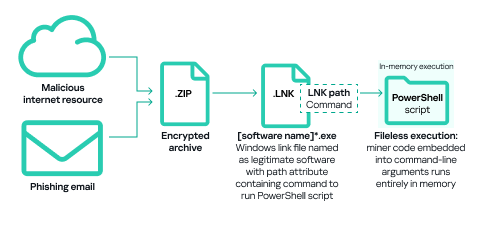
In the fourth quarter of 2024, similar to the previous quarter, a significant portion of Windows miners found on ICS computers consisted of archives with names mimicking legitimate software. These archives did not contain actual software but included a Windows LNK file, commonly known as a shortcut. However, the target (or path) that the LNK file points to is not a regular application, but rather a command capable of executing malicious code, such as a PowerShell script. Nowadays, threat actors are increasingly using PowerShell to execute malware, including cryptominers, by embedding malicious code directly into command-line arguments. This code runs entirely in memory, enabling fileless execution and minimizing detection.
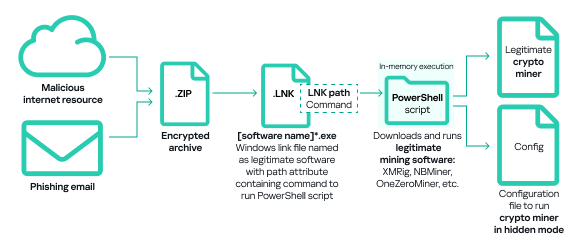
Another common method of deploying miners on ICS computers involves using legitimate cryptocurrency mining software such as XMRig, NBMiner, OneZeroMiner, and others. While these miners are not inherently malicious, they are classified as RiskTools by security systems. Attackers exploit these miners by combining them with customized configuration files that enable the miner’s activity to be concealed from the user’s view.
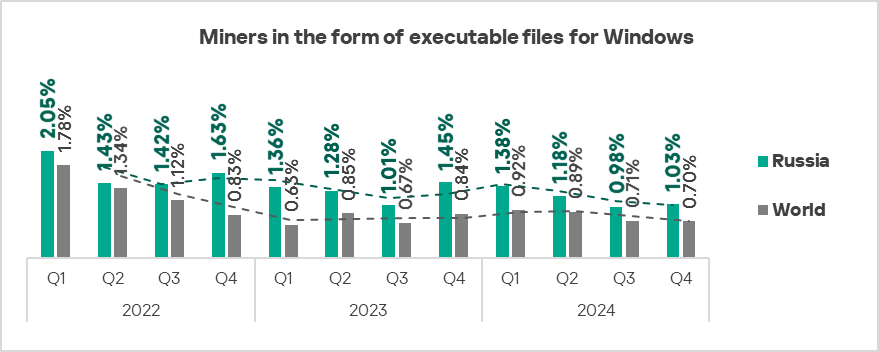
The top three regions by percentage of ICS computers on which miners in the form of executable files for Windows were blocked were Central Asia, Russia, and Eastern Europe.
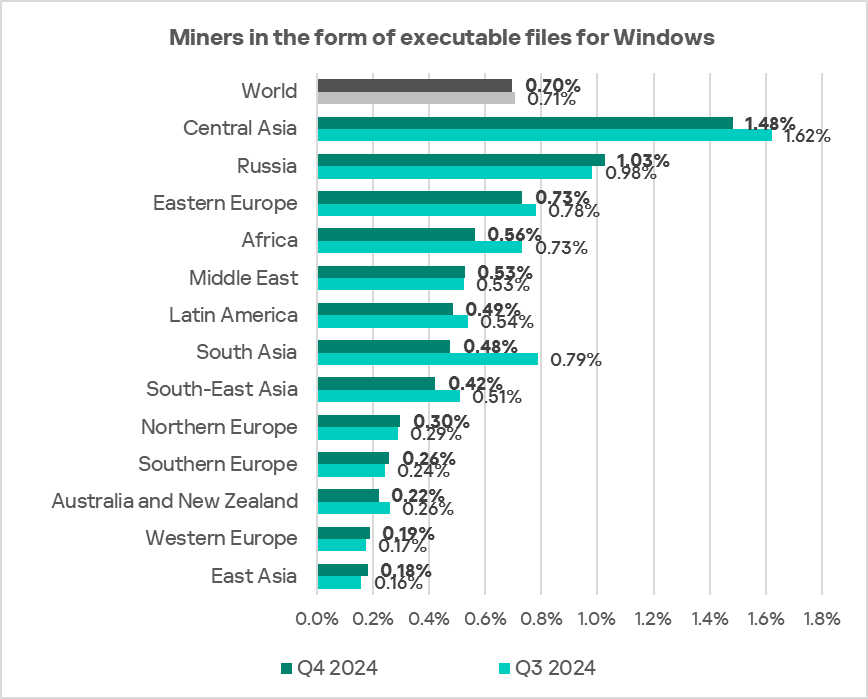
In the global ranking of threat categories by percentage of ICS computers on which they were blocked, miners in the form of Windows executable files are normally ranked seventh.
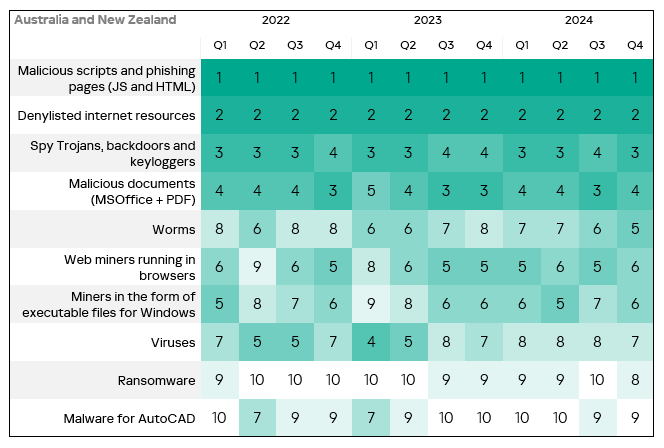
In the corresponding rankings in Russia, and Australia and New Zealand, they ranked fifth.
The top regions in terms of growth in the percentage of ICS computers on which miners in the form of Windows executable files were blocked were Russia, East Asia, Southern Europe, and Western Europe.
Covert cryptomining programs
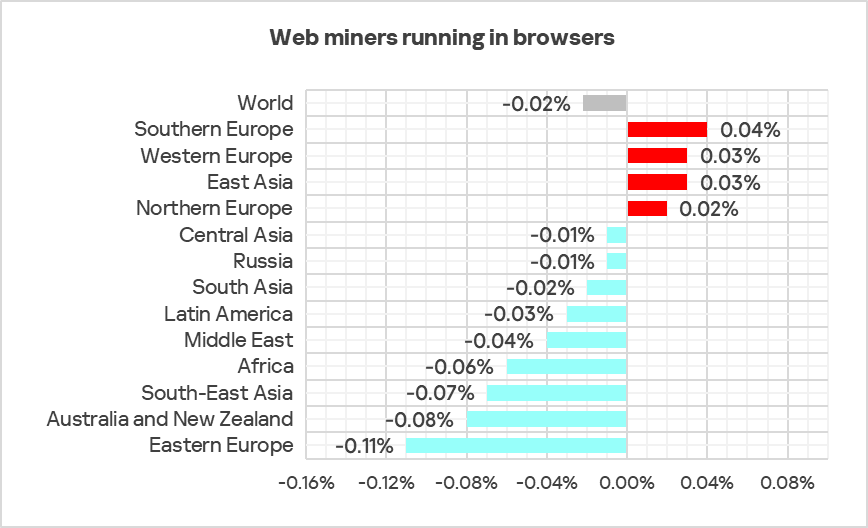
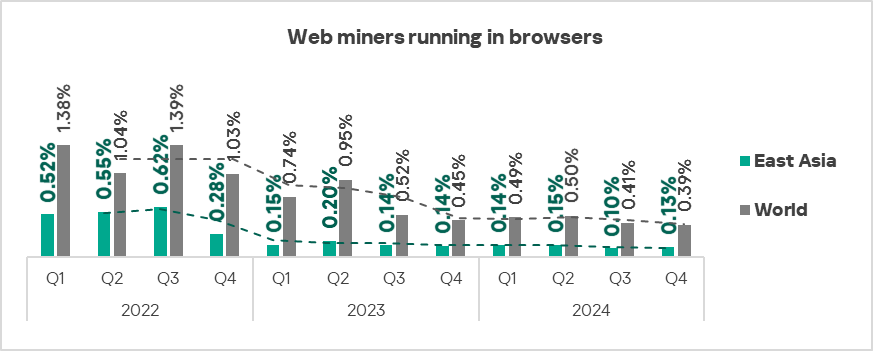
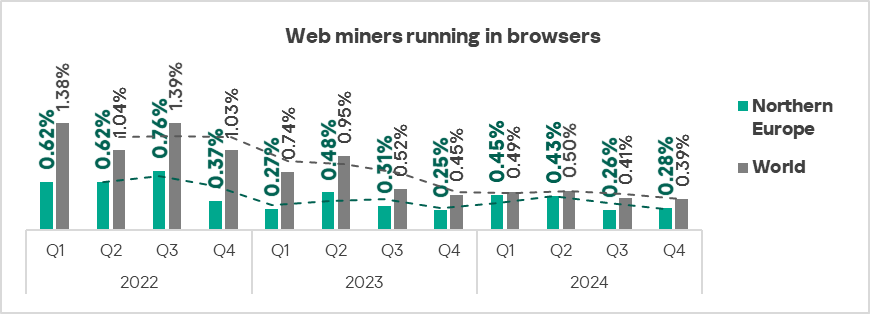
Web miners running in browsers
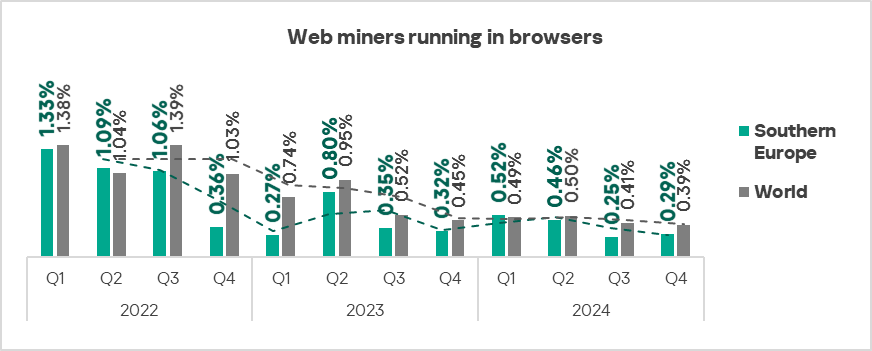
The three leading regions by percentage of ICS computers on which web miners running in browsers were blocked were: the Middle East, Africa, and Eastern Europe.
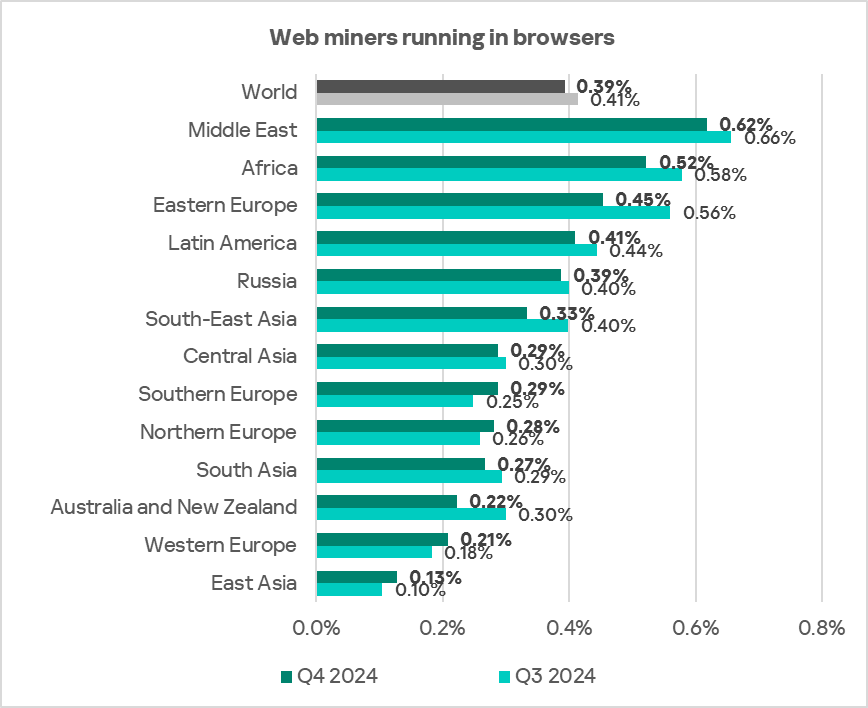
In the regional rankings of threat categories by percentage of ICS computers on which they were blocked, web miners ended up much higher regionally (eighth place globally) in Australia and New Zealand and Western Europe – sixth place in the respective regional rankings.
Southern Europe, Western Europe, Northern Europe, and East Asia were the only regions that experienced growth in the percentage of ICS computers on which web miners were blocked.
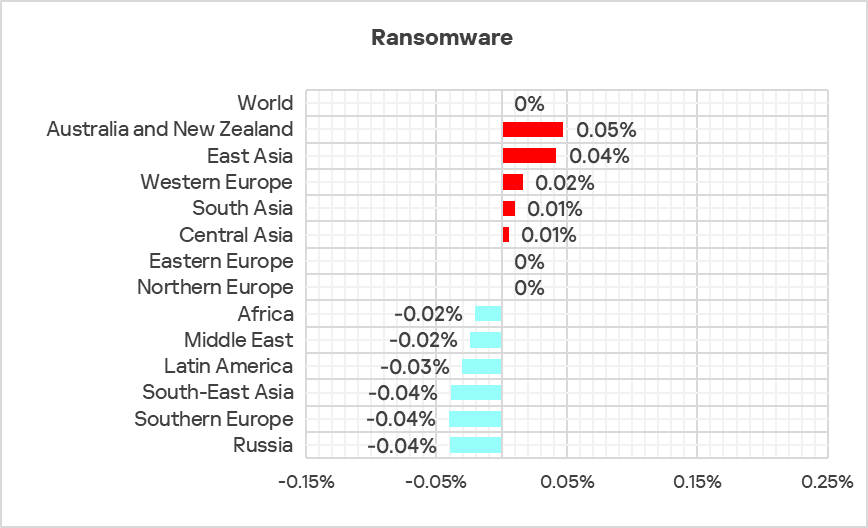
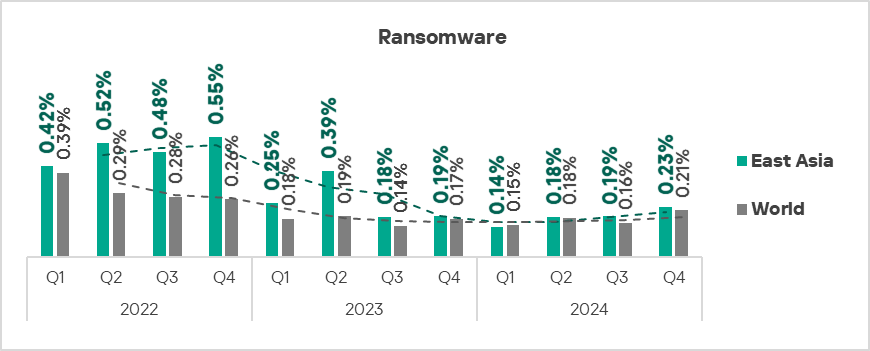
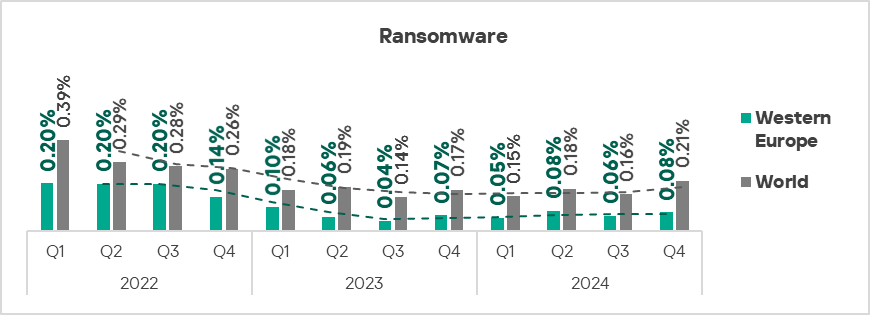
Ransomware
The top three regions with the highest percentage of ICS computers on which ransomware was blocked were the Middle East, Africa, and South Asia.
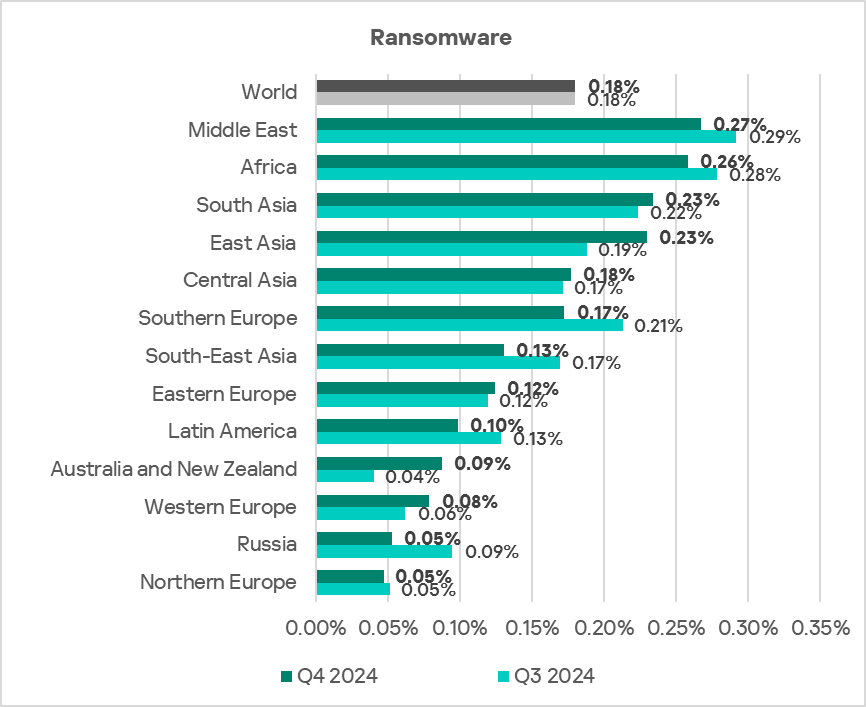
The top three regions in terms of growth in the percentage of ICS computers on which ransomware was blocked were Australia and New Zealand, East Asia, and Western Europe.
Self-propagating malware. Worms and viruses
Worms and virus-infected files were originally used for initial infection, but as botnet functionality evolved, they took on next-stage characteristics.
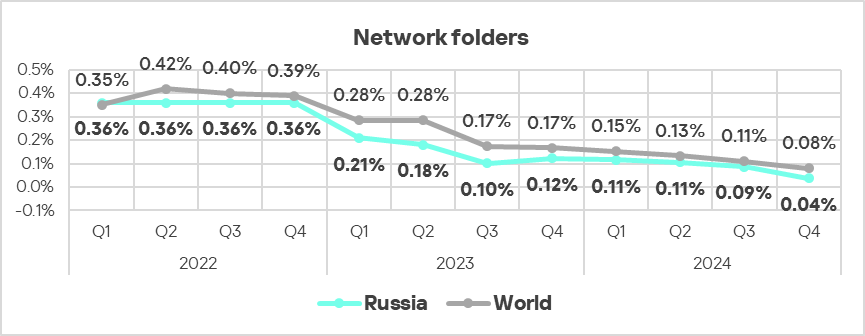
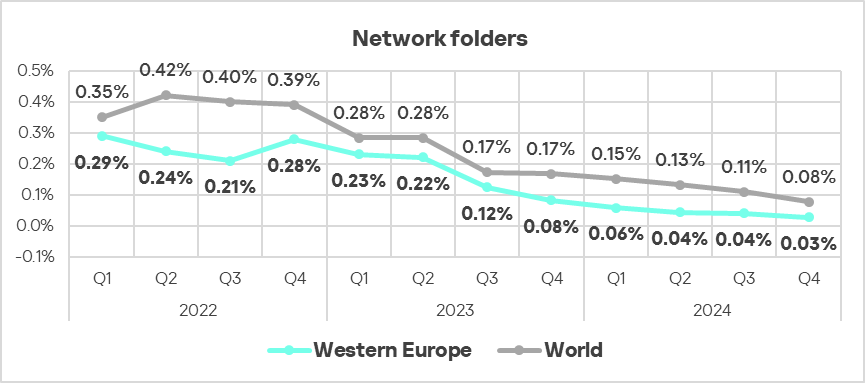
To spread across ICS networks, viruses and worms rely on removable media, network folders, infected files including backups, and network attacks on outdated software.
High rates of self-propagating malware and malware spreading via network folders at the industry, country, or regional level likely indicate the presence of unprotected OT infrastructure that lacks even basic endpoint protection.
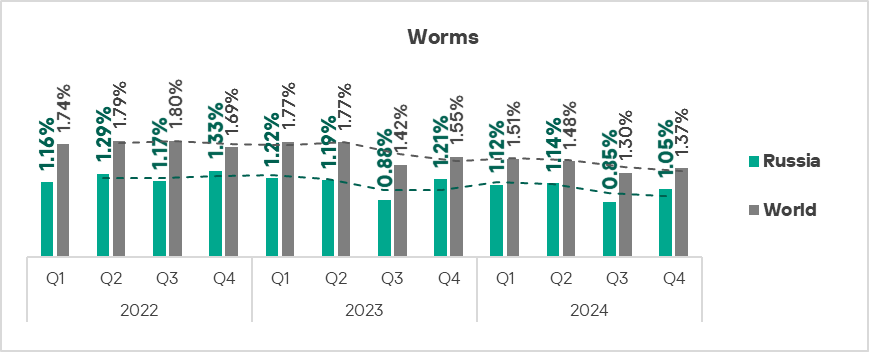
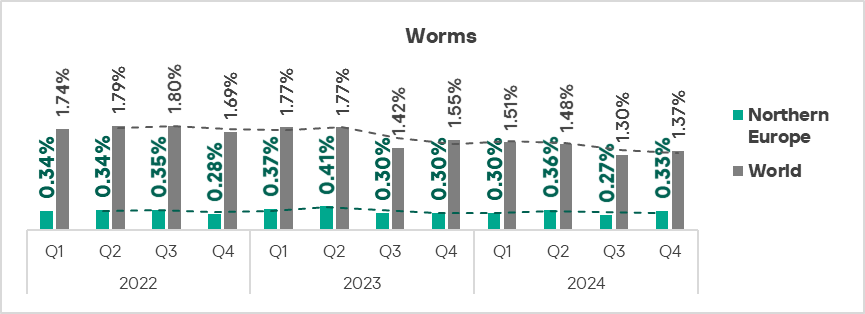
Worms
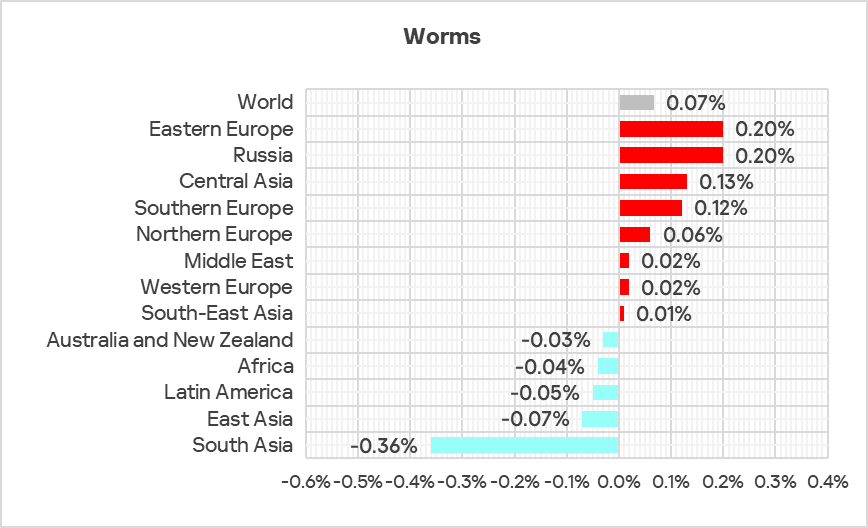
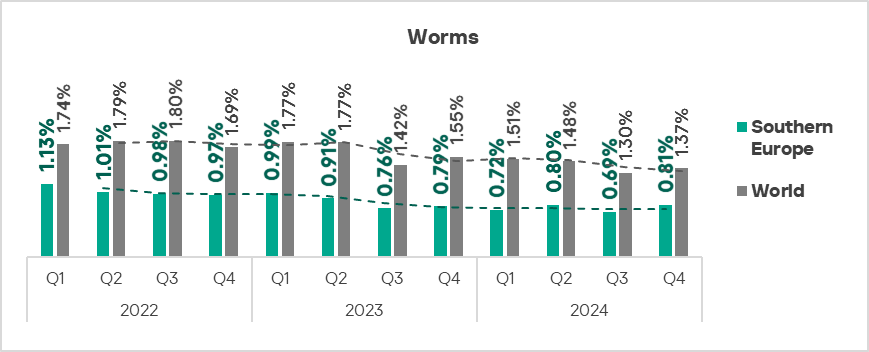
The top three regions by percentage of ICS computers on which worms were blocked were Africa, Central Asia, and the Middle East.
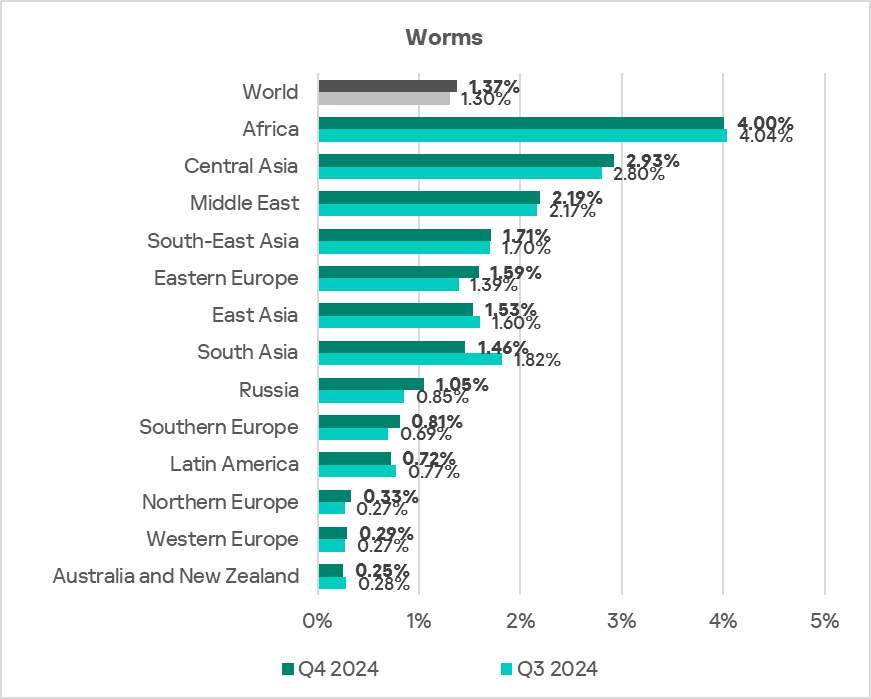
Globally, worms are in sixth place in the threat category ranking by percentage of ICS computers on which they were blocked. In similar regional rankings, worms rank much higher in the following regions: Russia, Central Asia – fourth place in the respective regional ranking.
The top three regions in terms of growth in the percentage of ICS computers on which worms were blocked were Eastern Europe, Russia, and Central Asia.
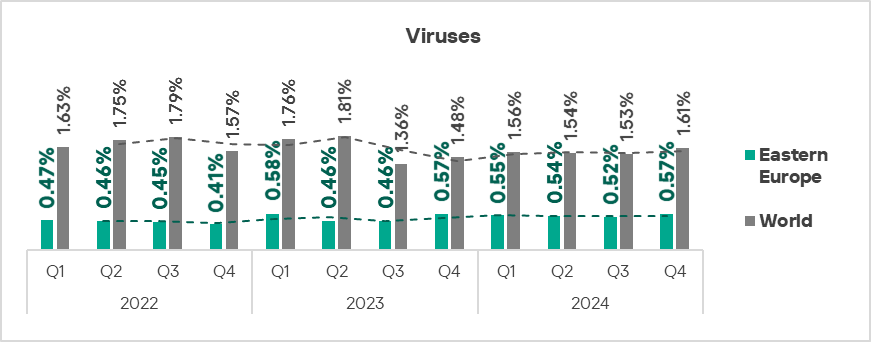
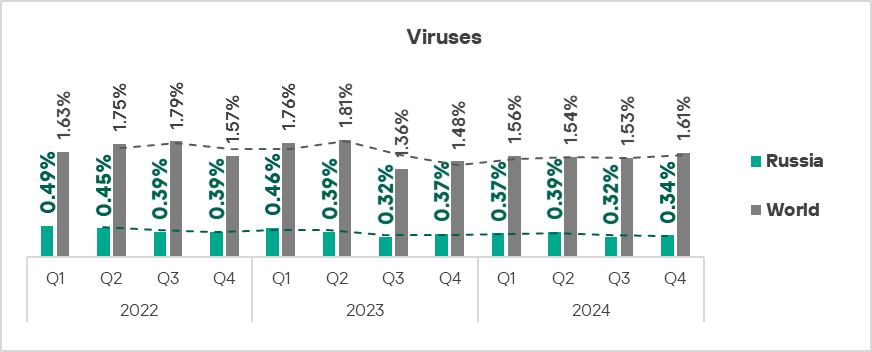
Viruses
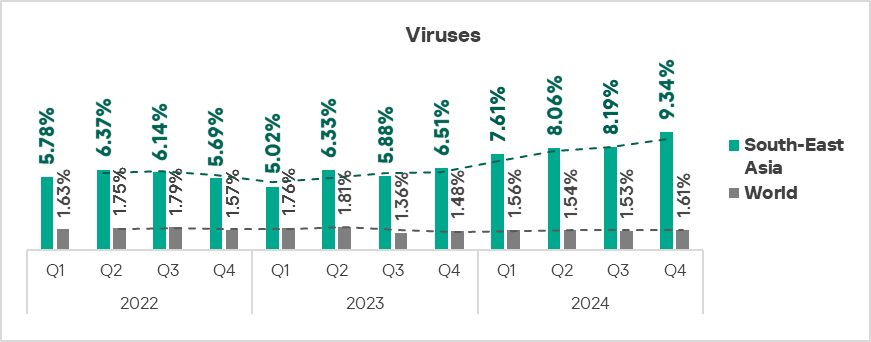
The top three regions by percentage of ICS computers on which viruses were blocked remained South-East Asia, Africa, and East Asia.
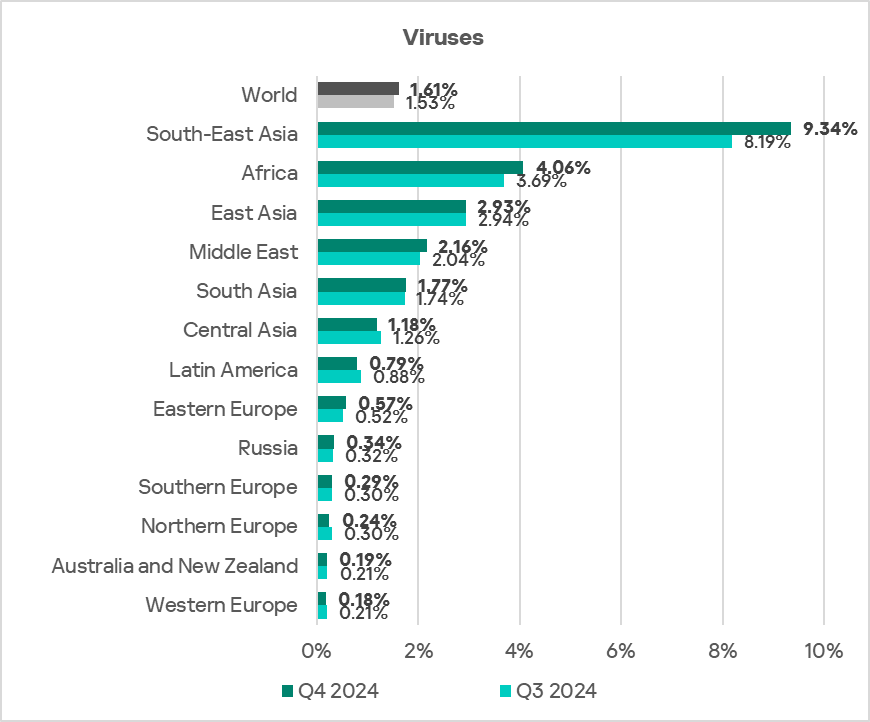
In South-East Asia, viruses are in second place in the regional threat category ranking by percentage of ICS computers on which they were blocked.
The top three regions in terms of growth in the percentage of ICS computers on which viruses were blocked were South-East Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
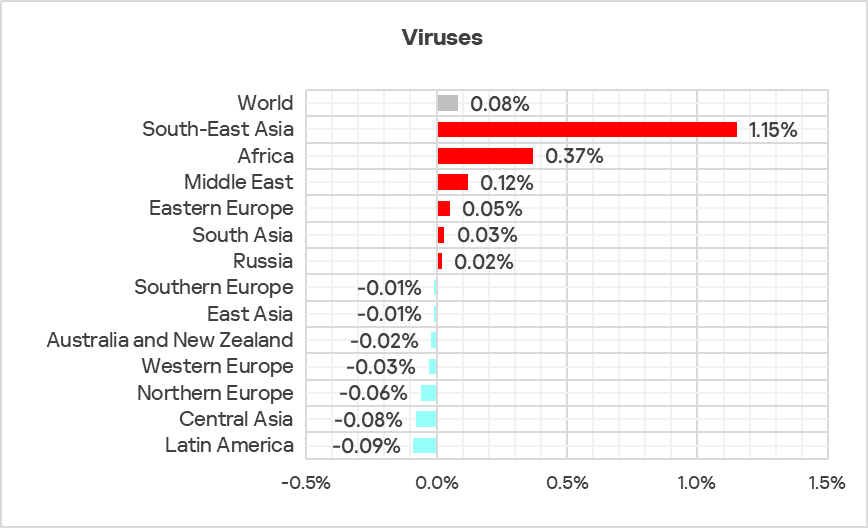
Note that there is an overlap between the leading regions in viruses and leaders by percentage of ICS computers on which network folder threats were blocked.
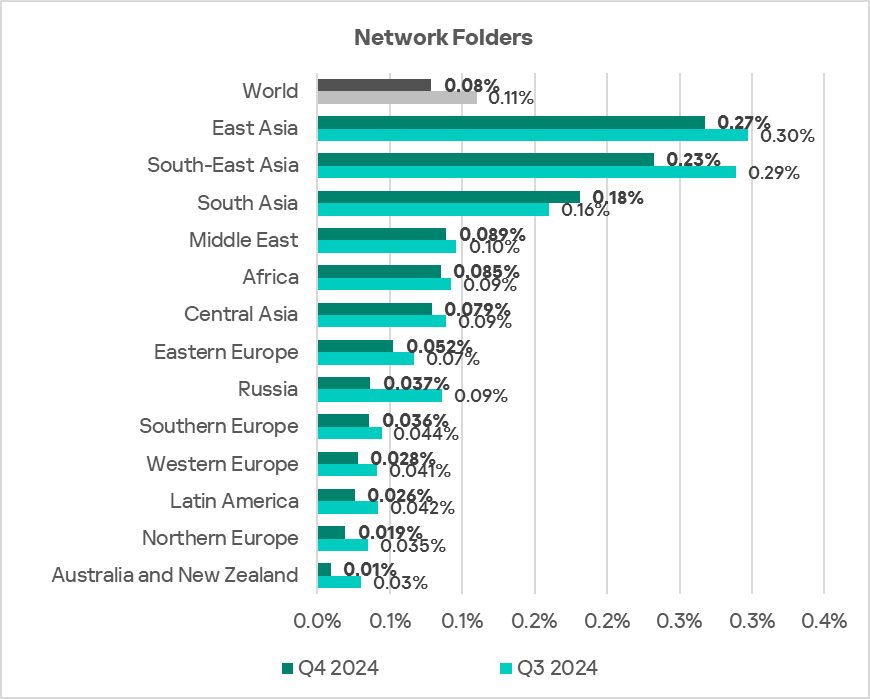
AutoCAD malware
This category of malware can spread in a variety of ways, so it does not belong to a specific group.
The same regions that lead in the virus ranking are also the leaders by percentage of ICS computers on which AutoCAD malware was blocked: South-East Asia, East Asia, and Africa.
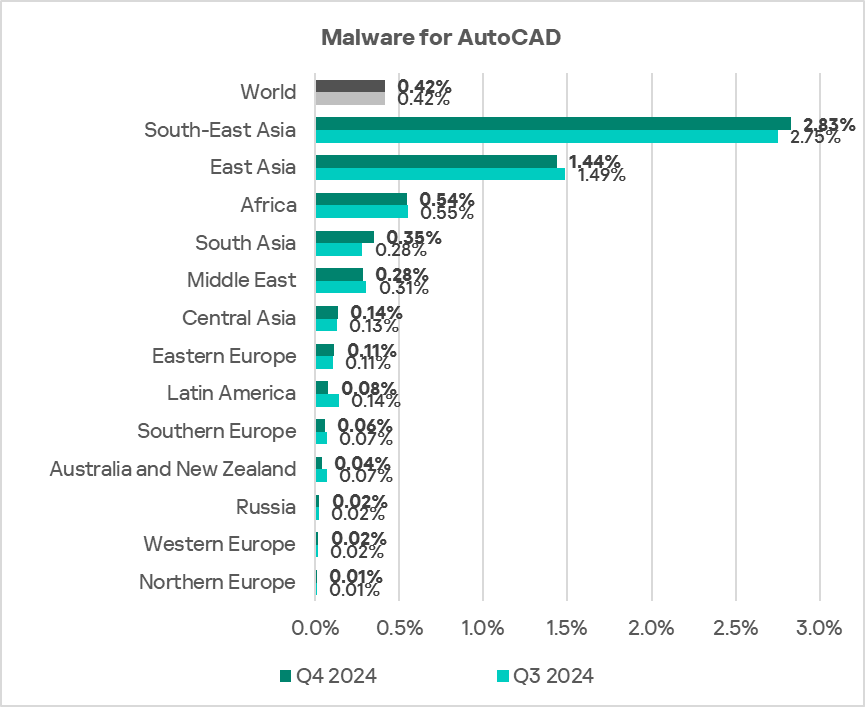
Normally, AutoCAD malware is a minor threat and usually comes bottom of the malware category rankings by percentage of ICS computers on which it was blocked.
However, in Q4 2024, this category ranked higher than the corresponding global ranking (ninth place) in the following regions:
- South-East Asia – fifth place in the regional ranking
- East Asia – seventh place in the regional ranking
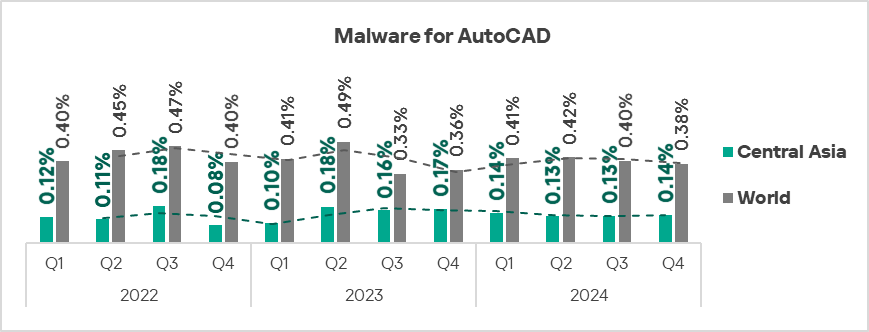
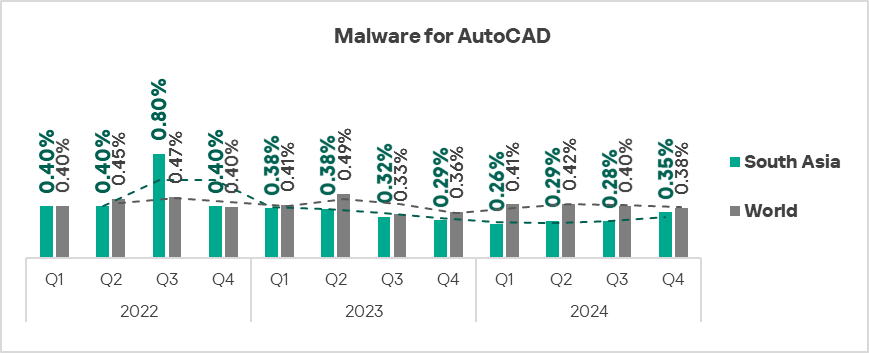
The only three regions with growth in the percentage of ICS computers on which malware for AutoCAD was blocked were South-East Asia, South Asia, and Central Asia.
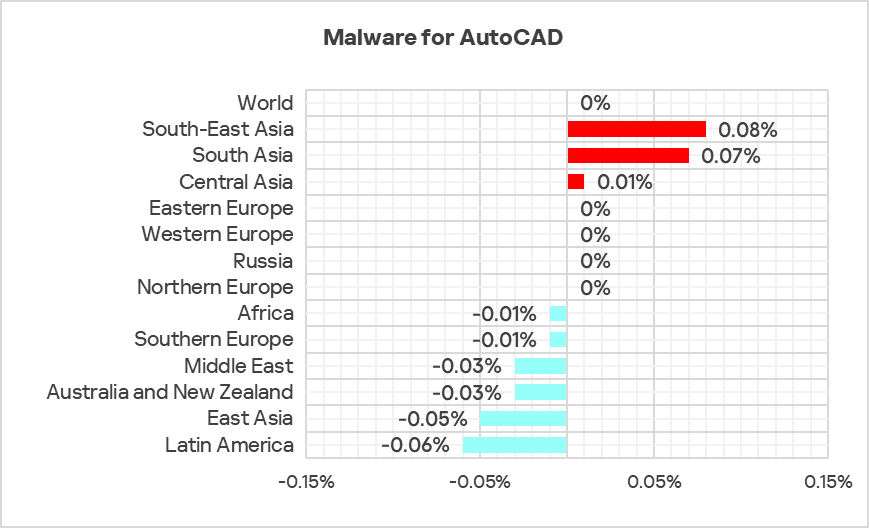
Regions. Special considerations
To see the specific distinctions of regions, you can compare them to other regions and to the global average statistics.
In most regions as well as globally, first place in the rankings by percentage of ICS computers on which specific threat categories were blocked are occupied by spyware and by the malicious objects used for the initial infection of computers. The internet leads the ranking of top threat sources in all regions.
Some of the regional rankings have their own peculiarities and distinctions, which are noted below.
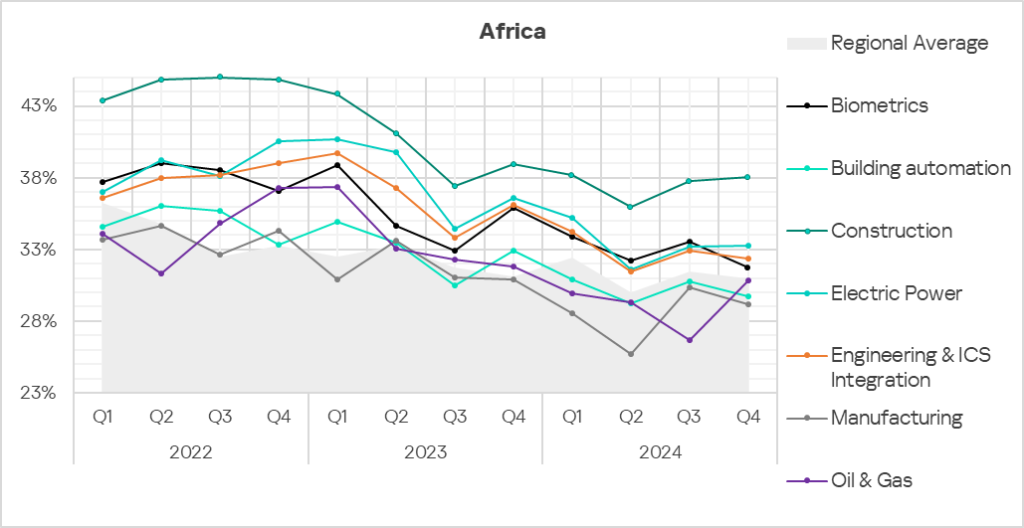
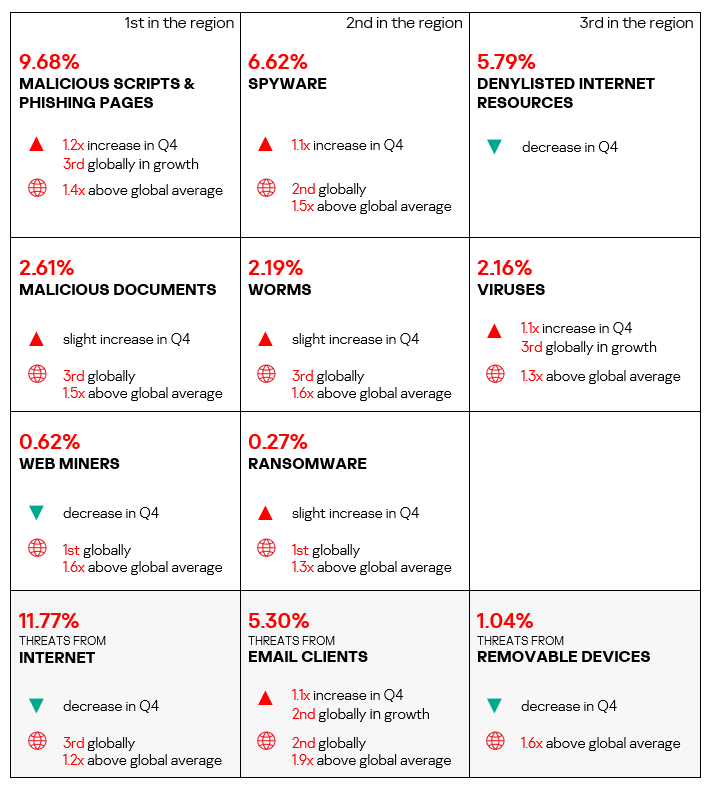
Africa
Current threats
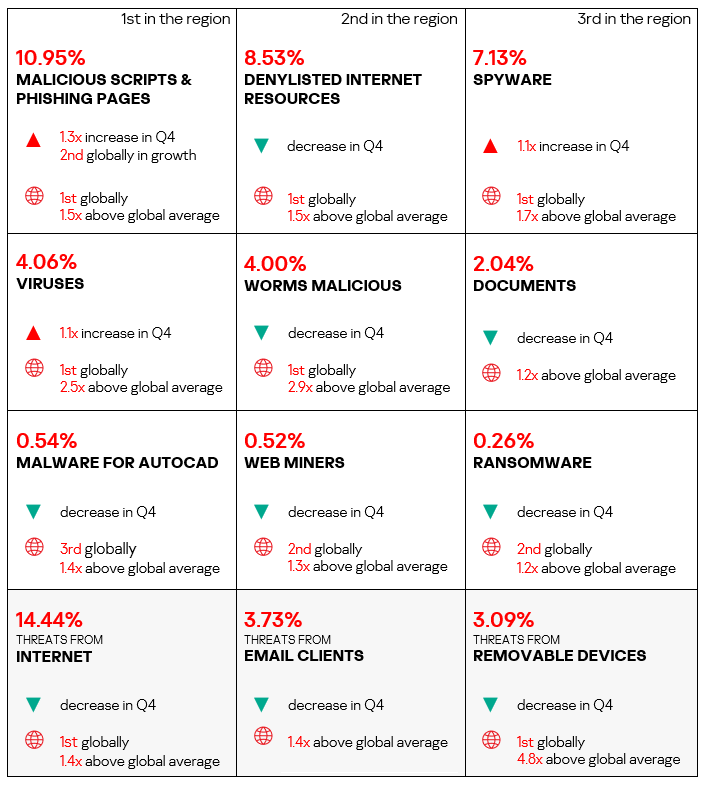
Overall
- First place in the global ranking by percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
- Of all regions, Africa traditionally has the highest percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
- The percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked is higher than the global average. In Q4 2024, the value was 1.4 times higher than the global average.
- The region exhibits a slight downward trend with fluctuations.
- In Q4 2024, the region showed a decrease in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
Comparative analysis
Threat categories
- Compared to the global figures, the region has a higher percentage of ICS computers on which threats were blocked across most threat categories.
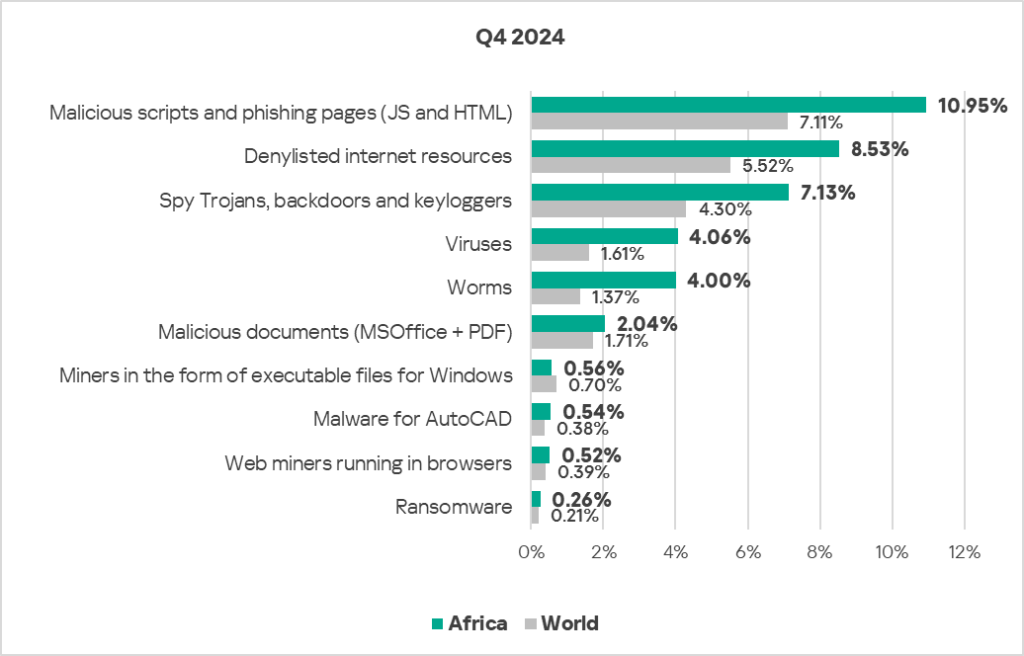
- The region has a significantly higher percentage than the respective global average percentages of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Worms: 2.9 times higher, ranks first by value globally.
- Viruses: 2.5 times higher (surpassing Q3 2024 levels), ranks second by value globally.
- Worms and viruses outpace malicious documents in the threat category ranking by percentage of ICS computers on which they were blocked. Worms are in fourth place (sixth place globally). High rates of self-propagating malware on a large scale indicate that a significant portion of the OT infrastructure lacks even basic endpoint protection, making it a source of malware infection attempts.
- Spyware: 1.7 times higher, ranks first by value globally.
- Denylisted internet resources: 1.5 times higher, ranks first by value globally.
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: 1.5 times higher (surpassing Q3 2024 levels), ranks first by value globally.
- Malware for AutoCAD: 1.4 times higher, ranks third by value globally.
- Web miners: 1.3 times higher, ranks second by value globally.
- Ransomware: 1.2 times higher, ranks second by value globally.
- Malicious documents: 1.2 times higher (surpassing Q3 2024 levels).
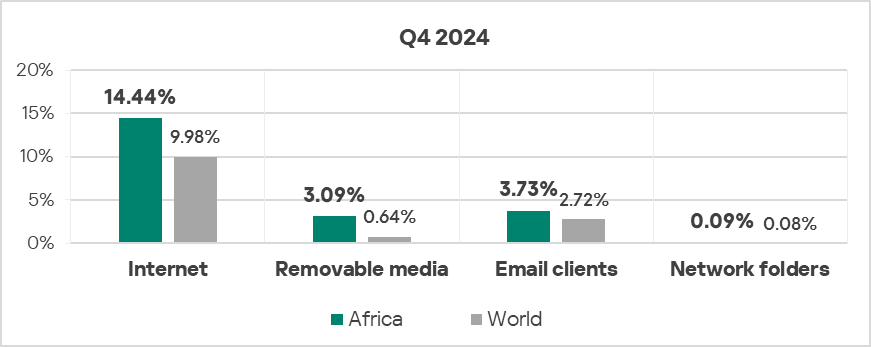
Threat sources
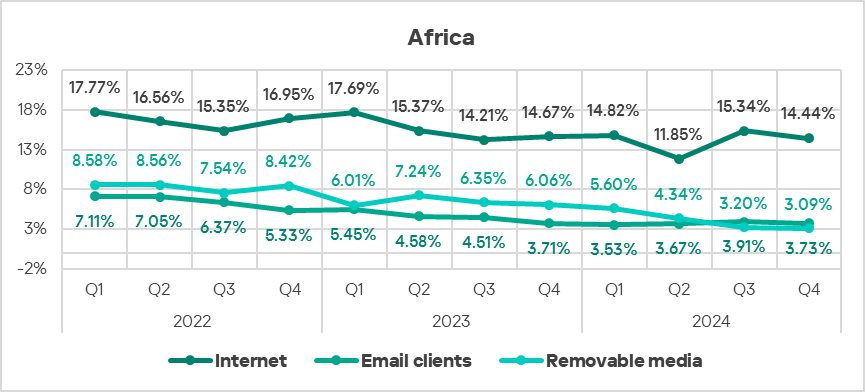
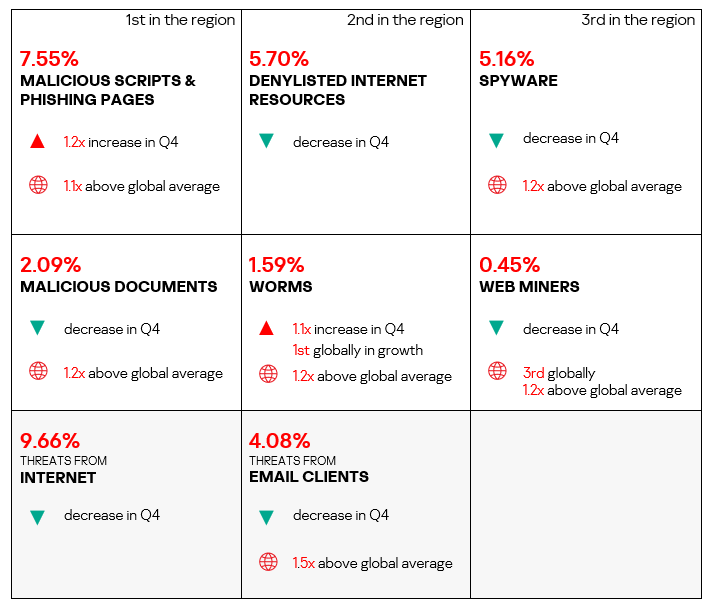
- The region ranked first in the world both by percentage of ICS computers on which threats from the internet and removable devices were blocked:
- Removable devices: 4.8 times higher (surpassing Q3 2024 levels).
- Internet: 1.4 times higher.
- With regard to threats from email clients, the region exceeded the global average by 1.4 times (surpassing Q3 2024 levels).
Quarterly changes and trends
Threat categories
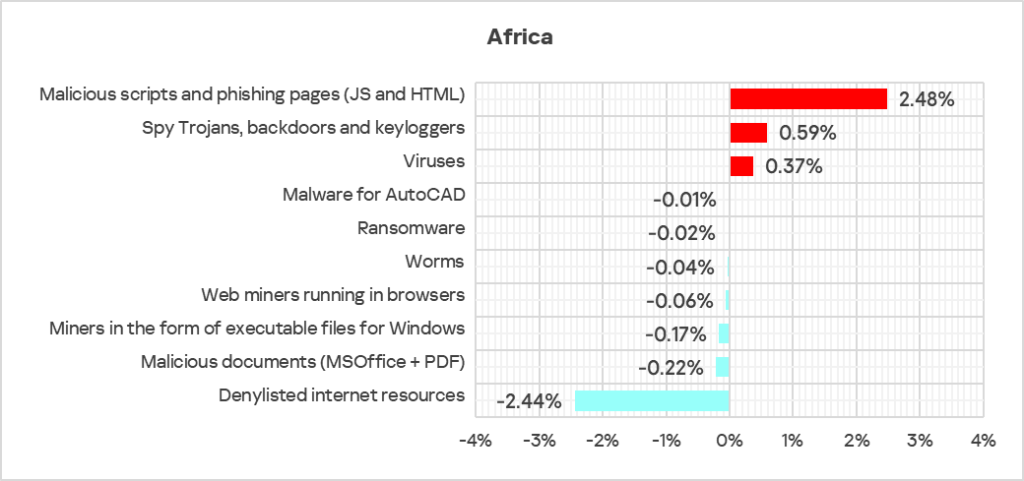
- The largest proportional increase in Q4 2024 was in the percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: by 1.3 times, first in the world in terms of growth.
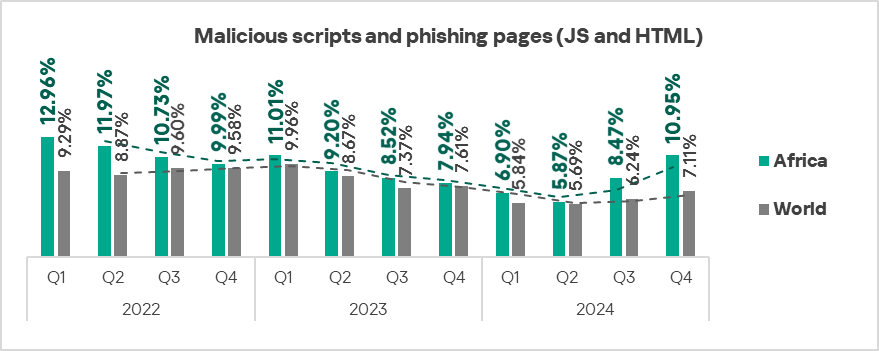
- Spyware: by 1.1 times.
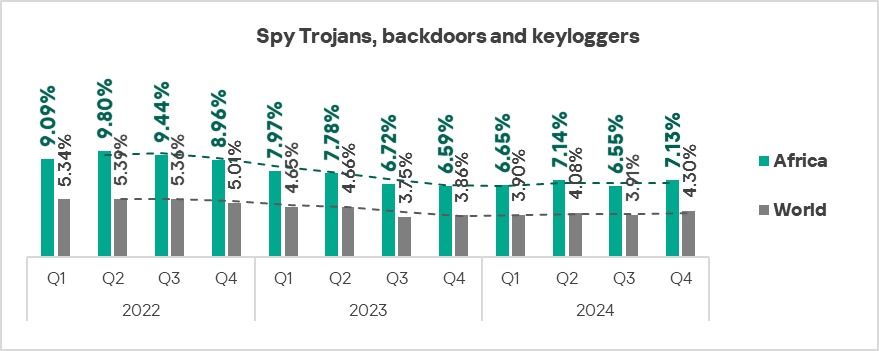
- Viruses: by 1.1 times, second in the world in terms of growth.
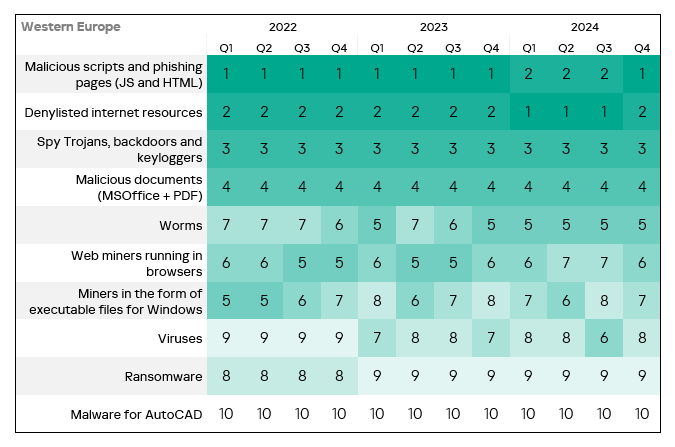
- The heatmap below illustrates changes in the ranking of threat categories in the region since the beginning of 2022. Malicious scripts and phishing moved from second to first place in Q4 2024. Viruses moved from fifth to fourth place in Q4 2024.
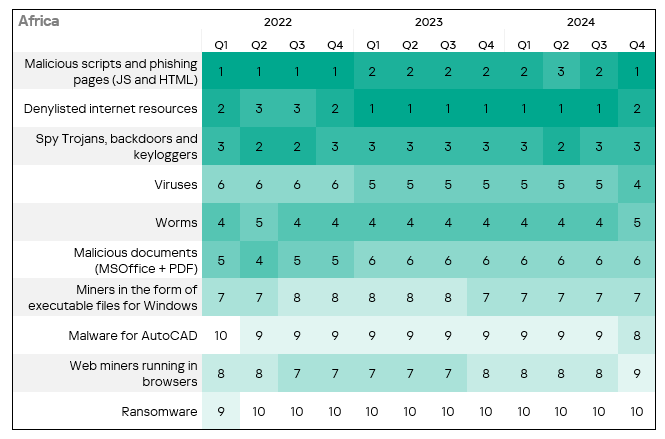
Threat sources
In Q4 2024, all threat sources exhibited a decrease in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects from them were blocked.
Industries
- In Q4 2024, construction remained the most affected industry in the region, as selected for this report.
- Compared to the global averages, the following industries had a significantly higher percentage of ICS computers with blocked malicious objects compared to the respective global averages:
- Construction – 1.7 times higher.
- Manufacturing – 1.7 times higher.
- Oil & Gas – 1.7 times higher.
- Engineering & ICS Integration – 1.5 times higher.
- Electric Power – 1.4 times higher.
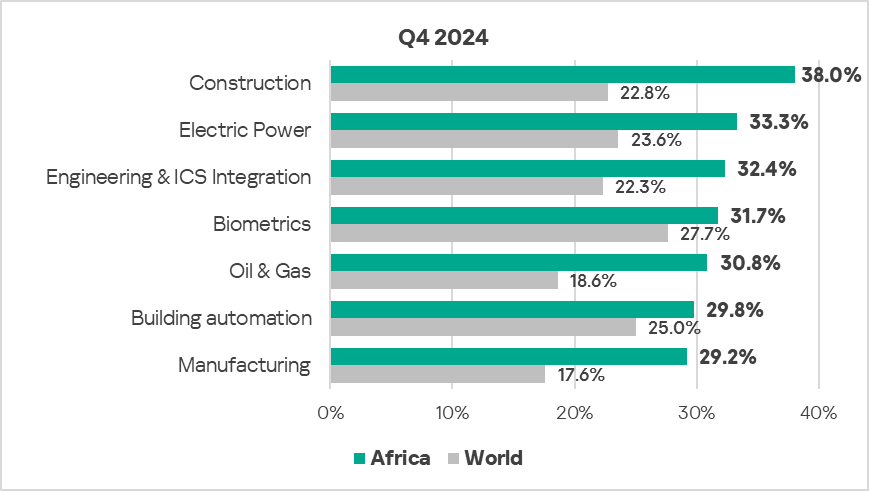
In Q4 2024, the oil and gas sector in the region exhibited a notable increase in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked – by 1.2 times compared to the previous quarter.
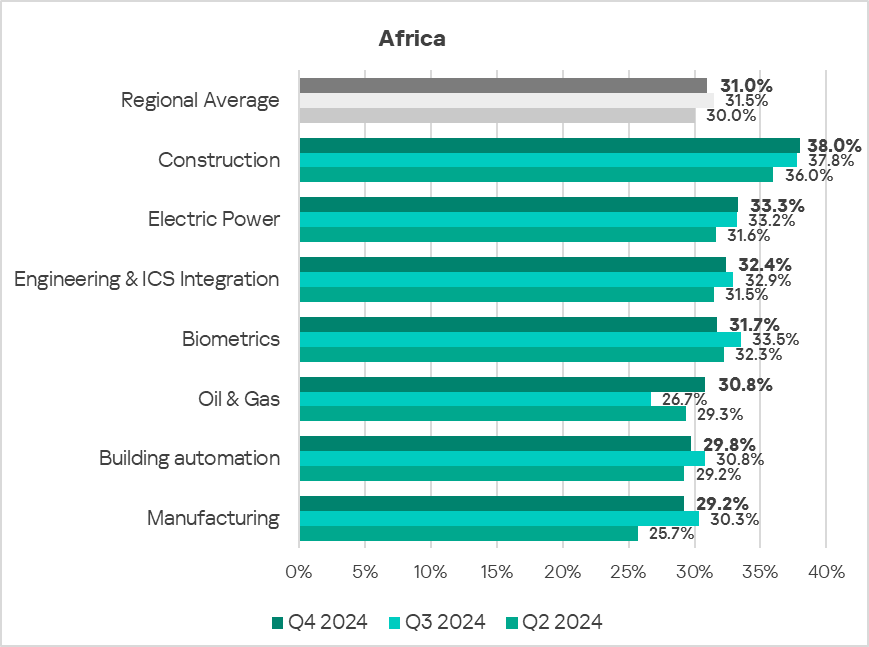
- Overall, the selected sectors show positive dynamics in their long-term trends with occasional major fluctuations.
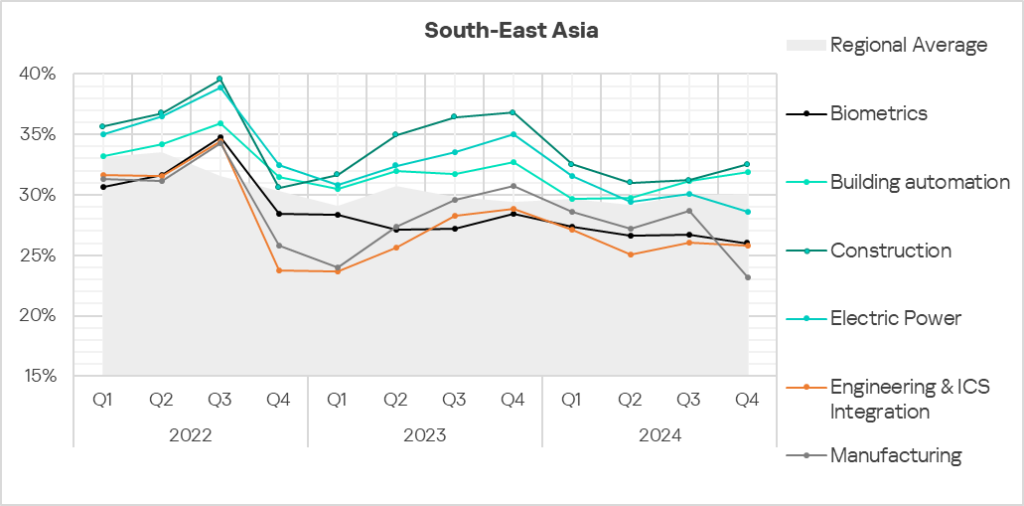
South-East Asia
Current threats
Overall
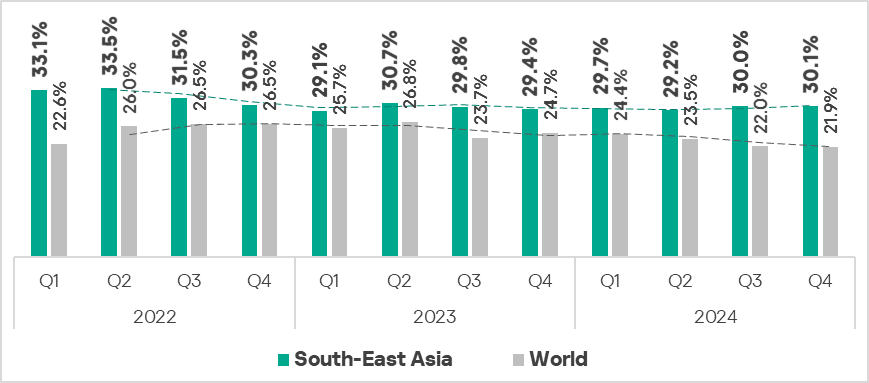
- Second place in the global ranking by percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
- The percentage of ICS computers where malicious objects were blocked remains consistently higher than the global average, reflecting a long‑term trend. In Q4 2024, the value was 1.4 times higher than the global average.
- In Q4 2024, the region showed an increase in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked, compared to the previous quarter.
Comparative analysis
Threat categories
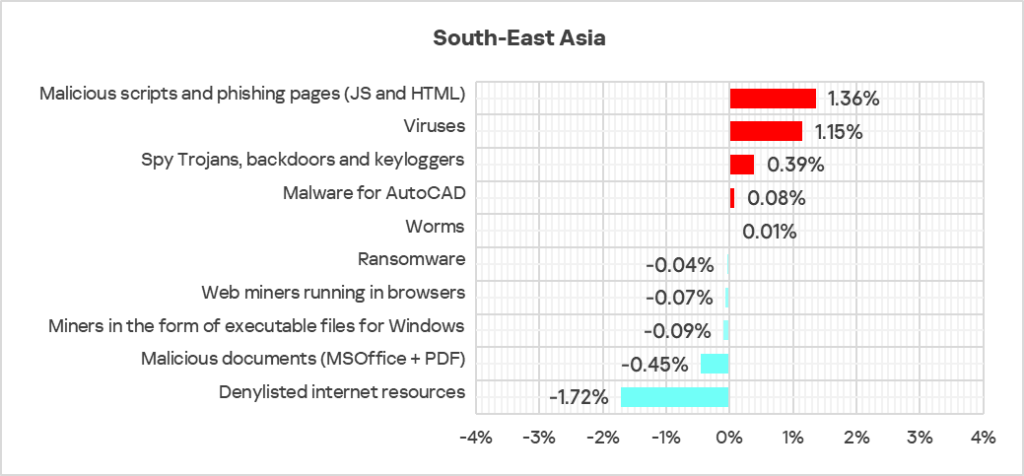
- Compared to the global figures, the region has a higher percentage of ICS computers on which threats were blocked across most threat categories.
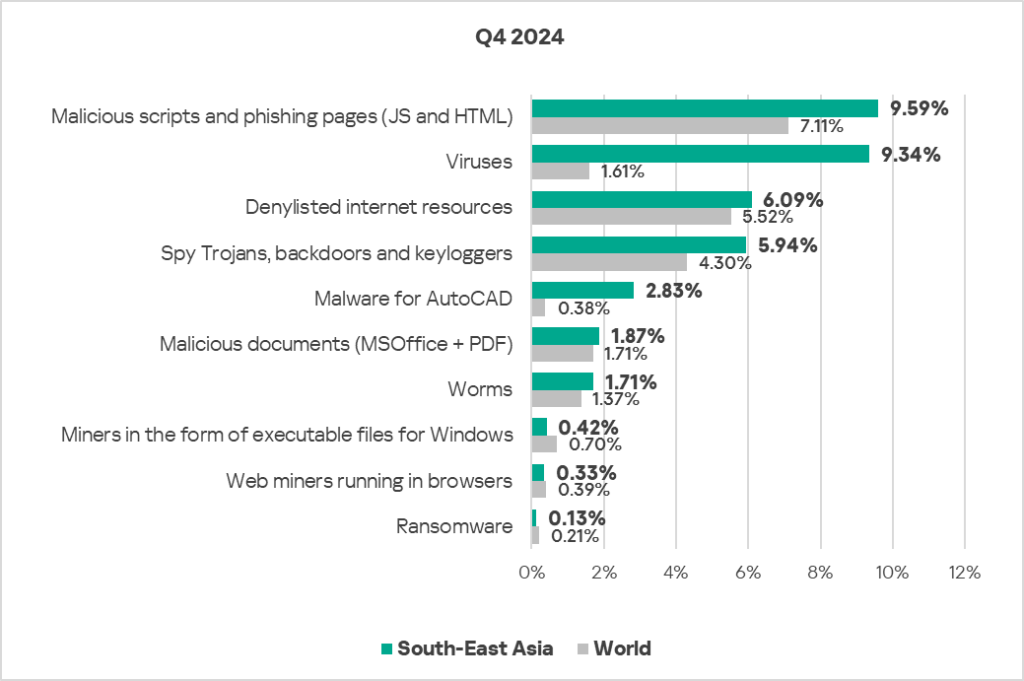
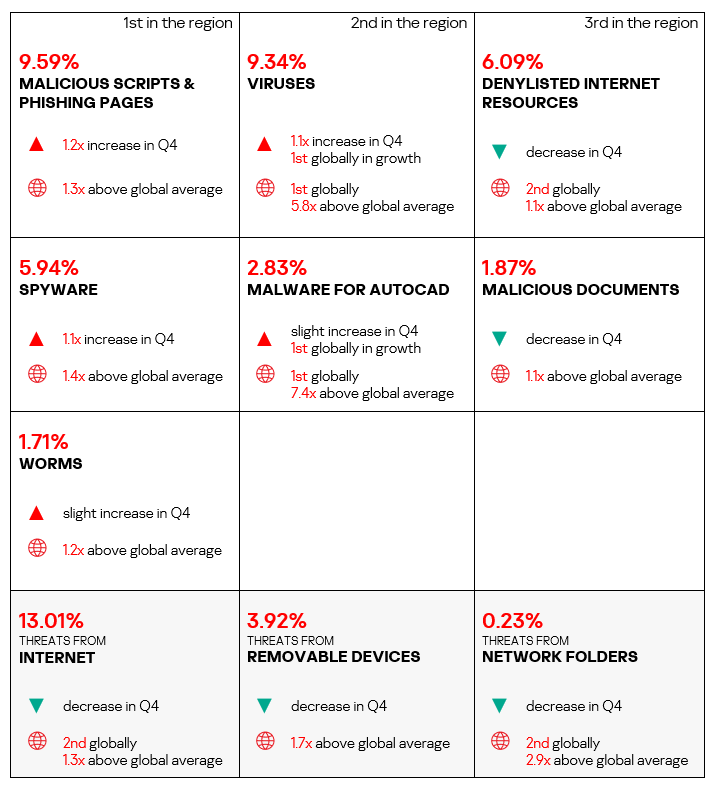
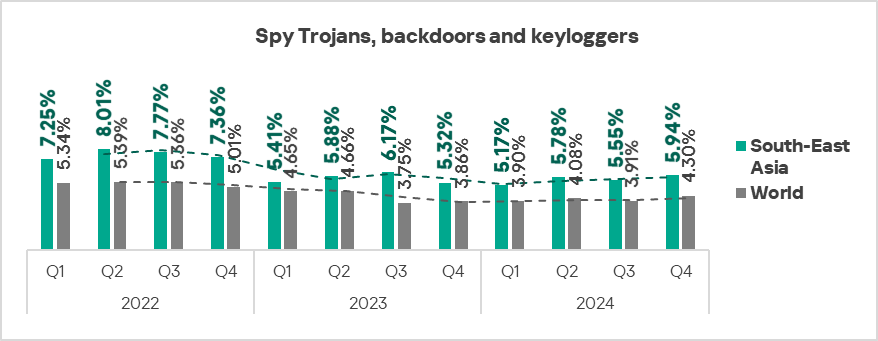
- Viruses came second in the ranking of malware categories by percentage of ICS computers on which they were blocked. In South-East Asia, this percentage is 5.8 times higher than the global average (surpassing Q3 2024 levels) and ranks first by value globally.
- AutoCAD malware is in fifth place in this ranking (the global percentage of ICS computers on which this malware was blocked is one of the lowest among all categories). The indicators value is 7.4 times higher than the global average (surpassing Q3 2024 levels) and ranks first by value globally.
- Compared to the global figures, the region also has a significantly higher percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Spyware: 1.4 times higher.
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: 1.3 times higher.
- Worms: 1.2 times higher.
- Denylisted internet resources: 1.1 times higher, ranks second by value globally.
- Malicious documents: 1.1 times higher.
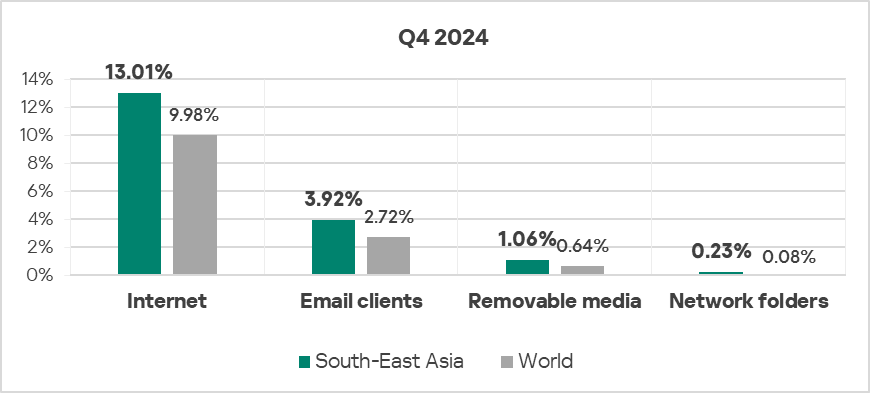
Threat sources
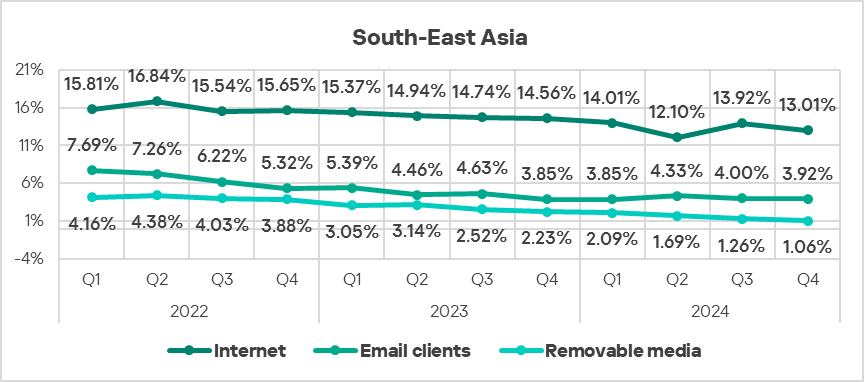
- The region ranked second in the world by percentage of ICS computers on which threats from network folders were blocked, exceeding the global average by 2.9 times (surpassing Q3 2024 levels).
- With regard to threats from the internet, the region also ranked second in the world, exceeding the global average by 1.3 times.
- The percentage of computers on which threats from removable devices were blocked exceeded the global average by 1.7 times.
- The percentage of computers on which threats from email clients were blocked exceeded the global average by 1.4 times in Q4 2024.
Quarterly changes and trends
Threat categories
- The largest proportional increase in Q4 2024 was in the percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
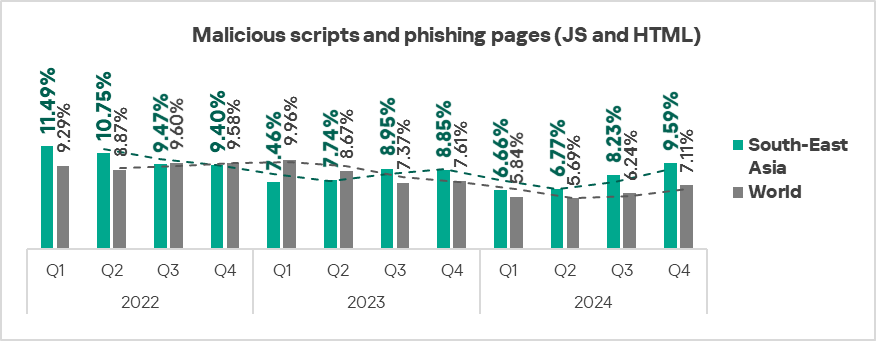
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: by 1.2 times.
- Viruses: by 1.1 times, first in the world in terms of growth.
- Spyware: by 1.1 times.
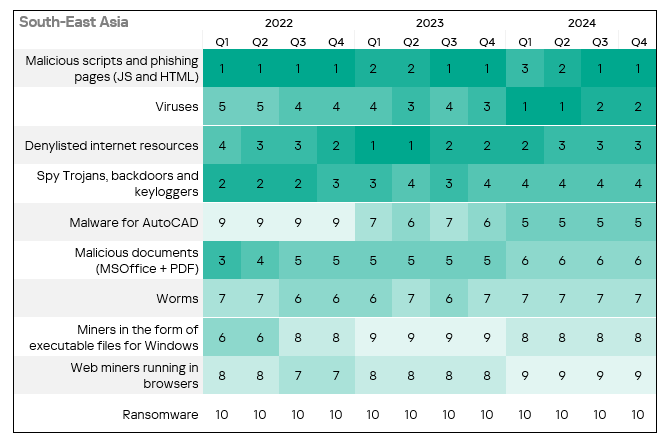
- The heatmap below illustrates changes in the ranking of threat categories in the region since the beginning of 2022.
Threat sources
In terms of quarterly changes, all threat sources showed a decrease in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
Industries
- The most affected industries in the region, as selected for this report, are:
- Construction.
- Building automation.
- Compared to the global averages, the following industries had a significantly higher percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked:
- Construction – 1.4 times.
- Manufacturing – 1.3 times higher.
- Building Automation – 1.3 times higher.
- Electric Power – 1.2 times.
- Engineering & ICS Integration – 1.2 times.
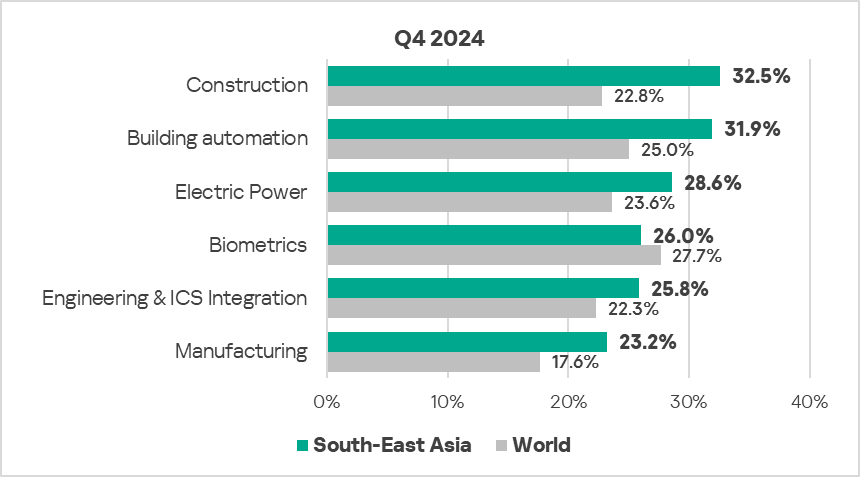
In Q4 2024, the construction and building automation sectors experienced an increase in the percentage of ICS computers where malicious objects were blocked.
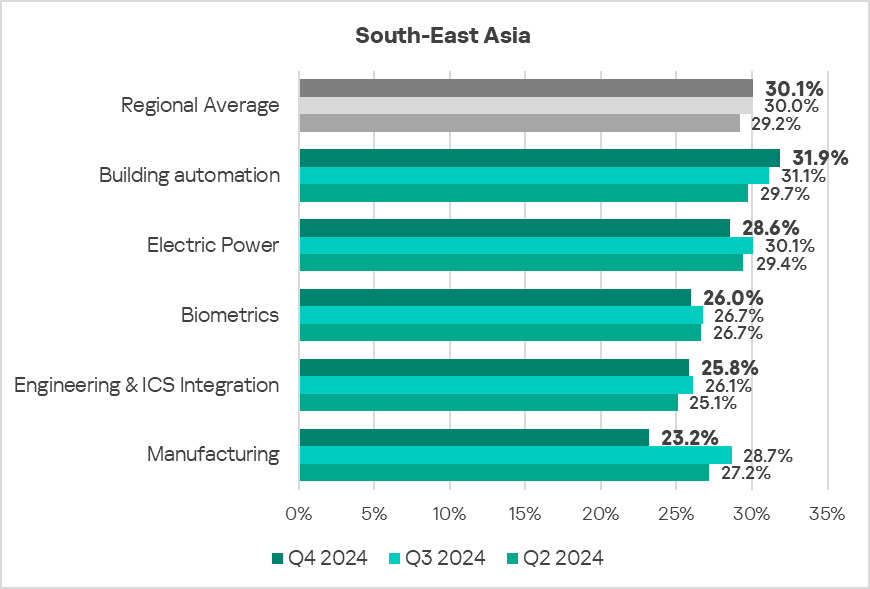
- The trends in the selected sectors demonstrate an overall positive dynamic, though they are marked by steep jumps and extended periods of slow increases and decreases.
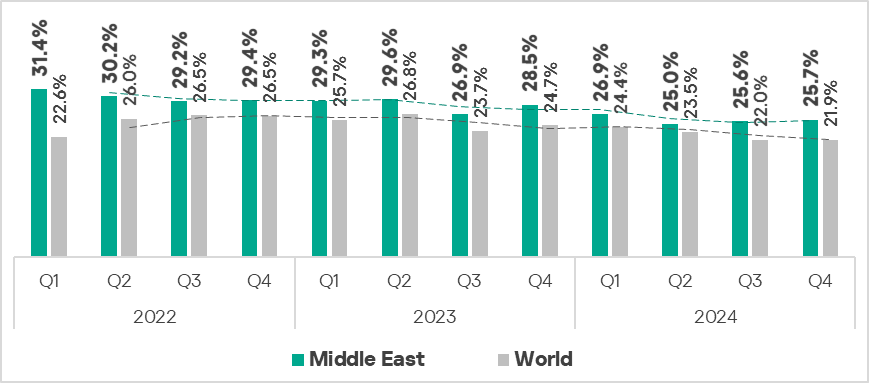
Middle East
Current threats
Overall
- Third place in the global ranking by percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked in Q4 2024.
- The percentage of ICS computers where malicious objects were blocked remains higher than the global average throughout the observed period. In Q4 2024, the value was 1.2 times higher than the global average.
- In Q4 2024, the region showed a slight increase in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked compared to the previous quarter.
Comparative analysis
Threat categories
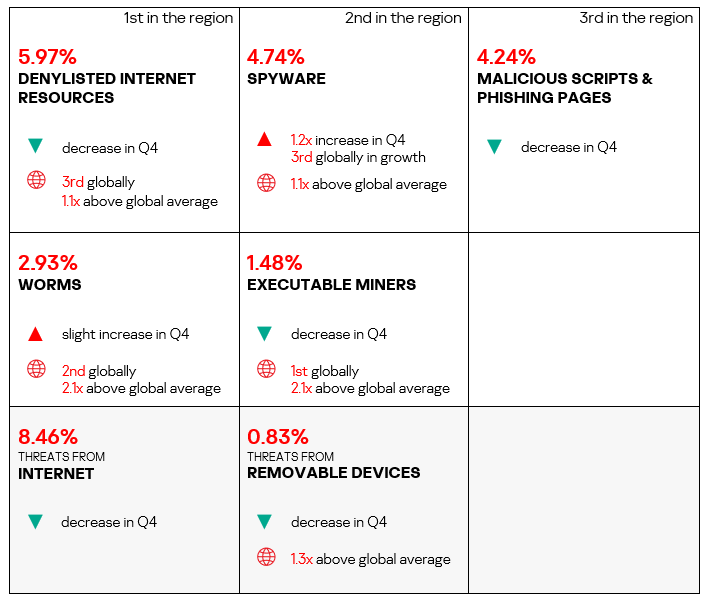
- Compared to the global figures, the region has a higher percentage of ICS computers on which all categories of threats were blocked, except for executable miners, and malware for AutoCAD.
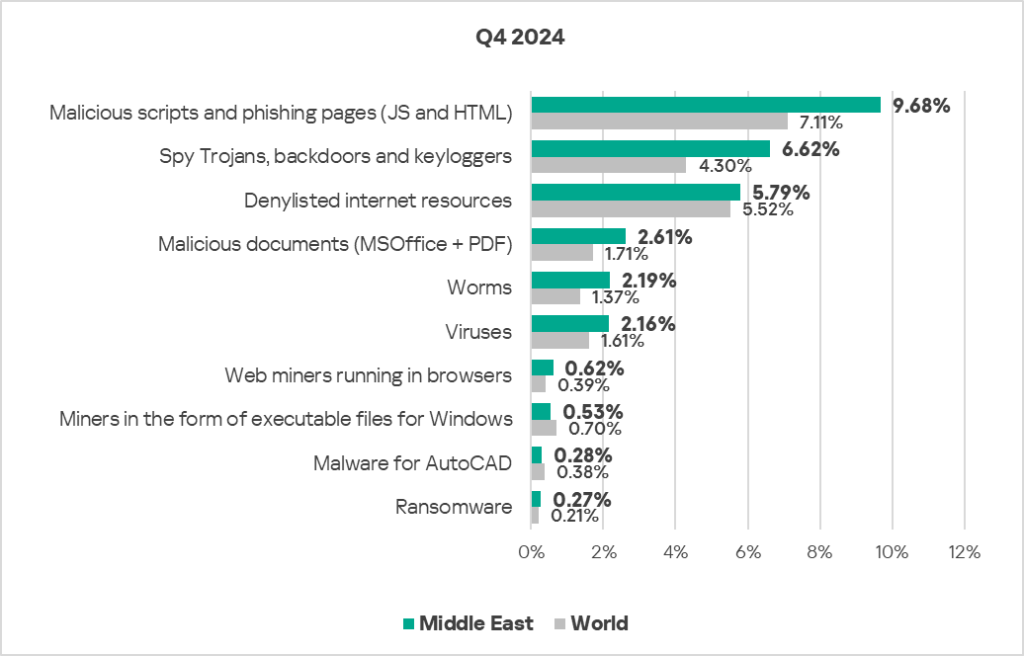
- Specifically, the following threat categories showed significantly higher values:
- Worms: 1.6 times higher, ranks third by value globally.
- Web miners: 1.6 times higher, ranks first by value globally.
- Spyware: 1.5 times higher, ranks second by value globally.
- Malicious documents: 1.5 times higher (surpassing Q3 2024 levels), ranks third by value globally.
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: 1.4 times higher (surpassing Q3 2024 levels).
- Viruses: 1.3 times higher.
- Ransomware: 1.3 times higher, ranks first by value globally.
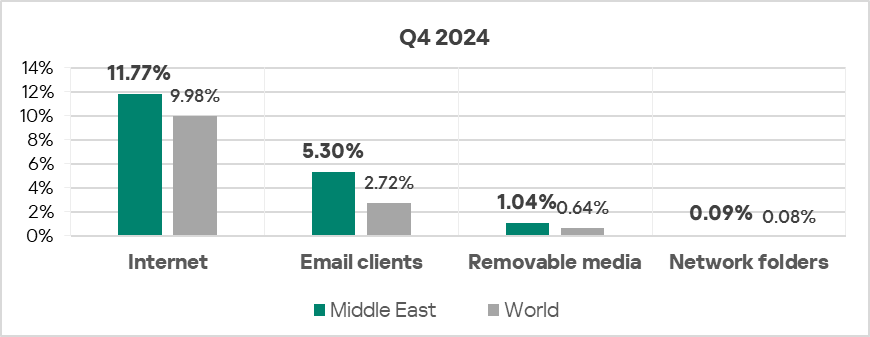
Threat sources
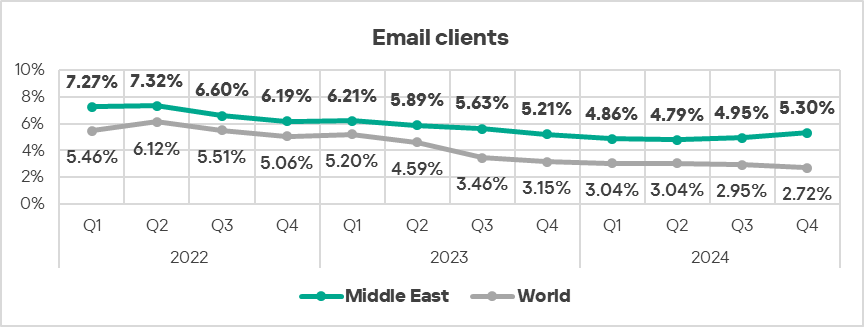
- The region ranked second in the world by percentage of ICS computers on which threats from email clients were blocked, exceeding the global average by a factor of 1.9, which is higher than in Q3 2024.
- The region ranked third in the world by percentage of ICS computers on which threats from the internet were blocked, exceeding the global average by a factor of 1.2, which is higher than in Q3 2024.
- The percentage of computers on which threats from removable devices were blocked exceeded the global average by 1.6 times in Q4 2024.
Quarterly changes and trends
Threat categories
- In terms of quarterly growth, five threat categories out of 10 showed an increase in Q4 2024.
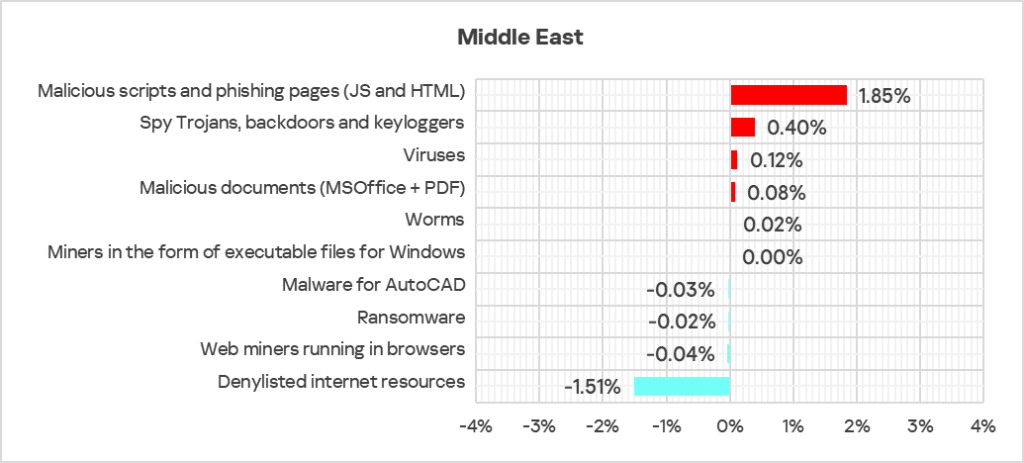
- The largest proportional increase in Q4 2024 was in the percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: by 1.2 times, third in the world in terms of growth.
- Spyware: by 1.1 times.
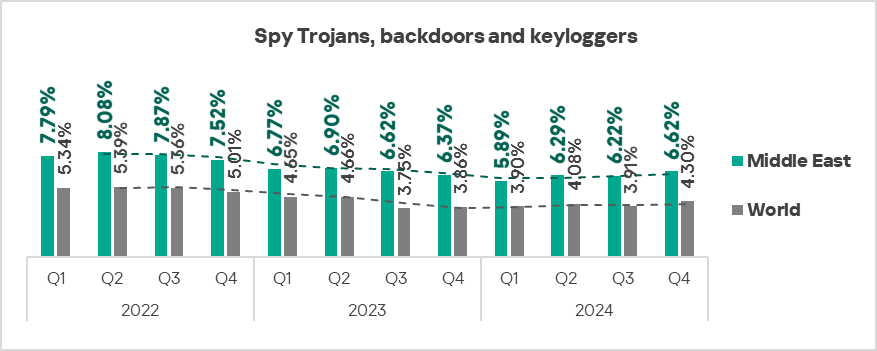
- Viruses: by 1.1 times, third in the world in terms of growth.
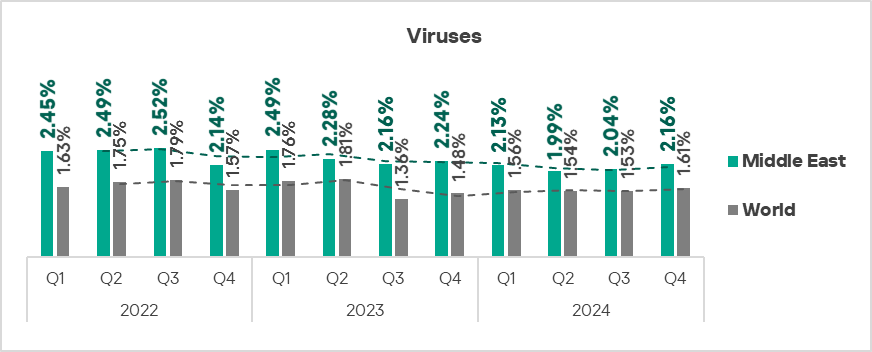
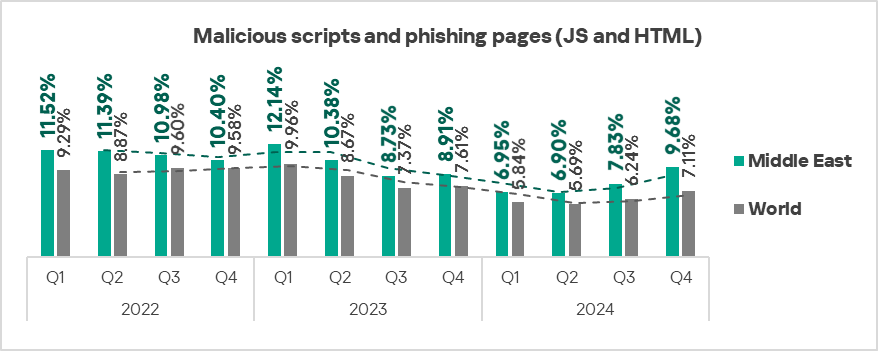
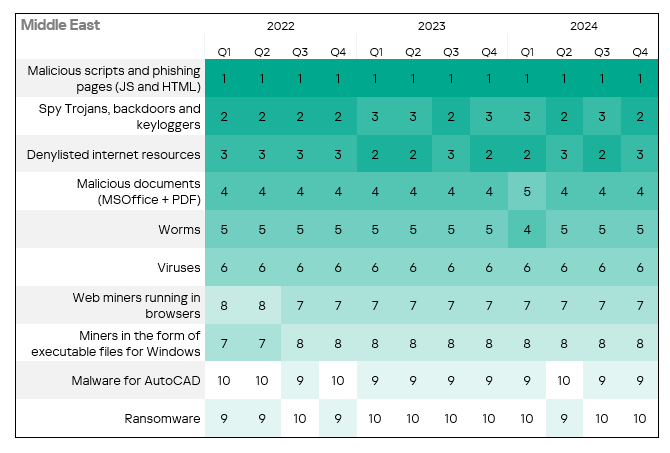
- The heatmap below illustrates changes in the rankings of threat categories in the region since the beginning of 2022. Malicious scripts and phishing pages have been the leading threat category throughout the observed period. Spyware returned from third to second place in Q4 2024.
Threat sources
- In Q4 2024, the threat sources, except for email clients, exhibited a decrease in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects from them were blocked.
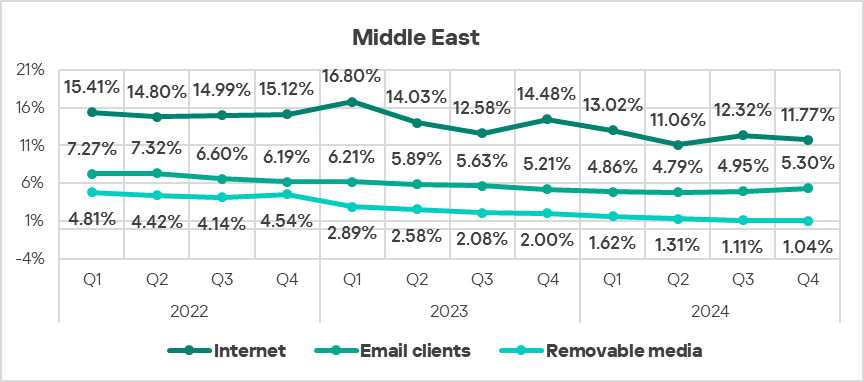
- In Q4 2024, the trend for threats from email clients widened the gap between the global average due to an increase by a factor of 1.1 in the percentage of ICS computers on which threats from email clients were blocked, while the global trend kept declining.
The region ranked second in the world in terms of growth of threats from email clients.
Industries
- The most affected industry in the region, as selected for this report, was building automation.
- From a global perspective, the following industries saw a higher percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked:
- Construction – 1.2 times higher.
- Electric Power – 1.2 times higher.
- Oil & Gas – 1.2 times higher.
- Building Automation – 1.1 times higher.
- Engineering & ICS Integration – 1.1 times higher.
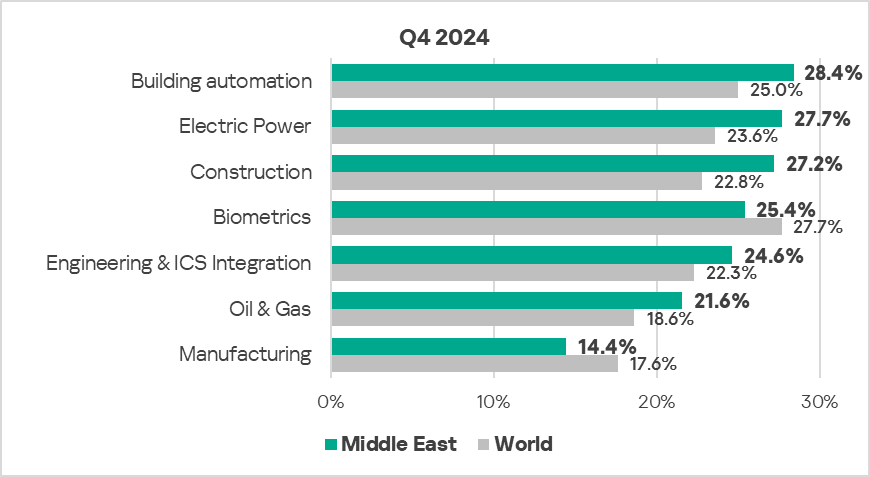
- In Q4 2024, the manufacturing sector exhibited the most noticeable increase (by a factor of 1.2) in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked, compared to the previous quarter.
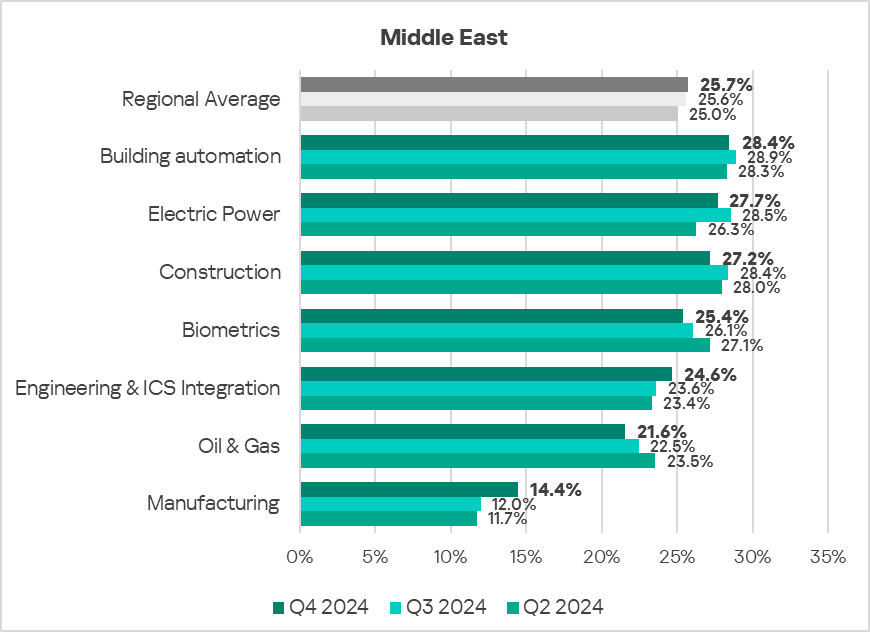
- Despite occasional fluctuations, the trends in the selected sectors show an overall positive dynamic.

Central Asia
Current threats
Overall
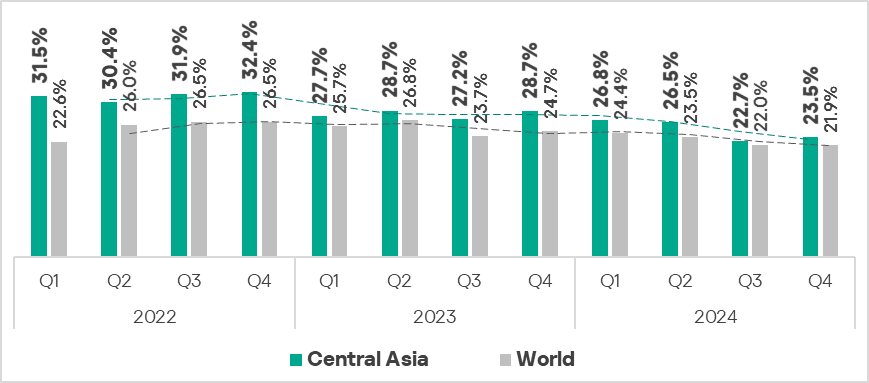
- Fourth place in the global ranking by percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
- The indicator remains higher than the global average, although shows a positive trend of narrowing the gap.
- In Q4 2024, the region showed a slight increase in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked compared to the previous quarter.
Comparative analysis
Threat categories
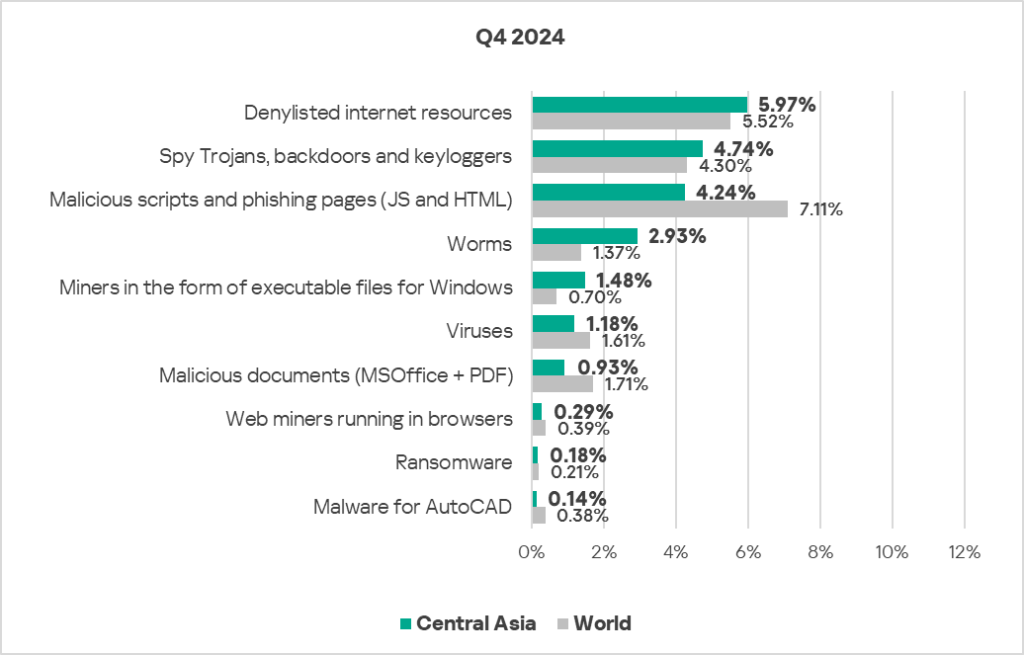
- Compared to the global average, the region has a higher percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Miners in the form of executable files for Windows: 2.1 times higher, ranks first by value globally.
- Worms: 2.1 times higher, ranks second by value globally.
- Denylisted internet resources: 1.1 times higher, ranks third by value globally.
- Spyware: 1.1 times higher.
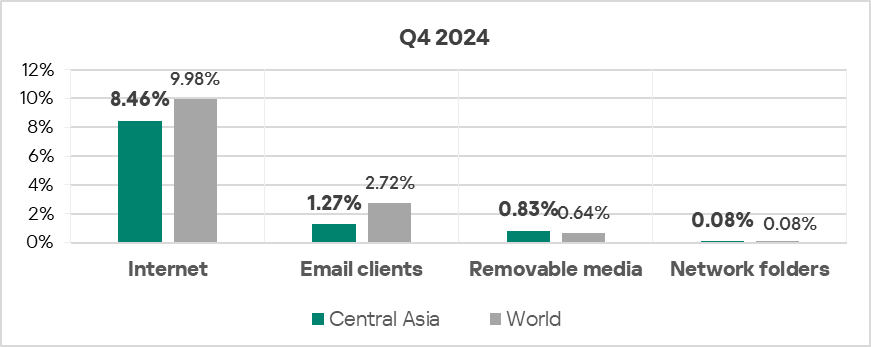
Threat sources
- The percentage of ICS computers on which threats from removable devices were blocked exceeded the global average by 1.3 times in Q4 2024.
Quarterly changes and trends
Threat categories
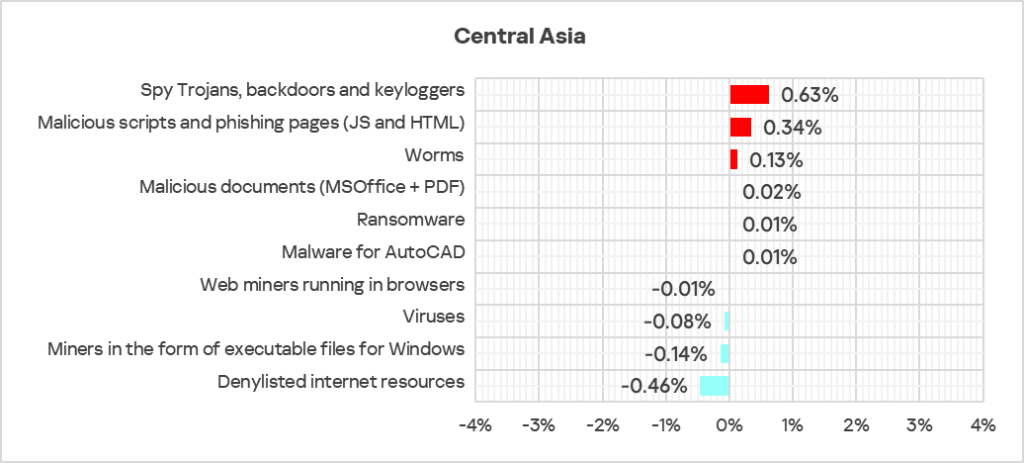
- The largest proportional increase in Q4 2024 was in the percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Spyware: by 1.2 times.
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: by 1.1 times.
- Malware for AutoCAD: by 1.1 times
- Ransomware: by 1.1 times.

- The heatmap below illustrates changes in the rankings of threat categories in the region since the beginning of 2022. Denylisted internet resources have been the leading threat category in the region since Q1 2022, with the exception of Q4 2022 and Q4 2023.
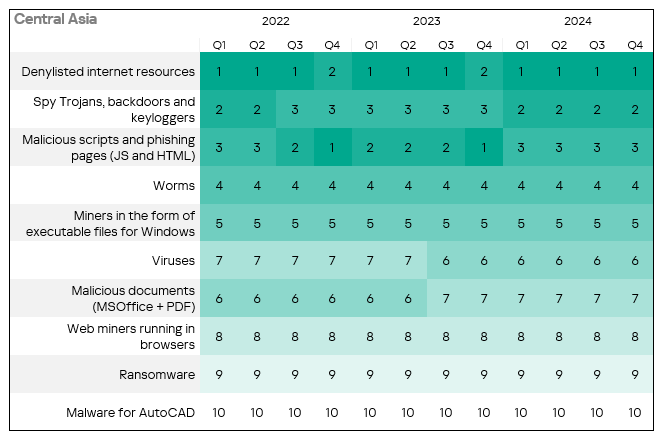
Threat sources
In Q4 2024, all sources of threats in the region exhibited a decrease in the percentage of ICS computers on which they were blocked.
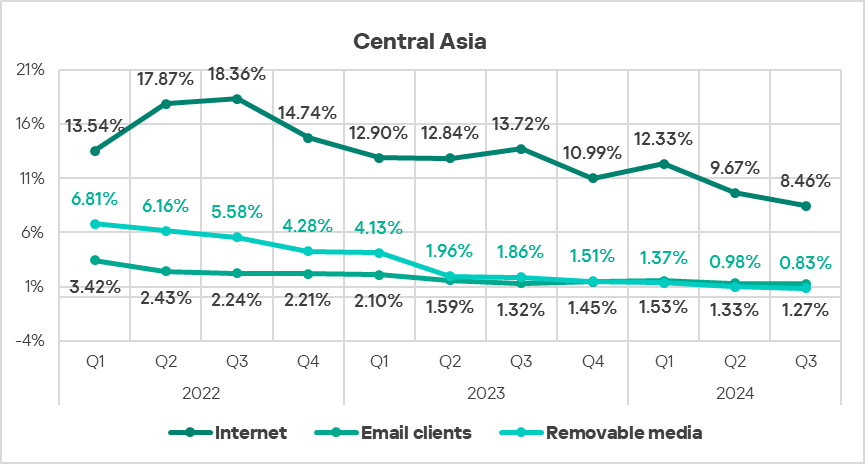
Industries
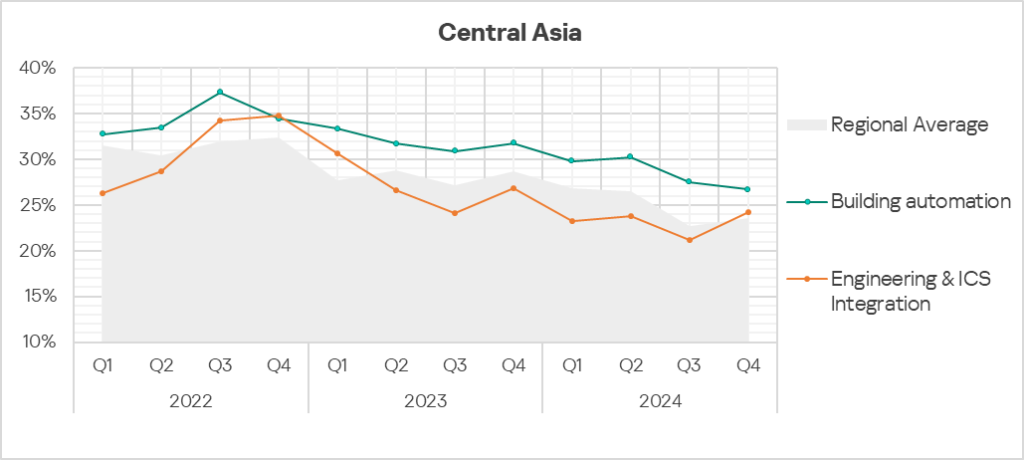
- The most affected industry in the region, as selected for this report, was building automation.
- From a global perspective, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked in the building automation, and engineering and ICS integration sectors was 1.1 times higher than the respective global averages for these industries.
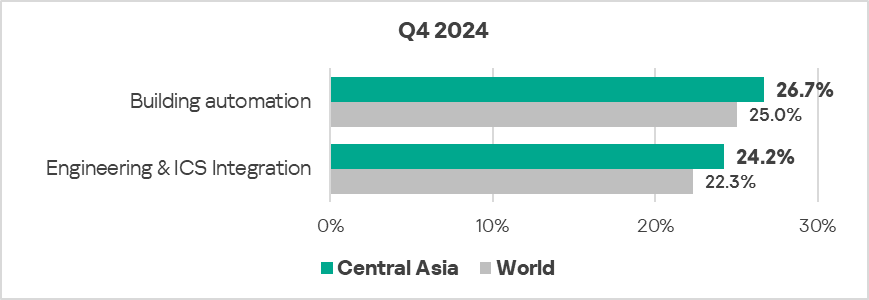
- In Q4 2024, the engineering and ICS integration sector saw an increase (by 1.1 times) in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
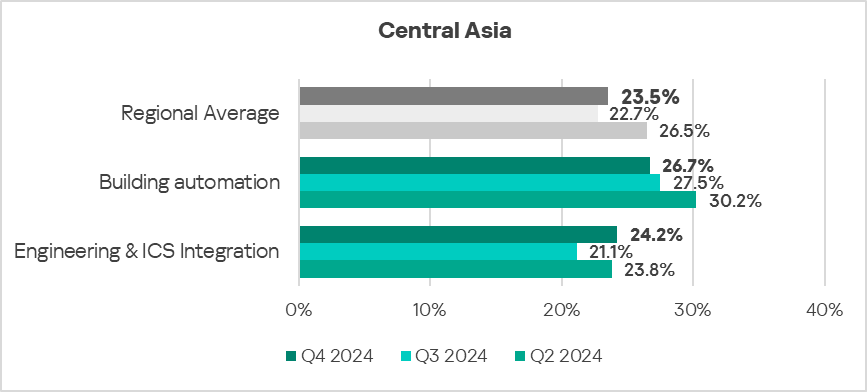
The trends in the selected sectors demonstrate an overall positive dynamic.
East Asia
Current threats
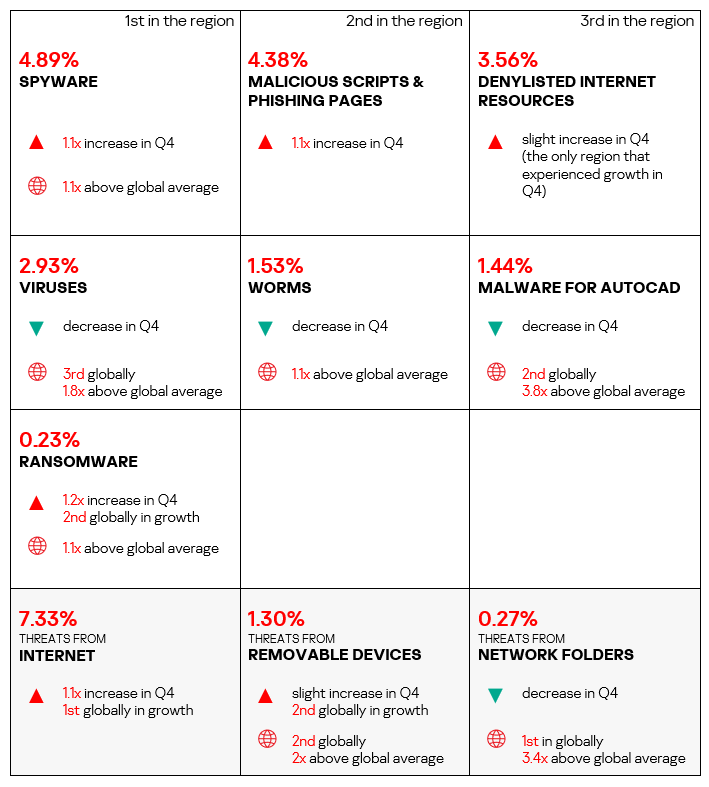
Overall
- Fifth place in the global ranking by percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked. The region moved up from eighth place in the ranking.
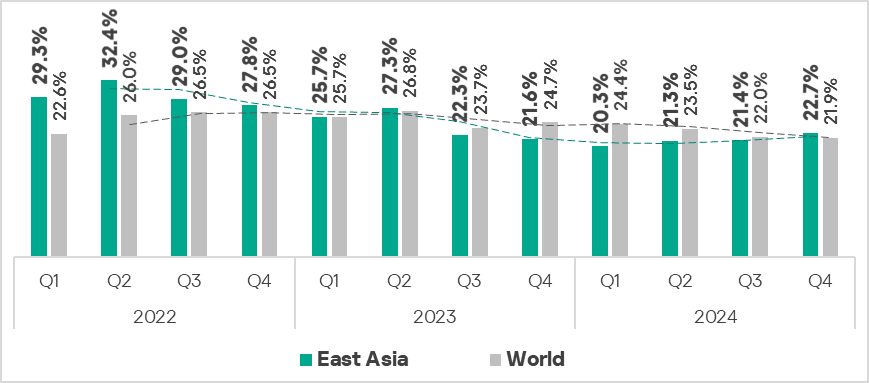
- East Asia demonstrates a downtrend with fluctuations.
- In Q4 2024, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked exceeded the global average for the first time since Q2 2023.
- In Q4 2024, the region showed an increase in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked – by 1.1 times. The region ranked first globally in terms of growth.
Comparative analysis
Threat categories
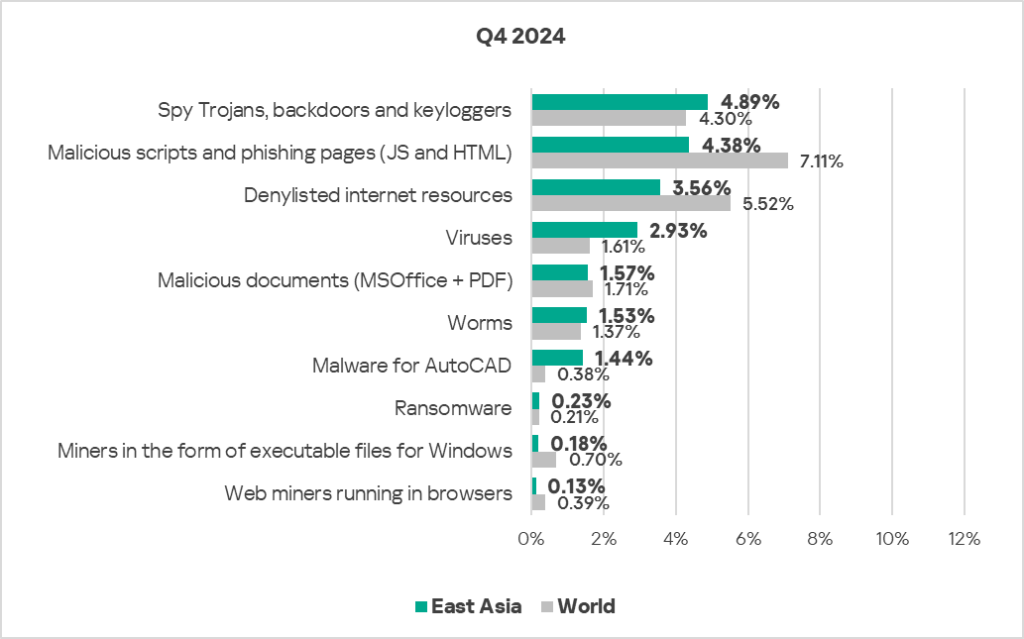
- Compared to the global average, the region has a noticeably higher percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Malware for AutoCAD: 3.8 times higher, ranked second by value globally.
- Viruses: 1.8 times higher (surpassing Q3 2024 levels), third by value globally.
- Worms: 1.1 times higher.
- Ransomware: 1.1 times higher.
- Spyware: 1.1 times higher.
Threat sources
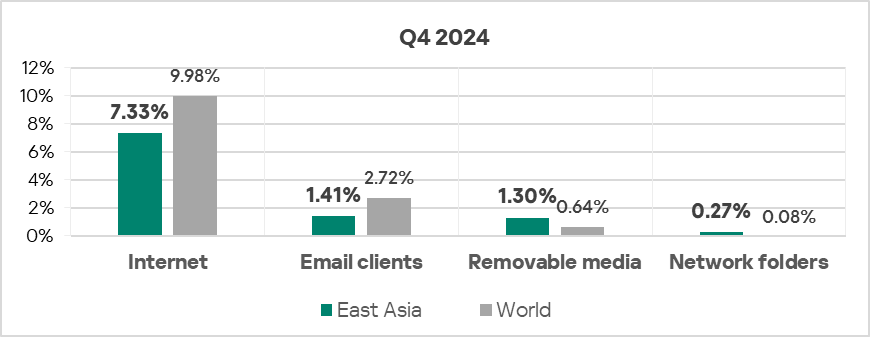
- In Q4 2024, East Asia ranked first again among the regions by percentage of ICS computers on which malicious threats from network folders were blocked, surpassing the global average by 3.4 times (exceeding Q3 2024 levels).
- The percentage of ICS computers on which threats from removable devices were blocked in the region was 2 times higher than the global average (exceeding Q3 2024 levels).
Quarterly changes and trends
Threat categories
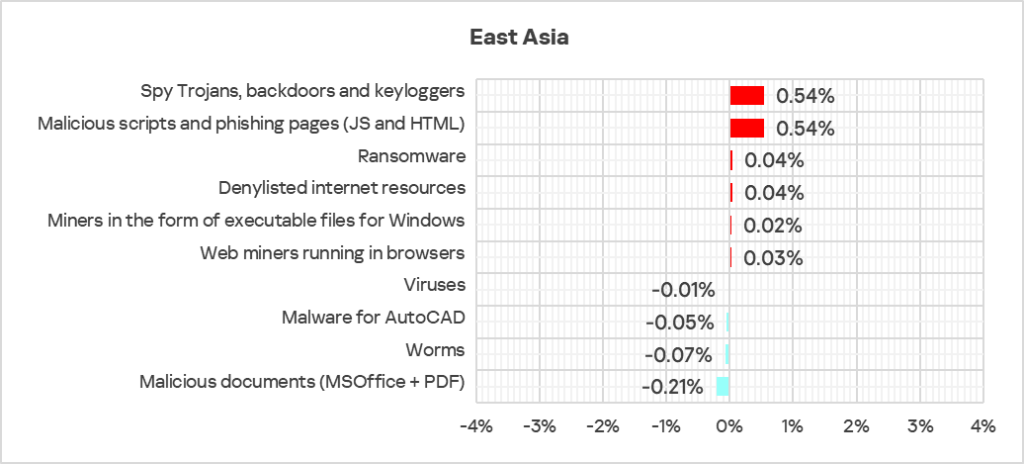
- The largest proportional increase in Q4 2024 was in the percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Web miners: by 1.3 times, third globally in terms of growth.
- Ransomware: by 1.2 times, second globally in terms of growth.
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: by 1.1 times.
- Executable miners: by 1.1 times.
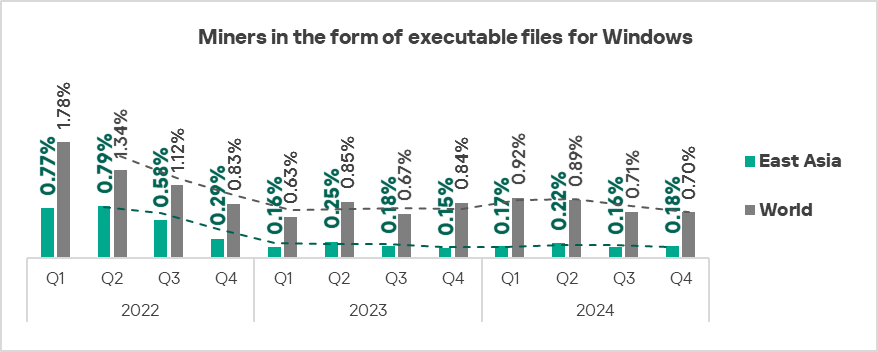
- Spyware – by 1.1 times.
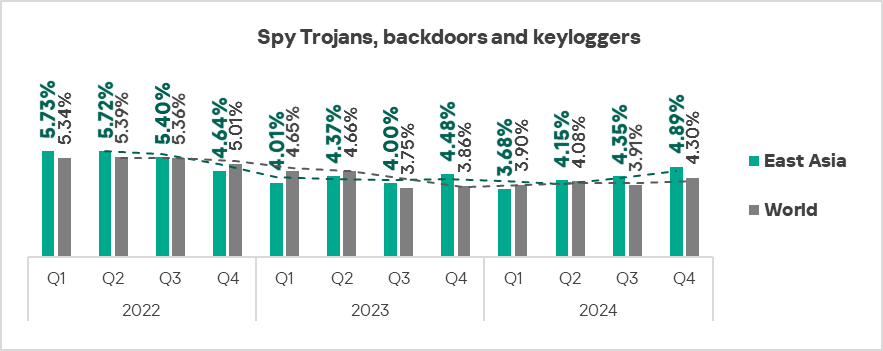
- The heatmap below illustrates changes in the rankings of threat categories in the region since the beginning of 2022. Spyware has been the leading threat category in the region since Q4 2023, jumping from third to first place and replacing malicious scripts and phishing pages.
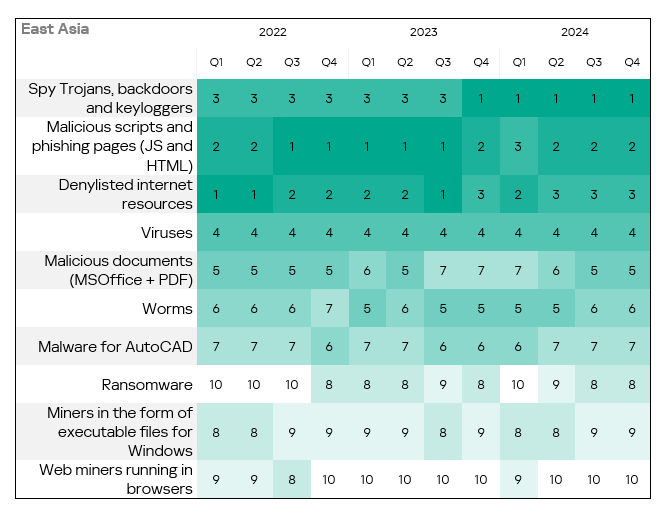
Threat sources
- Internet threats kept increasing in Q4 2024 (by 1.1 times), in contrast to the global average in terms of percentage of ICS computers on which they were blocked.
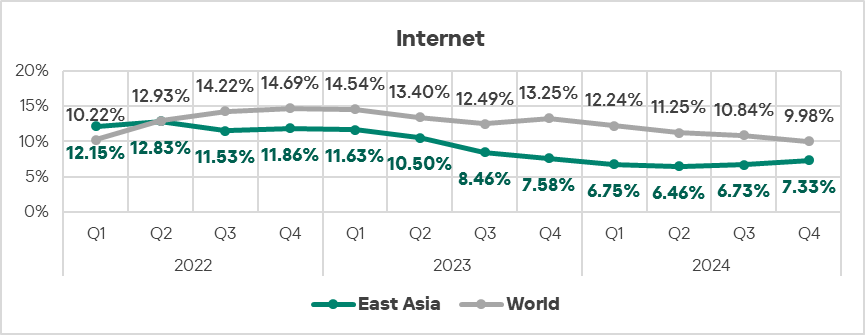
- Threats from network folders which were blocked on ICS computers in East Asia continued to show a mostly declining trend starting in the second half of 2022, staying significantly above the global average.
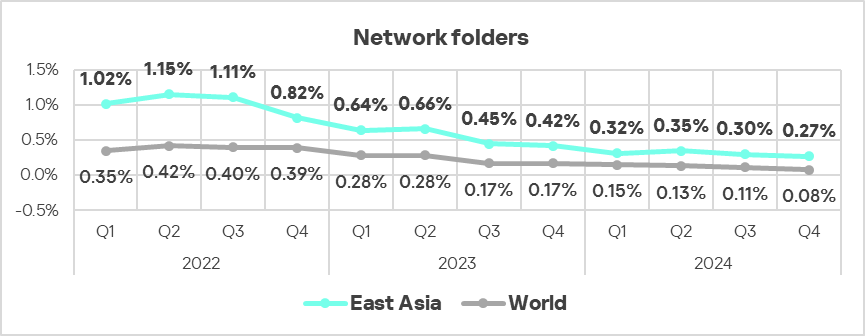
- The region exhibited an increase in threats distributed via removable devices.
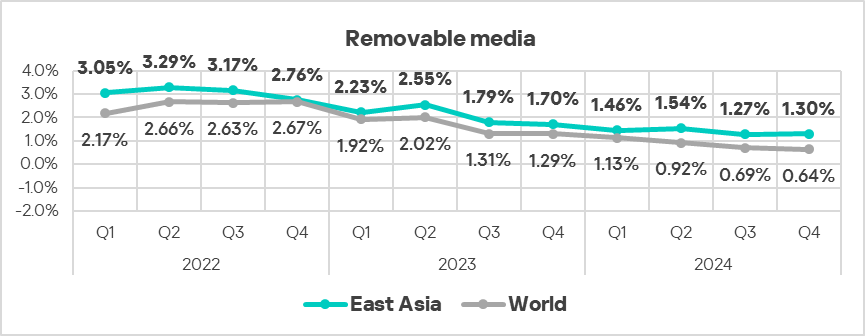
- Overall, all major sources exhibit downward long-term trends.
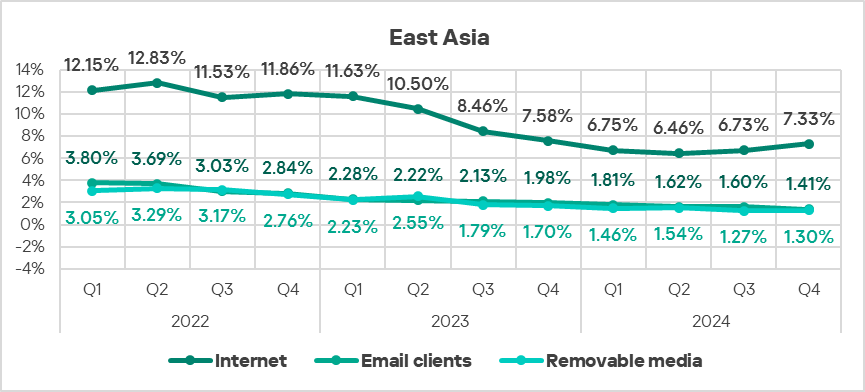
Industries
- The most affected industry in the region, as selected for this report, was electric power.
- Compared to the respective global averages, the following sectors in the region saw a higher percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked:
- Electric Power: 1.4 times higher.
- Construction: 1.3 times higher (surpassing Q3 2024 levels).
- Manufacturing: 1.3 times (surpassing Q3 2024 levels).
- Engineering & ICS Integration: 1.1 times (surpassing Q3 2024 levels).
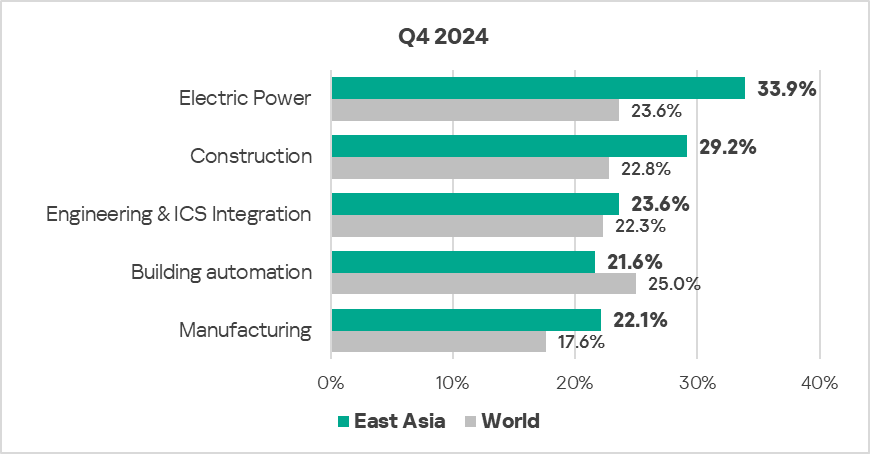
- In Q4 2024, all sectors showed an increase in terms of the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
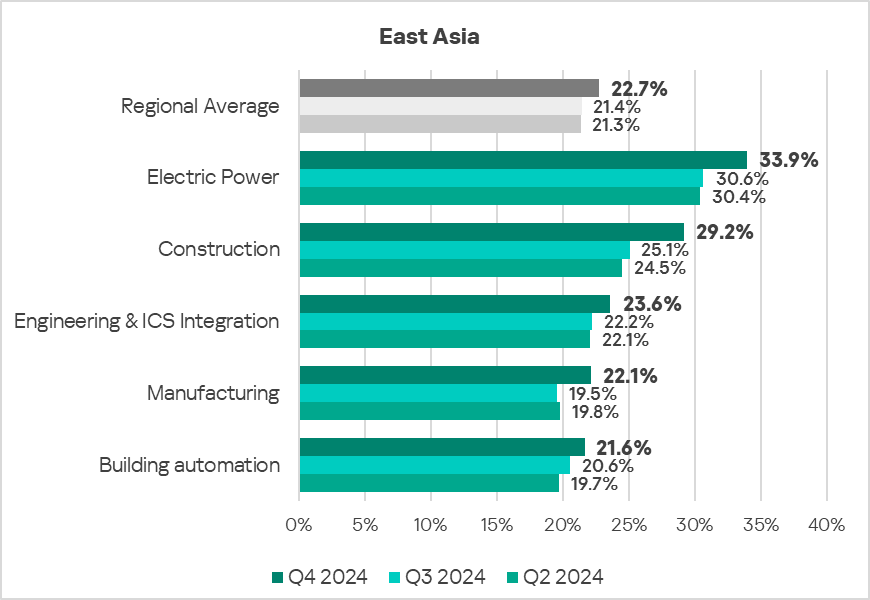
- The electric power sector consistently exhibited the highest rate of blocked malicious objects on ICS computers throughout the period, significantly above the regional average.
All sectors show an upward trend starting in Q2 2024.
Eastern Europe
Current threats
Overall
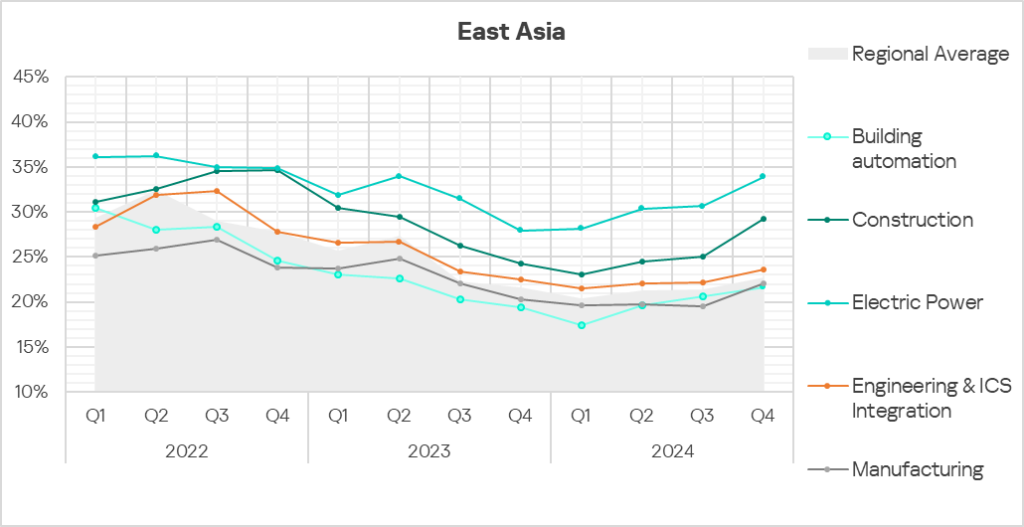
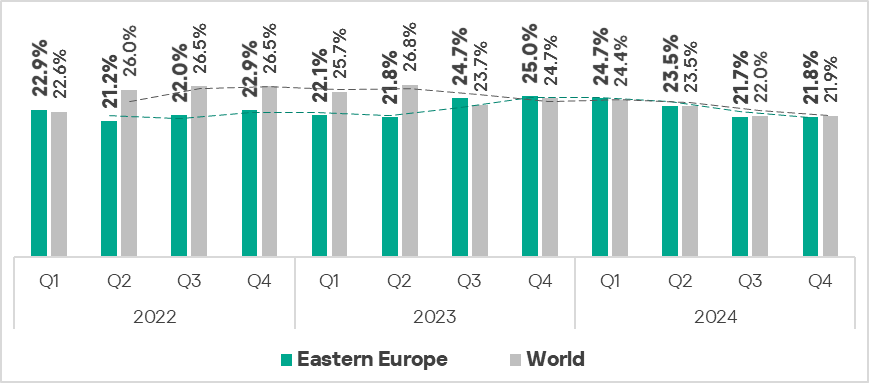
- Sixth place in the global ranking by percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked. The region moved up from seventh place in the global ranking. Before Q2 2023, the region did not rank higher than ninth place.
- In Q4 2024, the region showed a slight increase in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked compared to the previous quarter. The indicator was slightly below the global average.
Comparative analysis
Threat categories
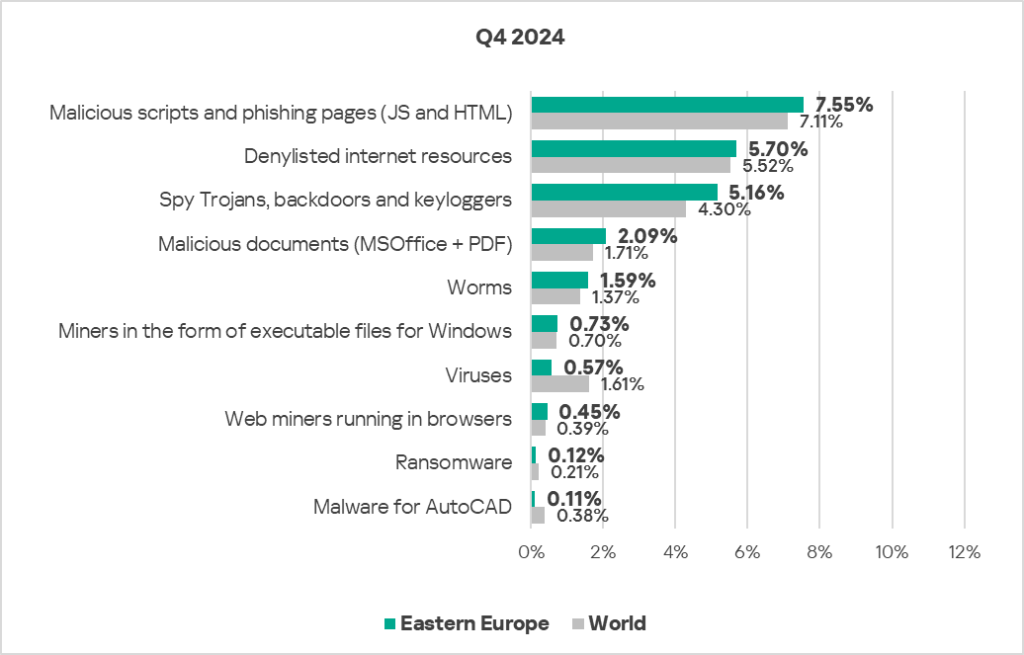
- Compared to the global figures, the region has a higher percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Malicious documents, 1.2 times higher (surpassing Q3 2024 levels).
- Spyware, 1.2 times higher.
- Worms, 1.2 times higher (surpassing Q3 2024 levels).
- Web miners, 1.2 times higher.
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages, 1.1 times higher (surpassing Q3 2024 levels).
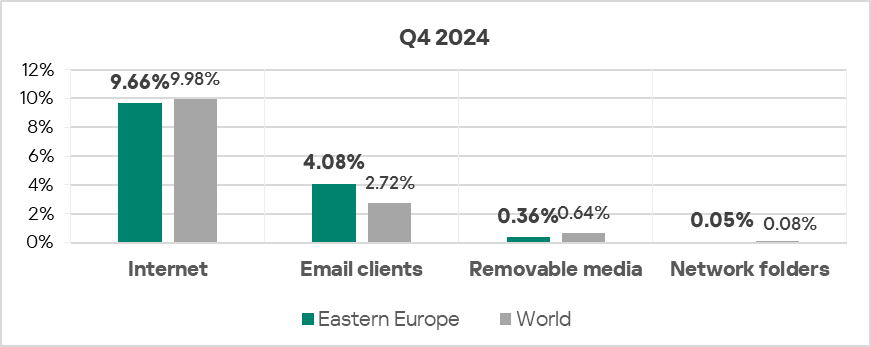
Threat sources
As in the previous quarter, threats that originated from email clients exceeded the global average by 1.5 times.
Quarterly changes and trends
Threat categories
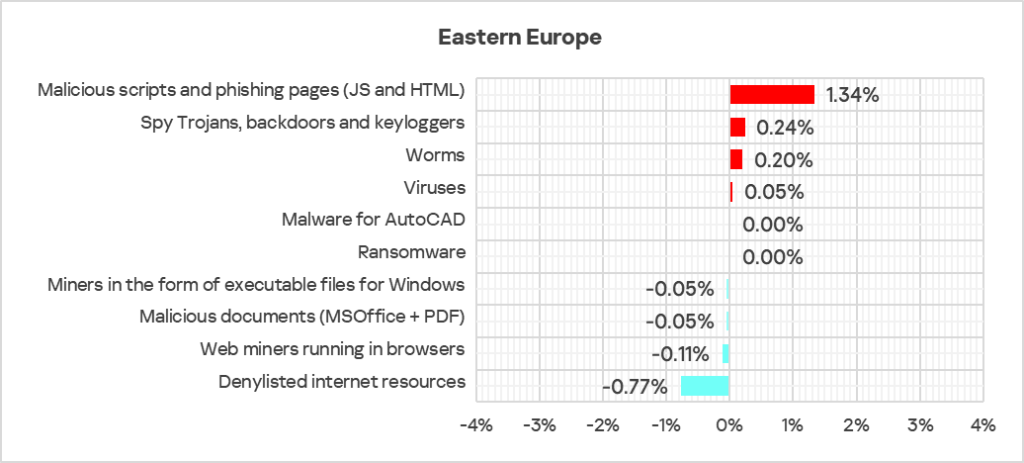
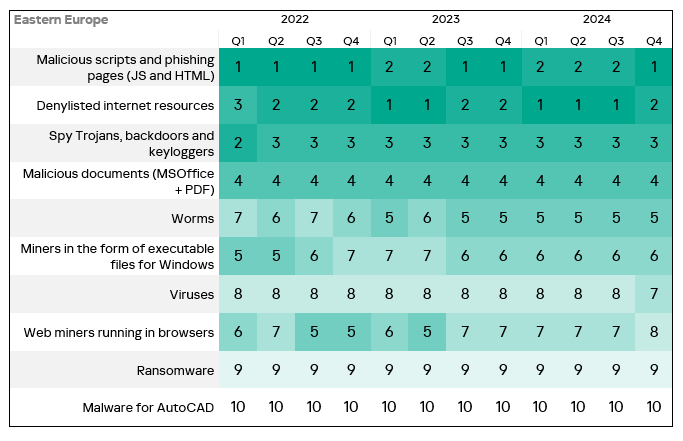
The largest quarterly increase was in the percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: by 1.2 times.
- Worms: by 1.1 times.
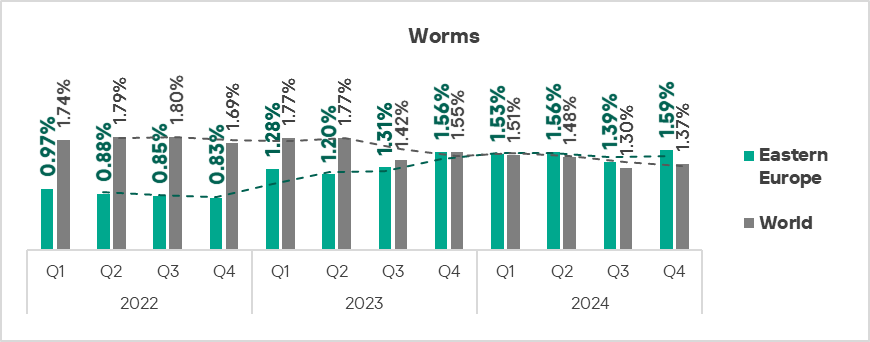
- Viruses: by 1.1 times.
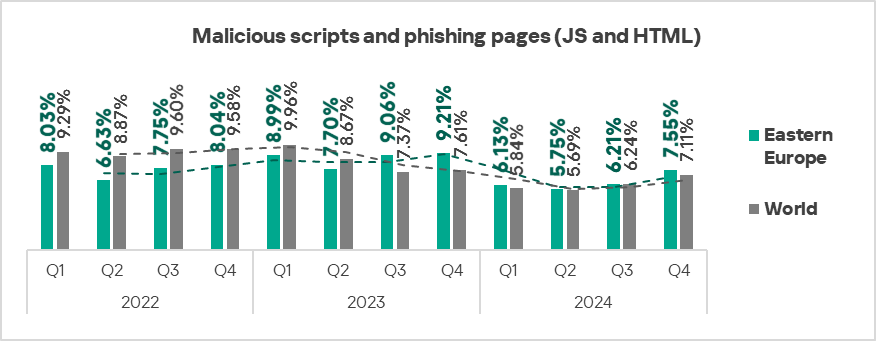
- The heatmap below illustrates changes in the rankings of threat categories in the region since the beginning of 2022. Malicious scripts and phishing pages returned to first place and viruses jumped one position in Q4 2024.
Threat sources
- In Q4 2024, all threats sources in Eastern Europe exhibited a decrease in the percentage of ICS computers on which they were blocked.
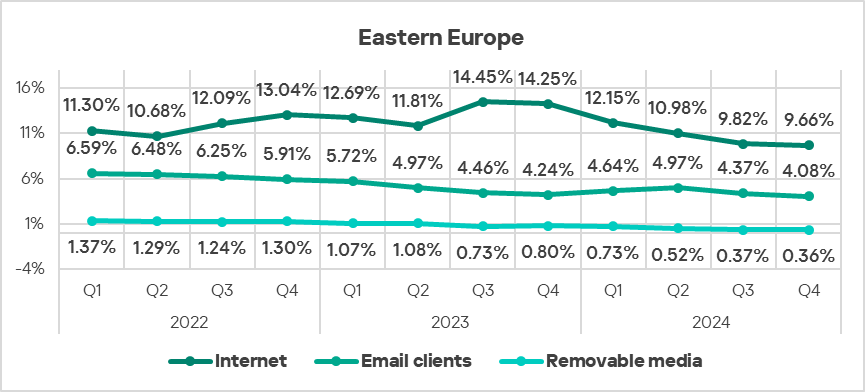
- Threats from email clients which were blocked on ICS computers in Eastern Europe show a declining trend, while staying significantly above the global average.
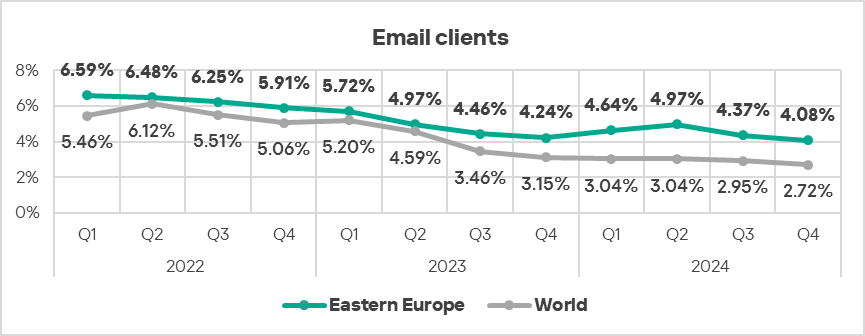
Industries
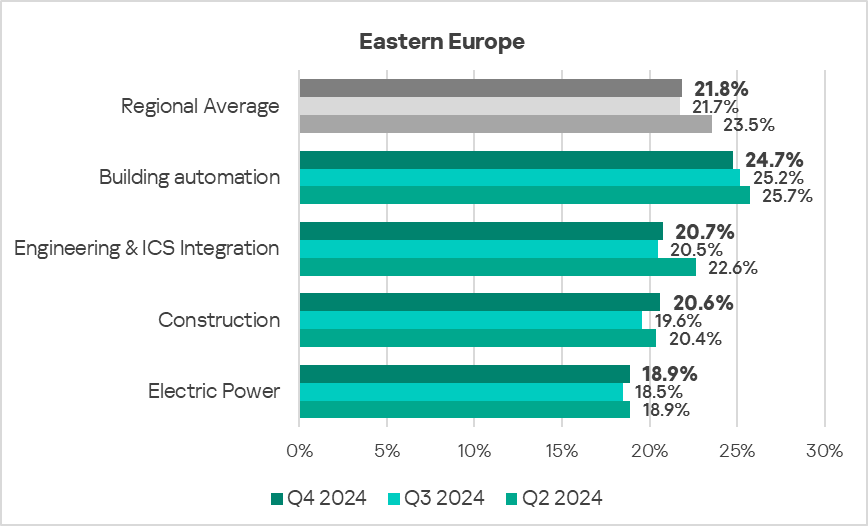
- The most affected industry in the region, as selected for this report, was building automation.
- Compared to the respective global averages, all selected industries demonstrated lower percentages of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
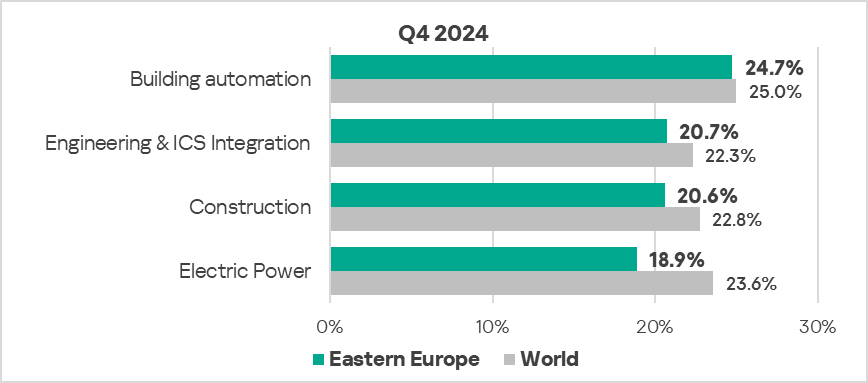
- In Q4 2024, all sectors under observation, except building automation, showed an increase in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked. The most significant proportional increase was in the construction sector – by 1.1 times.
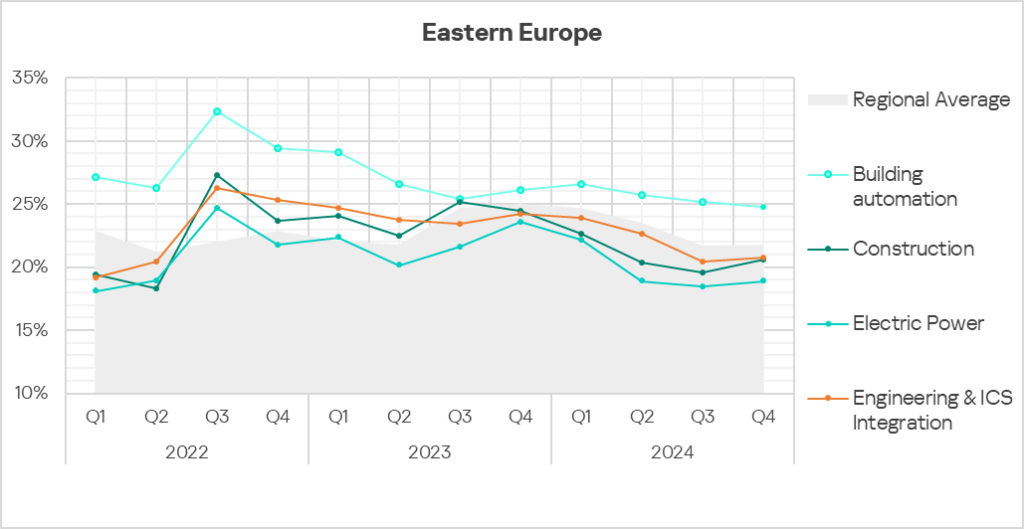
- The trends in the selected sectors still demonstrate a general stabilization after a notable rise in 2022.
Latin America
Current threats
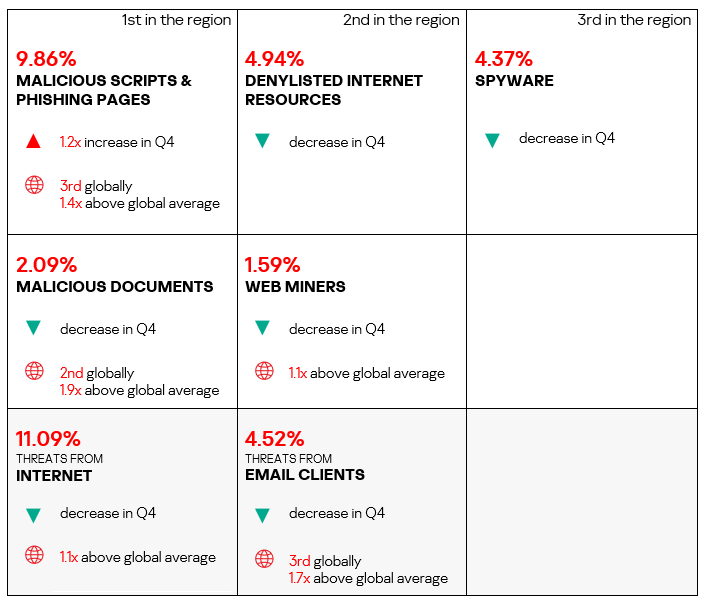
Overall
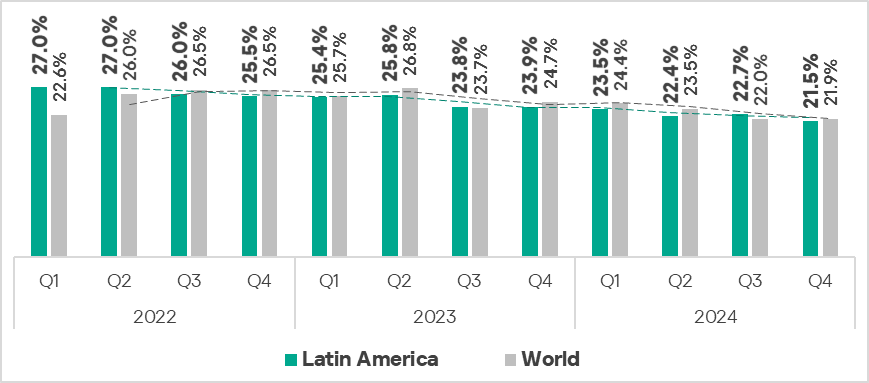
- Seventh place in the global ranking by percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked. The region moved down from fifth place in the ranking.
- In Q4 2024, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked decreased, falling slightly below the global average.
- Overall, the region demonstrates a downward trend.
Comparative analysis
Threat categories
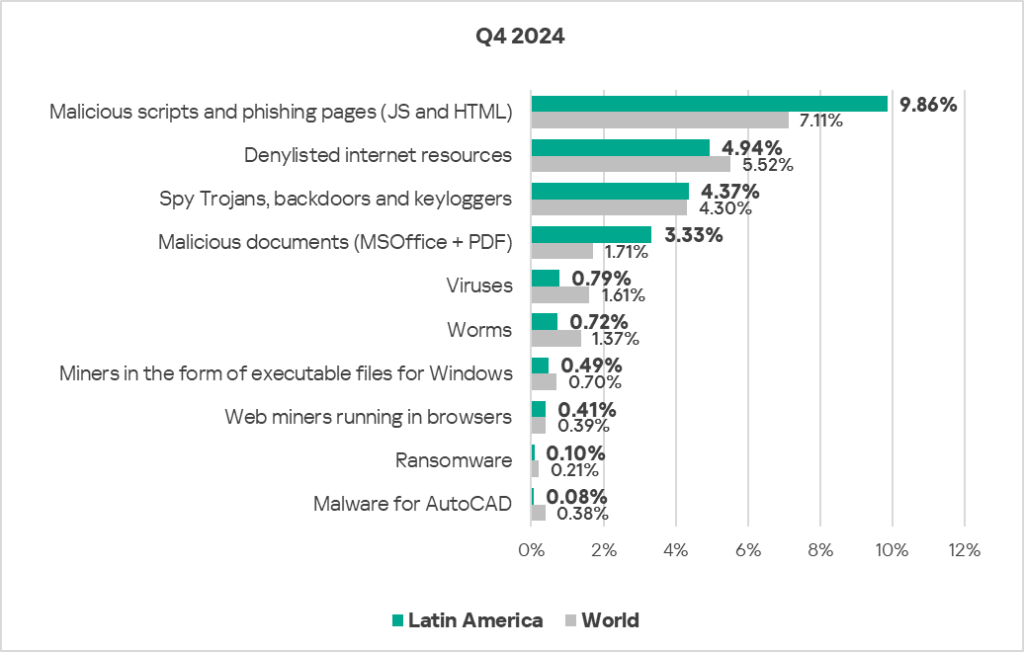
- Compared to the global figures, the region has a noticeably higher percentage of ICS computers on which the following threat categories were blocked:
- Malicious documents: 1.9 times higher, ranked second by value among the regions.
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: 1.4 times higher, ranked second by value among the regions.
- Web miners: 1.1 times higher.
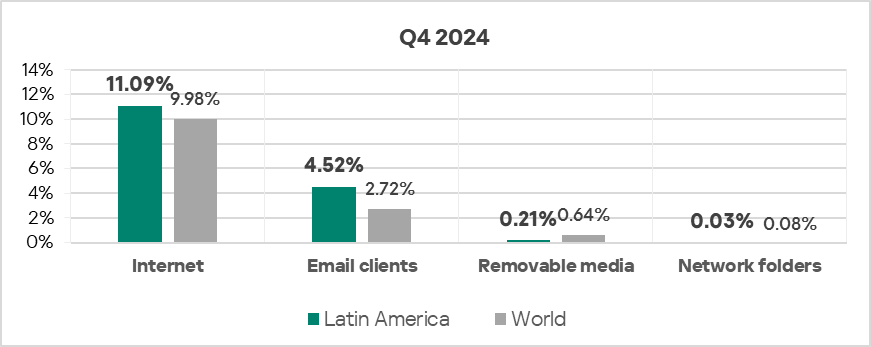
Threat sources
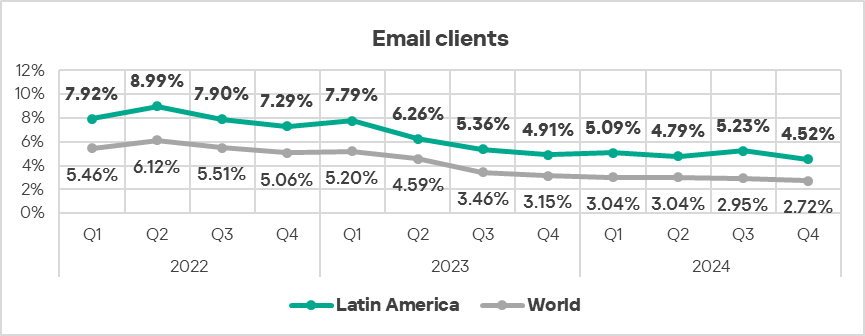
- The region ranked third in the world by percentage of ICS computers on which threats from email clients were blocked, exceeding the global average by 1.7 times.
- Threats from the internet were 1.1 times higher than the global average.
Quarterly changes and trends
Threat categories
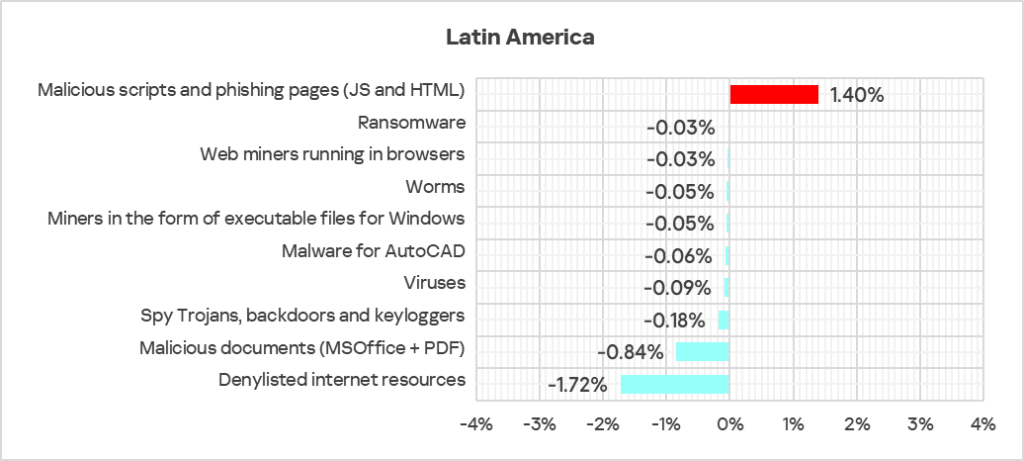
- The largest proportional increase in Q4 2024 was in the percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: by 1.2 times.
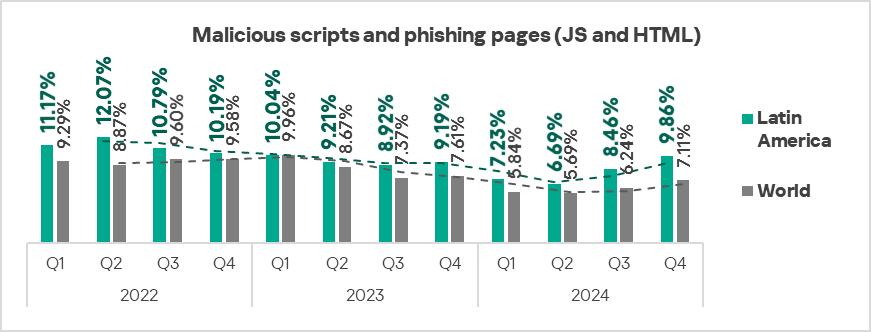
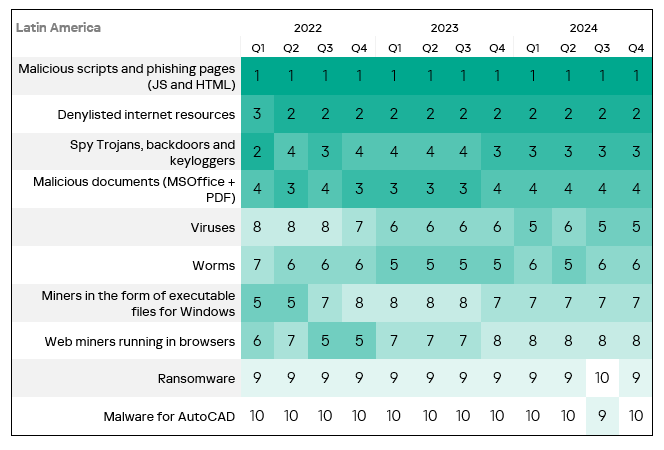
- The heatmap below illustrates changes in the rankings of threat categories in the region since the beginning of 2022. Malicious scripts and phishing pages have been the leading threat category in the region throughout the observed period. In Q4 2024, ransomware moved up one position.
Threat sources
In Q4 2024, all threats sources in Latin America exhibited a decrease of the percentage of ICS computers on which they were blocked.
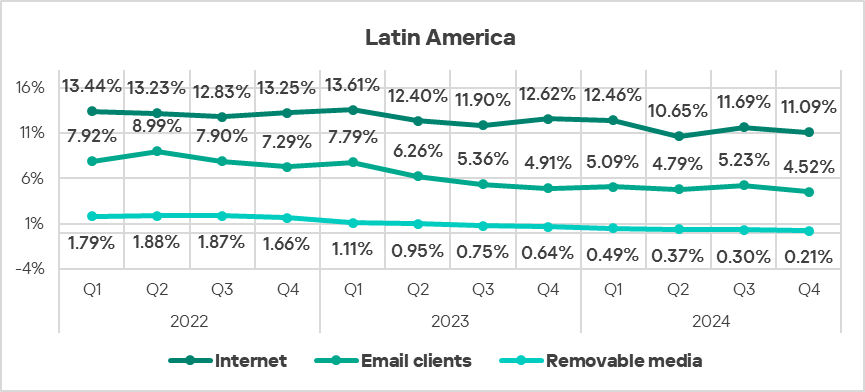
- Threats from email clients (in terms of the percentage of ICS computers on which they were blocked) exhibit a gradual downward trend mostly consistent with the global trend, but noticeably above the global average.
Industries
- The most affected industry in the region, as selected for this report, was biometrics.
- From a global perspective, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked in the oil and gas industry was 1.1 times higher than the sector’s global average.
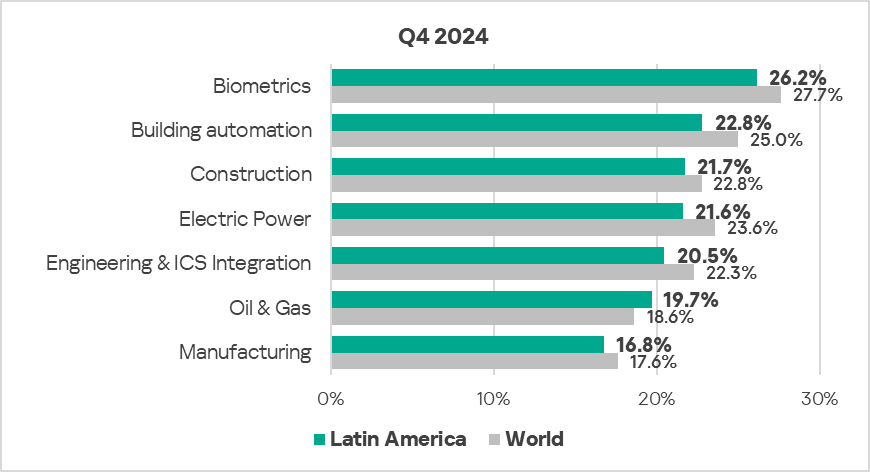
- In Q4 2024, all selected sectors in the region exhibited a decrease in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
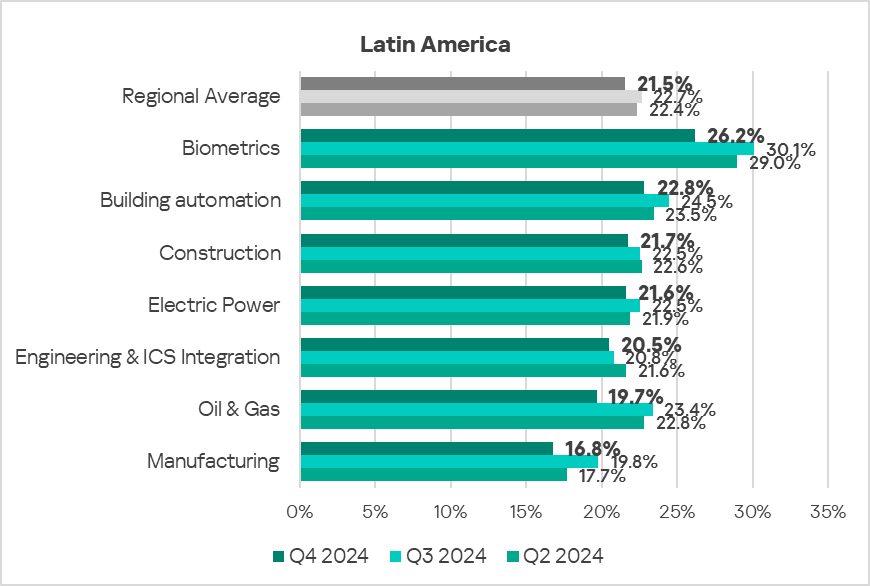
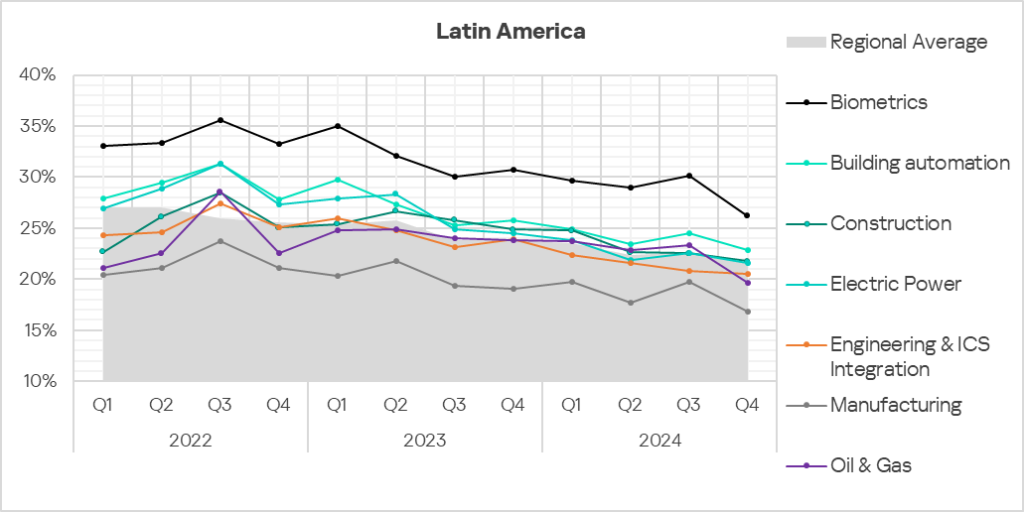
- The selected sectors, despite fluctuations, have shown mostly a positive dynamic in their long-term trends since Q1 2023.
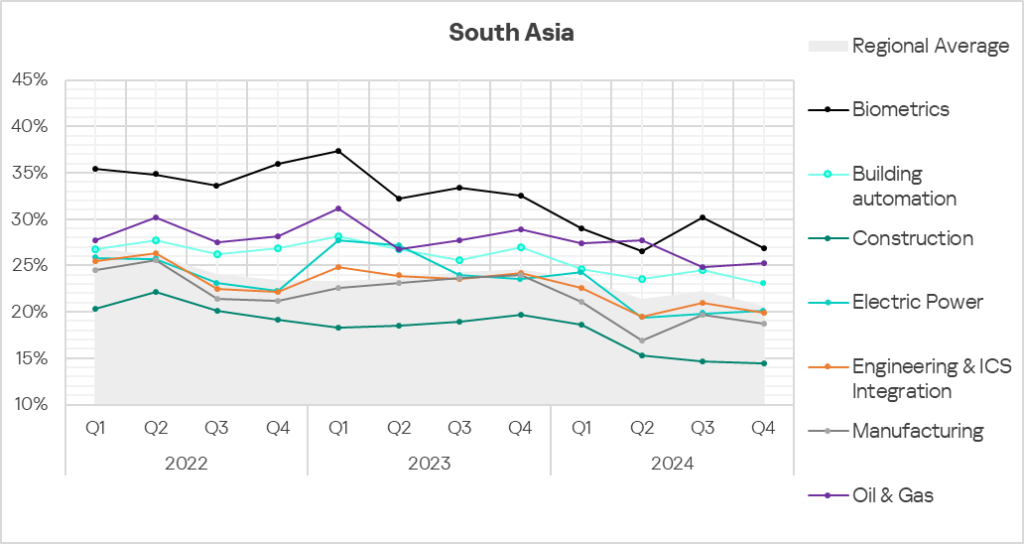
South Asia
Current threats
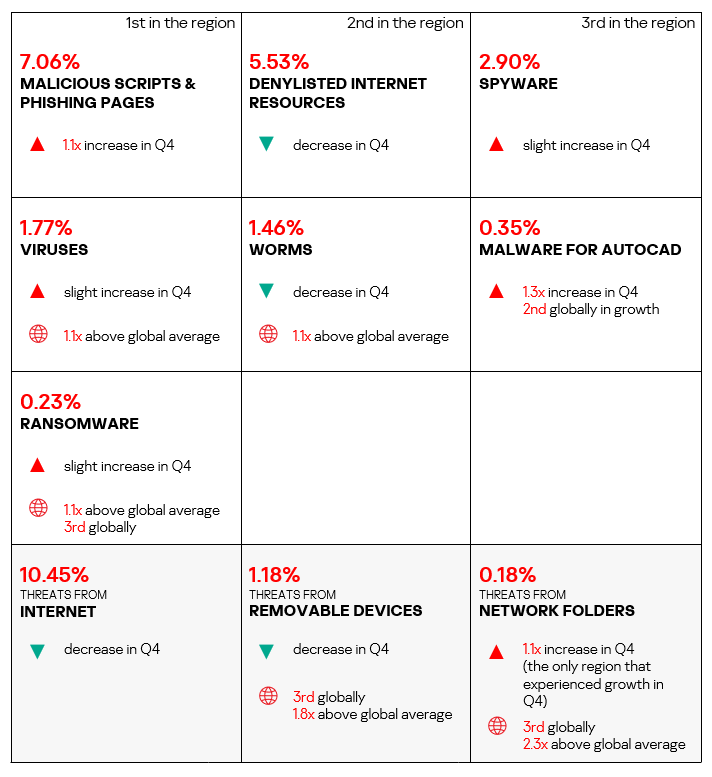
Overall
- Eighth place in the global ranking by percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
- The region demonstrates a slow downward trend with some fluctuations.
- In Q4 2024, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked decreased, falling below the global average.
Comparative analysis
Threat categories
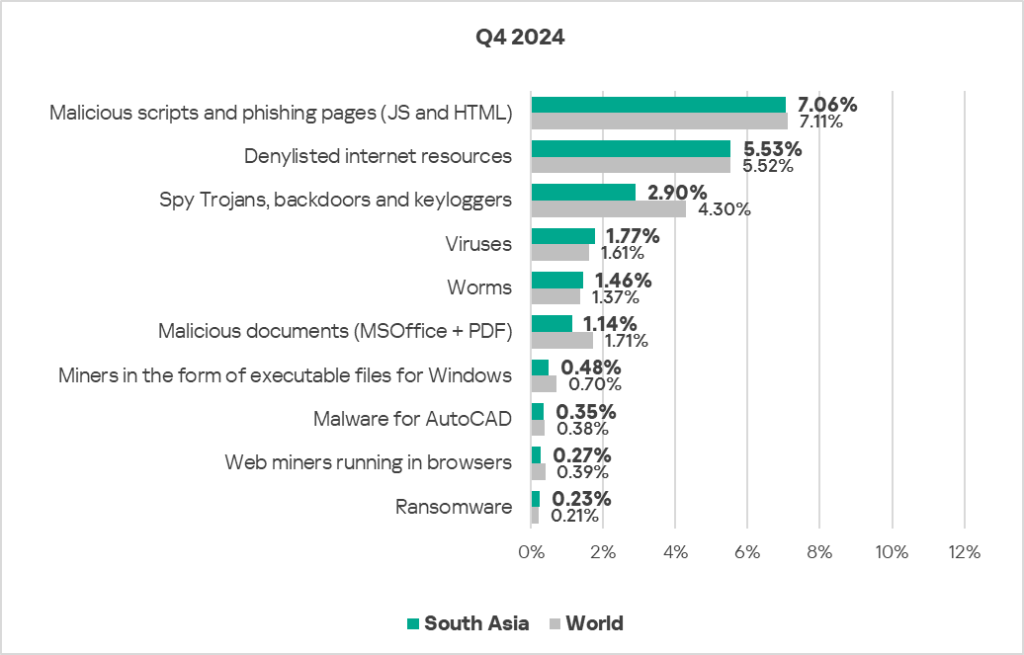
- Compared to the global average, the region has a noticeably higher percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Worms: 1.1 times higher.
- Viruses: 1.1 times higher.
- Ransomware: 1.1 times higher.
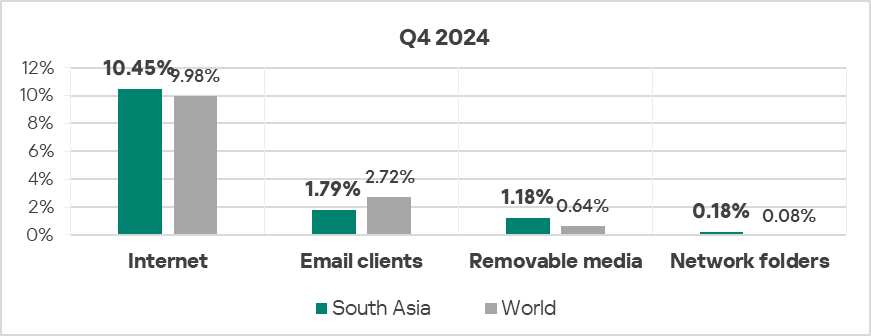
Threat sources
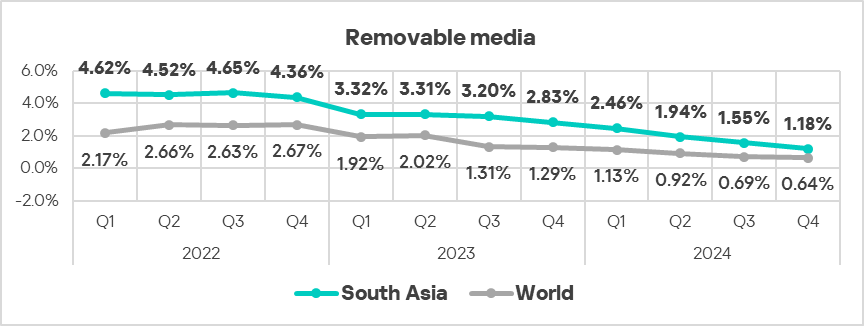
- South Asia ranks third globally by percentage of ICS computers on which malicious threats from removable devices were blocked, surpassing the global average by 1.8 times.
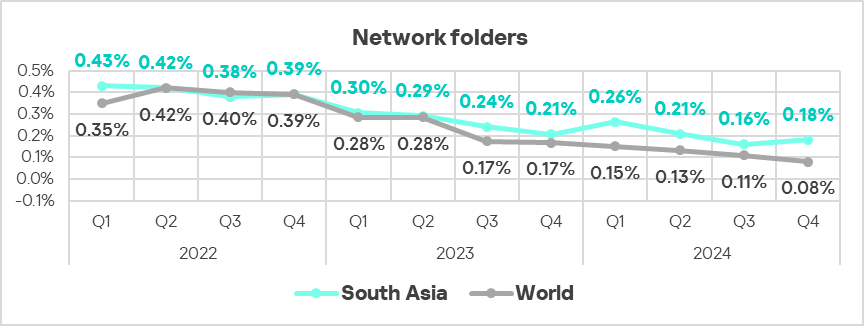
- Additionally, the region is third in the global ranking for the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious threats from network folders were blocked, exceeding the global average by a factor of 2.3.
Quarterly changes and trends
Threat categories
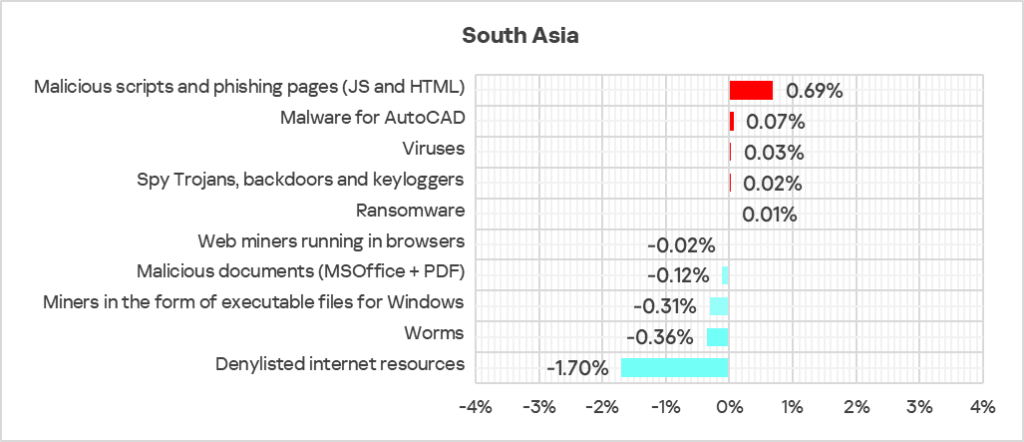
- The largest proportional increase in Q4 2024 was in the percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Malware for AutoCAD: by 1.3 times.
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: by 1.1 times.
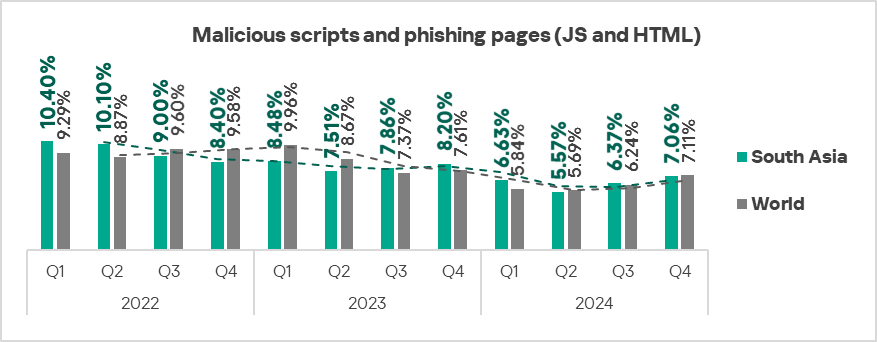
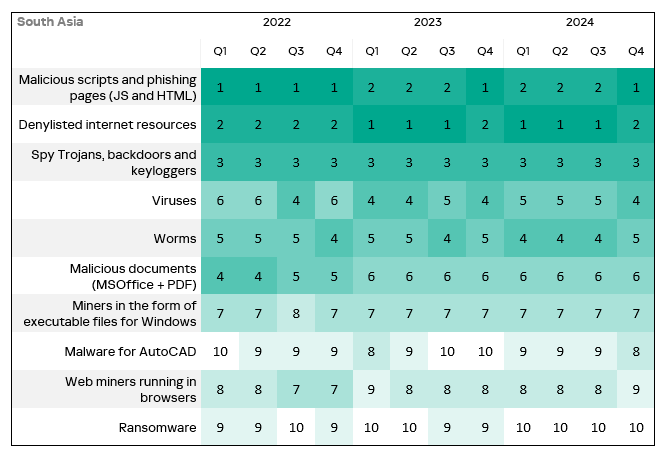
- The heat map below illustrates changes in the rankings of threat categories in the region since the beginning of 2022. Malicious scripts and phishing pages moved to first place in Q4 2024. Viruses moved to fourth place. Viruses and worms have consistently ranked high throughout the observed period. Malware for AutoCAD moved up one position to eighth place.
Threat sources
- In Q4 2024, the majority of the threat sources in South Asia exhibited a decrease in the percentage of ICS computers on which they were blocked.
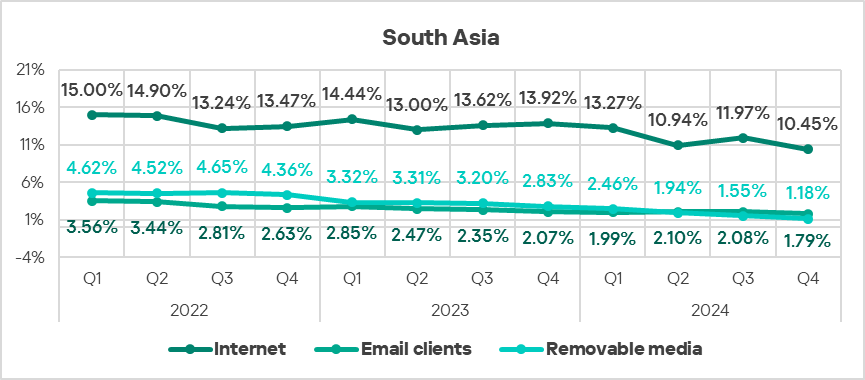
- However, threats from network folders increased in Q4 2024, staying well above the global average.
- Threats from removable drives continued to demonstrate a declining trend, though still significantly above the respective global trend.
Industries
- The most affected industry in the region, as selected for this report, was biometrics.
- From a global perspective, all sectors under consideration, except manufacturing, exhibited a lower percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked than the respective global averages.

- In Q4 2024, all selected sectors in the region, except electric power, exhibited a decrease in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
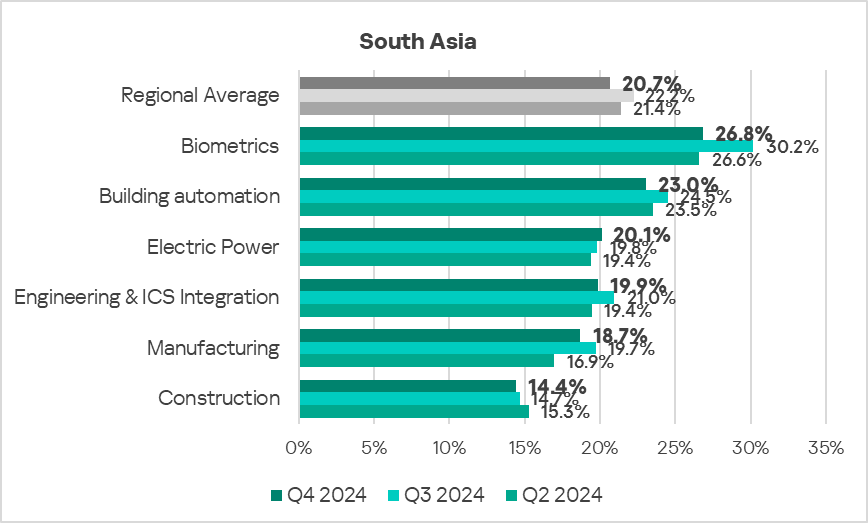
- The selected sectors for the most part show slow positive dynamics with noticeable fluctuations in their long-term trends.
Southern Europe
Current threats
Overall
- Eighth place in the regional ranking (shared with South Asia in Q4 2024).
- In Southern Europe, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked is normally below the global average.
- In Q4 2024, the region saw a 1.1-fold increase in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked. The region ranked second globally in terms of growth.

Comparative analysis
Threat categories

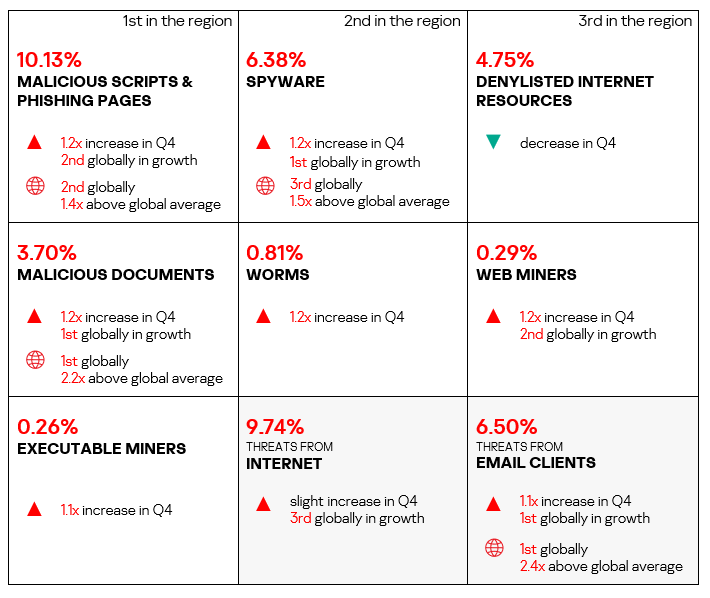
- Compared to the global average, the region has a higher percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
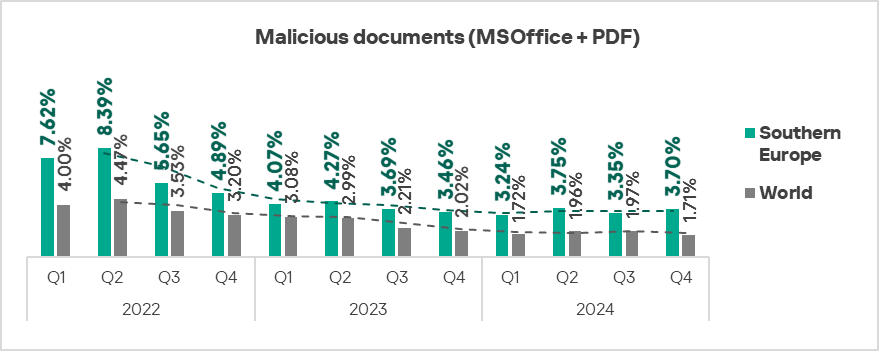
- Malicious documents: 2.2 times higher (surpassing Q3 2024 levels), ranked first by value among the regions.
- Spyware: 1.5 times higher (surpassing Q3 2024 levels), ranked third by value among the regions.
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: 1.4 times higher (surpassing Q3 2024 levels), ranked second by value among the regions.
Threat sources
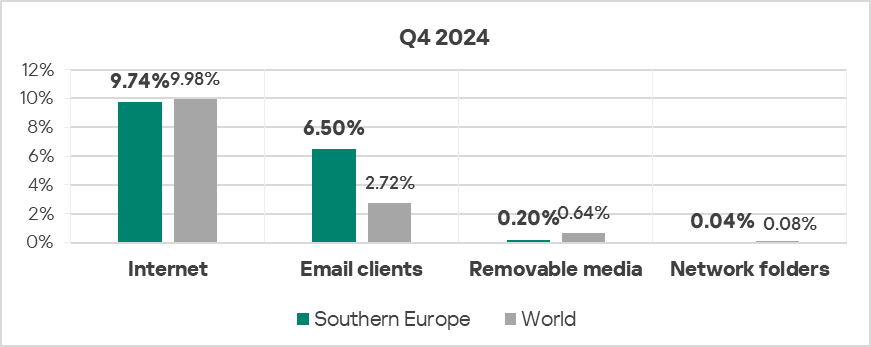
- In Q4 2024, Southern Europe again ranked first globally in the percentage of ICS computers where malicious threats from email clients were blocked, exceeding the global average by 2.4 times. The region showed an increase from Q3 2024.
Quarterly changes and trends
Threat categories
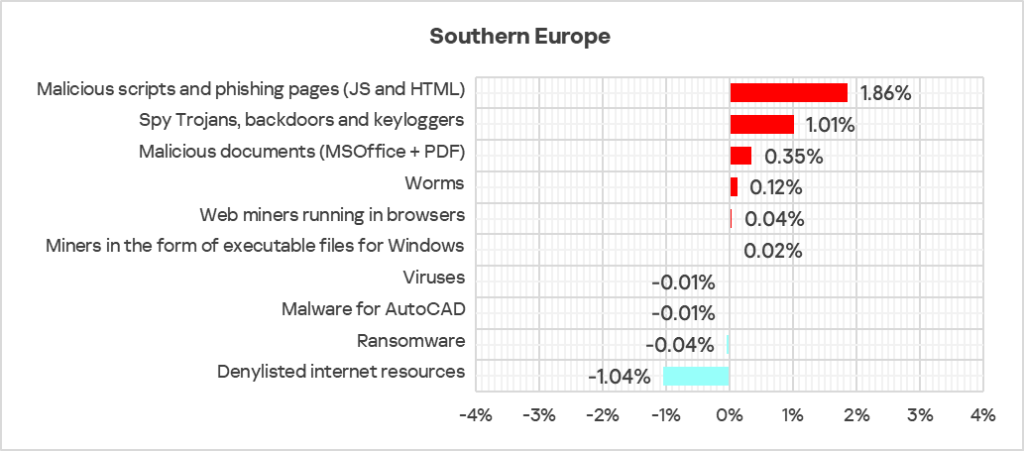
- In October 2024, industrial organizations in Southern Europe were hit by a wave of phishing emails. According to Kaspersky Security Network, most of the attacks targeted companies in Spain and Portugal. Among the analyzed malicious samples distributed via those emails were phishing PDF documents containing links to malicious web resources, executable files, and installer files containing malicious code in the form of scripts and shell code designed to download spyware.
The surge in the percentage of ICS computers in Southern Europe on which malicious scripts, malicious documents, and spyware were blocked reflects the scale of this wave. - The largest proportional increase in Q4 2024 was in the percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: by 1.2 times, ranked second globally in terms of growth.
- Spyware: by 1.2 times, ranked first globally in terms of growth.
- Worms: by 1.2 times.
- Web miners: by 1.2 times, ranked second globally in terms of growth.
- Malicious documents: by 1.1 times, ranked first globally in terms of growth.
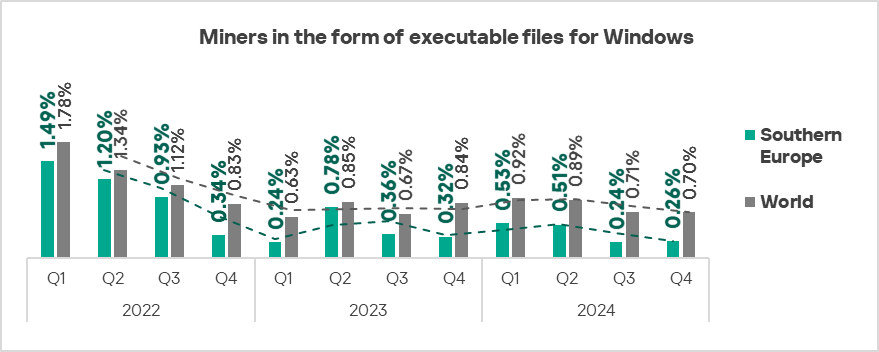
- Executable miners: by 1.1 times.
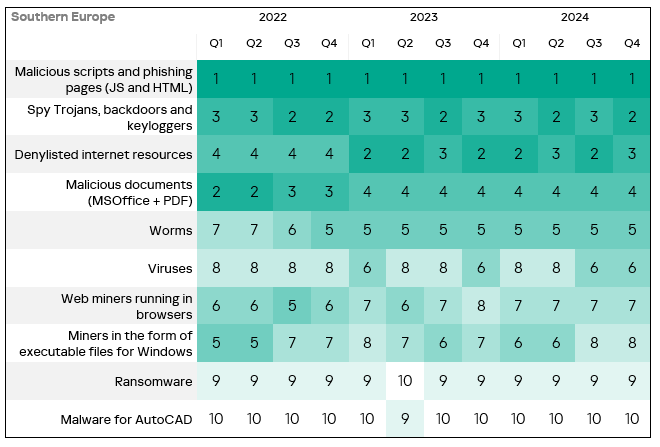
- The heatmap below illustrates changes in the rankings of threat categories in the region since the beginning of 2022. Malicious scripts and phishing pages have been the leading threat category in the region throughout the observed period. Spyware moved back to second from third place in Q4 2024.
Threat sources
- In Q4 2024, the percentage of ICS computers on which threats from the internet were blocked increased compared to the previous quarter, in contrast to the global trend.
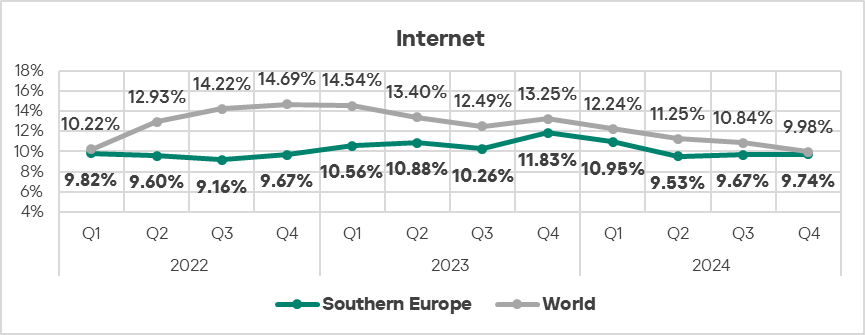
- Threats from email clients also showed an increase (by 1.1 times) in percentage of ICS computers on which they were blocked, compared to the previous quarter.
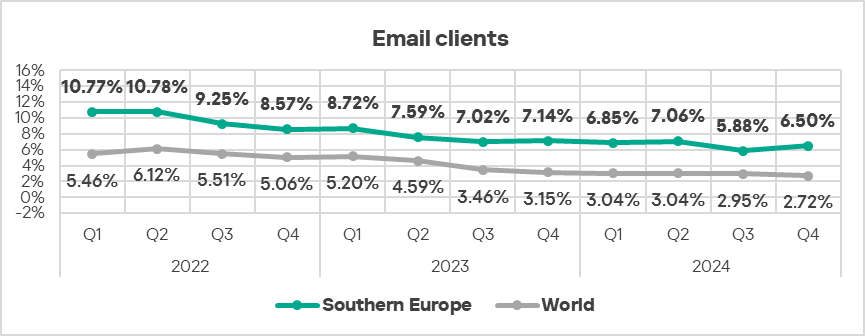
Industries
- The most affected industry in the region, as selected for this report, was biometrics.
- Compared to the respective global averages, the biometrics and building automation sectors saw a higher percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked in Q4 2024 – by 1.2 and 1.1 times respectively.
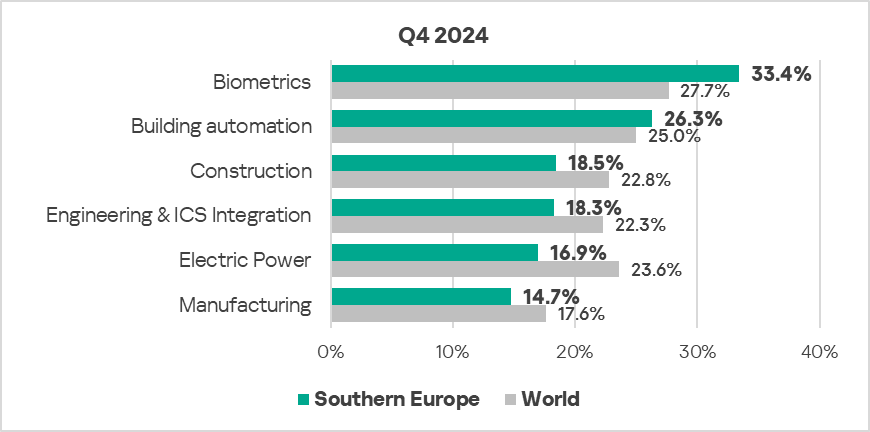
- In Q4 2024, all sectors under observation in the region exhibited an increase in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked:
The most significant proportional increase was in the following sectors:- Biometrics: by 1.1 times.
- Building automation: by 1.1 times.
- Manufacturing: by 1.1 times.
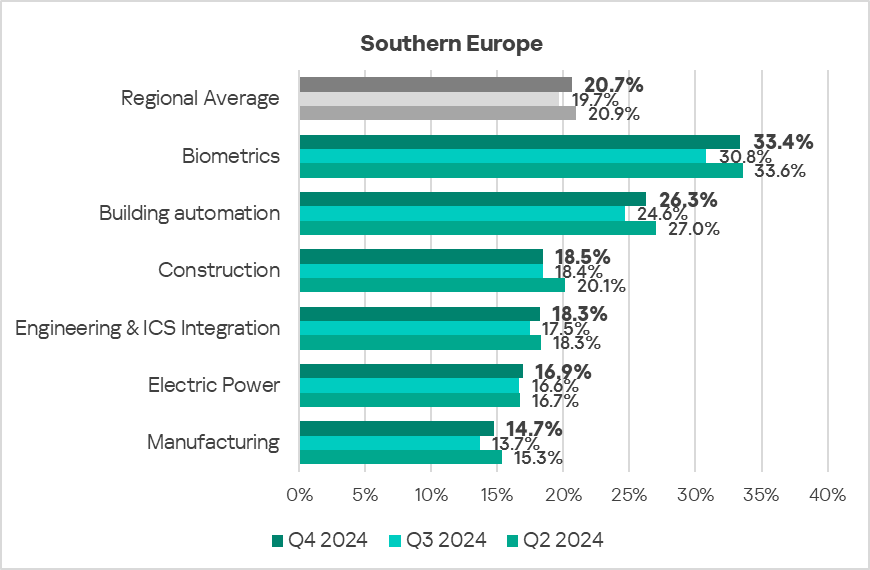
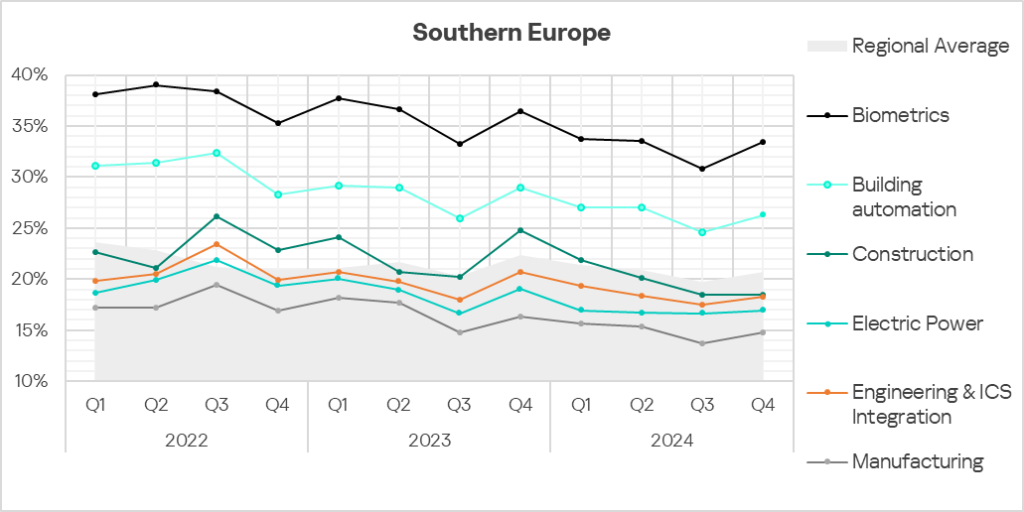
- All selected sectors exhibit fluctuating long-term trends in terms of the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked. The rates in the biometrics and building automation sectors remain significantly higher than the regional average.
Russia
Current threats
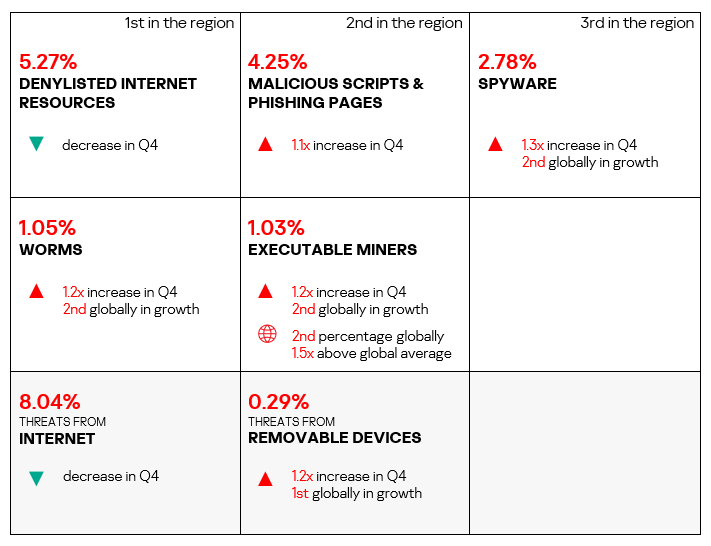
Overall
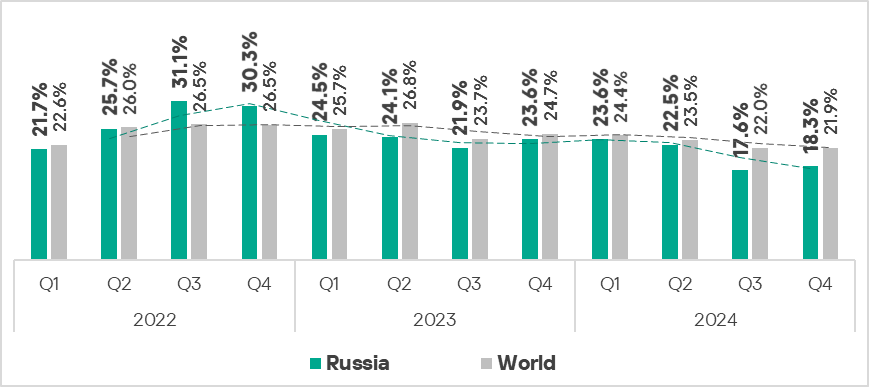
- Ninth in the global ranking by percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
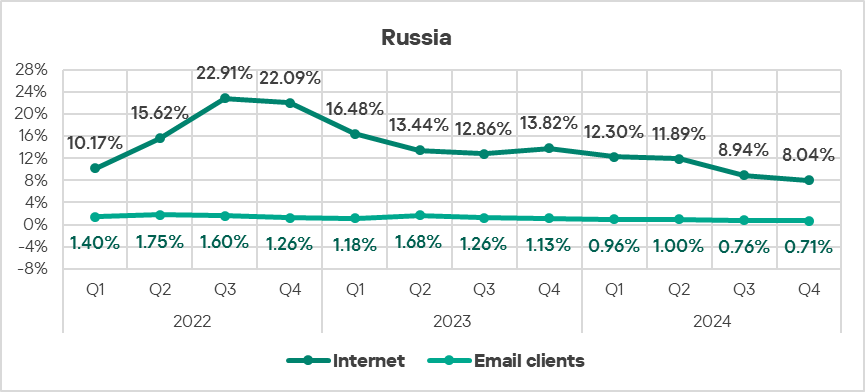
- In Russia, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked has remained below the global average since the beginning of 2023.
- In Q4 2024, the region saw an increase in threats that were blocked on ICS computers.
Comparative analysis
Threat categories
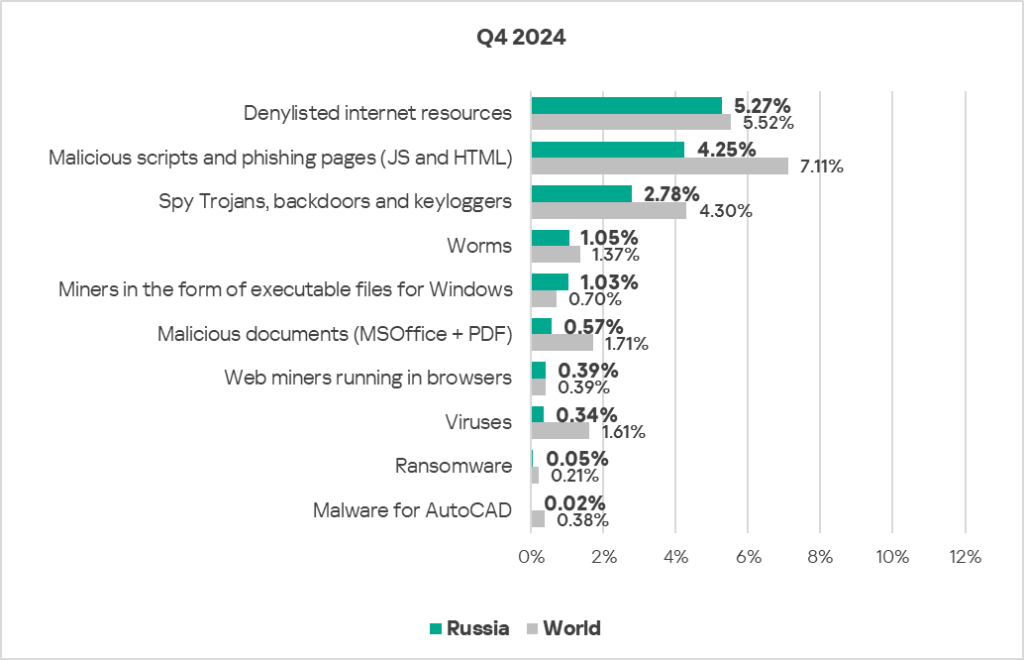
- Compared to the global figures, the region has a higher percentage of ICS computers on which miners in the form of executable files for Windows were blocked: 1.5 times higher (surpassing Q3 2024 levels), ranked second by value globally.
Threat sources
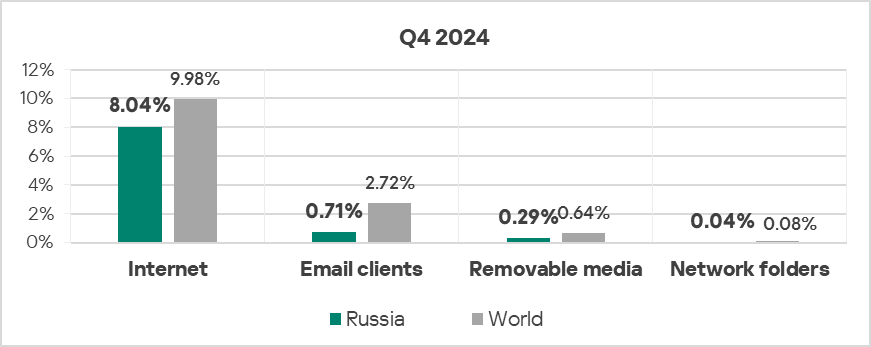
- The region showed lower rates for all threat sources compared to the respective global averages for these sources.
Quarterly changes and trends
Threat categories
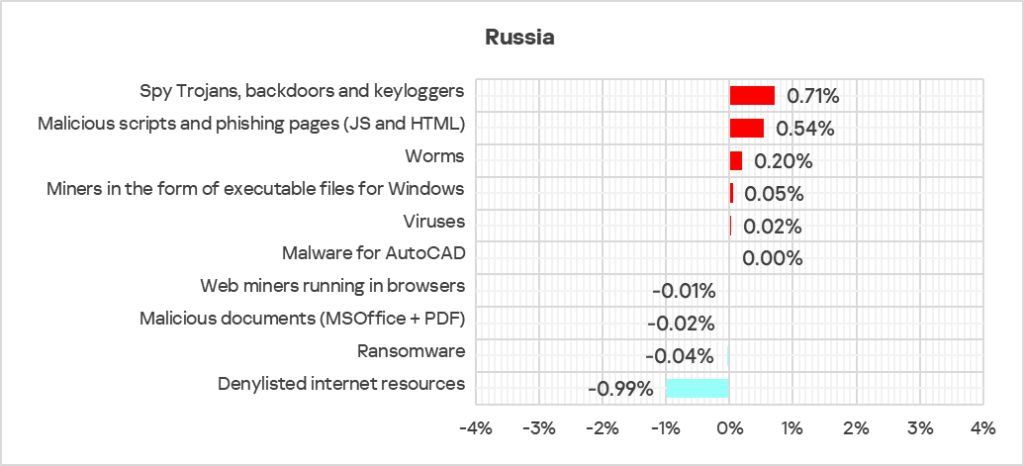
- The largest proportional increase in Q4 2024 was in the percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Spyware: by 1.3 times, ranked second globally in terms of growth.
- Worms: by 1.2 times, ranked second globally in terms of growth.
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: by 1.1 times.
- Viruses: by 1.1 times.
- Executable miners, by 1.1 times, in contrast to the average global trend, ranked second globally in terms of growth.
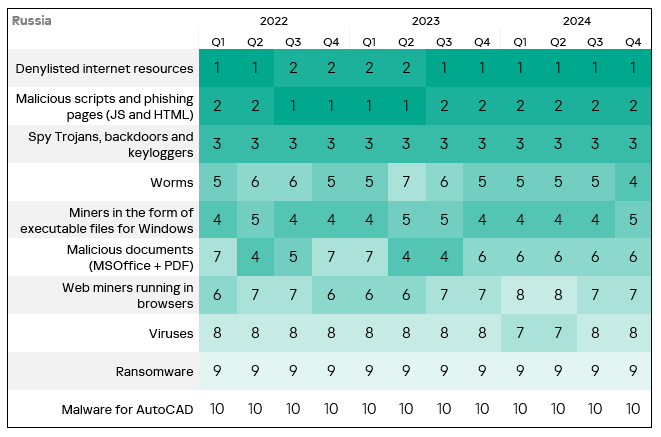
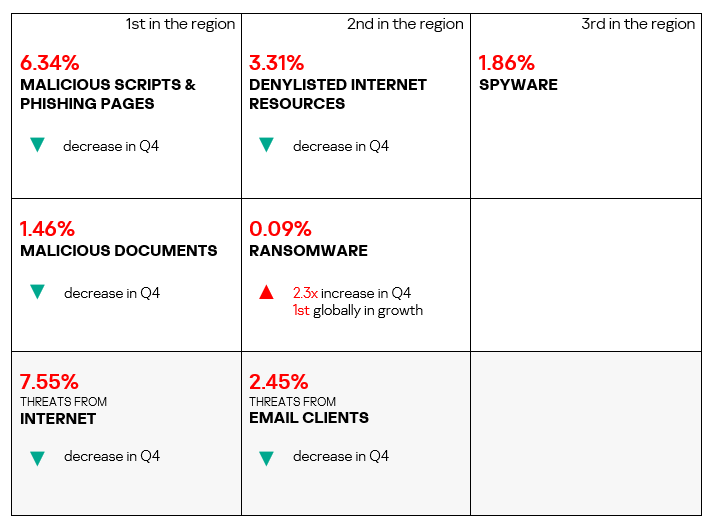
- The heatmap below illustrates changes in the rankings of threat categories in the region since the beginning of 2022. Denylisted internet resources have been the leading threat category in the region since Q3 2023. Worms moved up one position in Q4 2024 – from fifth to fourth.
Threat sources
- Threats from removable devices saw an increase of 1.2 times in Q4 2024. This indicator was first in terms of growth in the ranking of all global regions.

- Threats from the internet, email clients, and network folders exhibited a decrease in Q4 2024.
Industries
- The most affected industry in the region, as selected for this report, was biometrics.
- Compared to the global averages, all sectors under study saw a lower percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
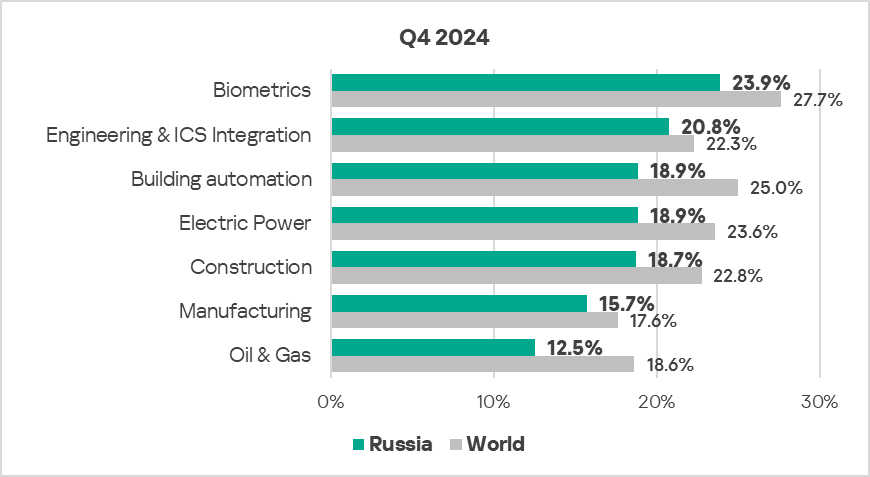
- In Q4 2024, the majority of the selected industries in the region exhibited a decrease in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked. The oil and gas and biometrics sectors showed an increase. The latter grew by 1.1 times.
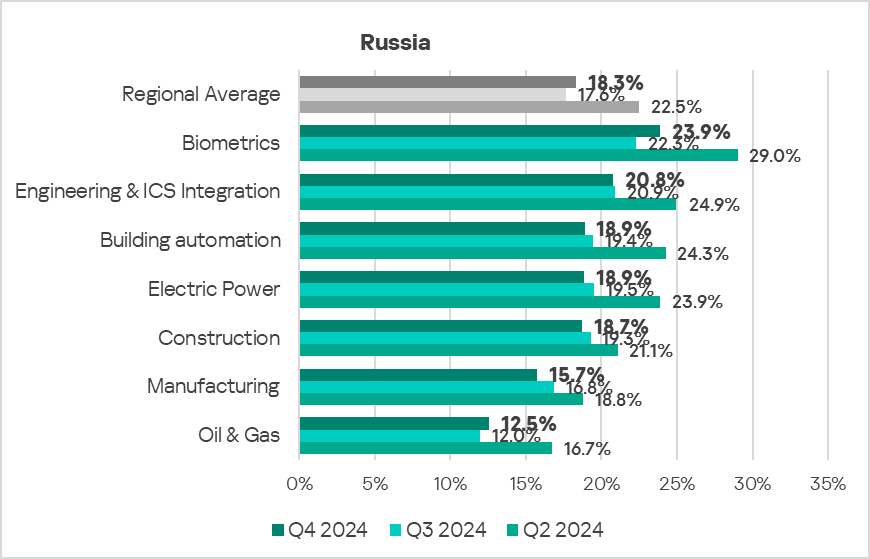
- The selected sectors have shown mostly positive dynamics in their long-term trends since Q4 2022.

Australia and New Zealand
Current threats
Overall
- Tenth place in the global ranking.
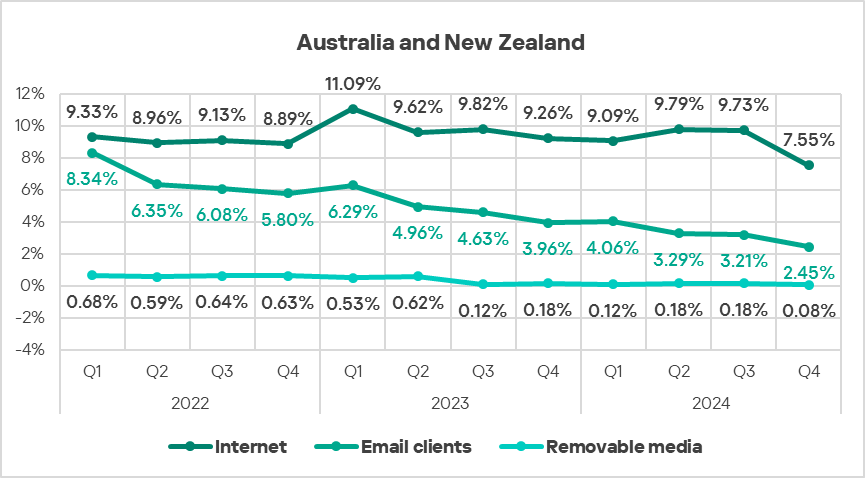
- In Q4 2024, the region saw a substantial decrease in threats that were blocked on ICS computers – around 1.2 times.
- The percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked in the region is noticeably less than the global figure.
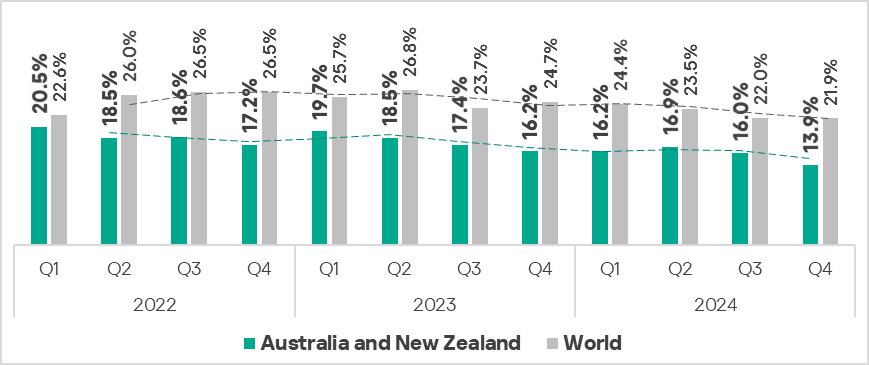
Comparative analysis
Threat categories
- Compared to the global average, the percentage of ICS computers in the region on which each threat type was blocked was lower across all threat types.
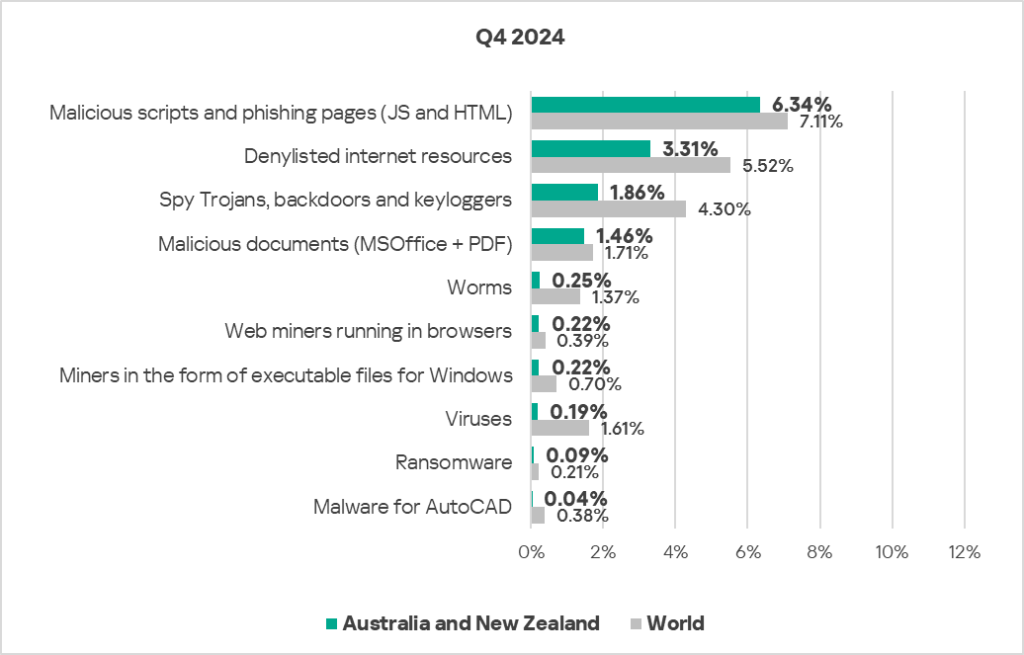
Threat sources
- The percentage of ICS computers on which threats from selected threat sources were blocked was below the global average.
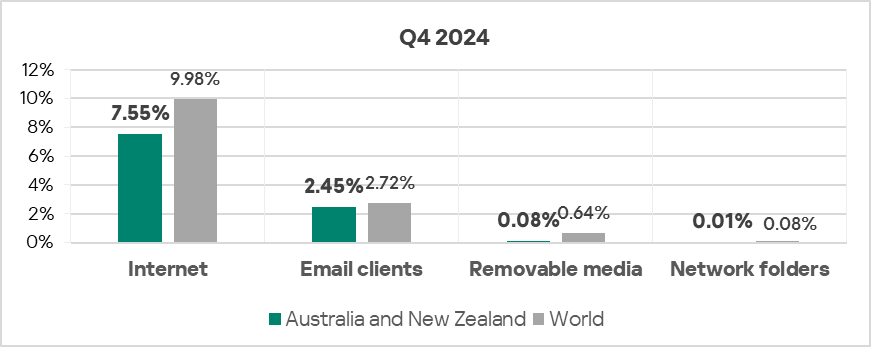
Quarterly changes and trends
Threat categories
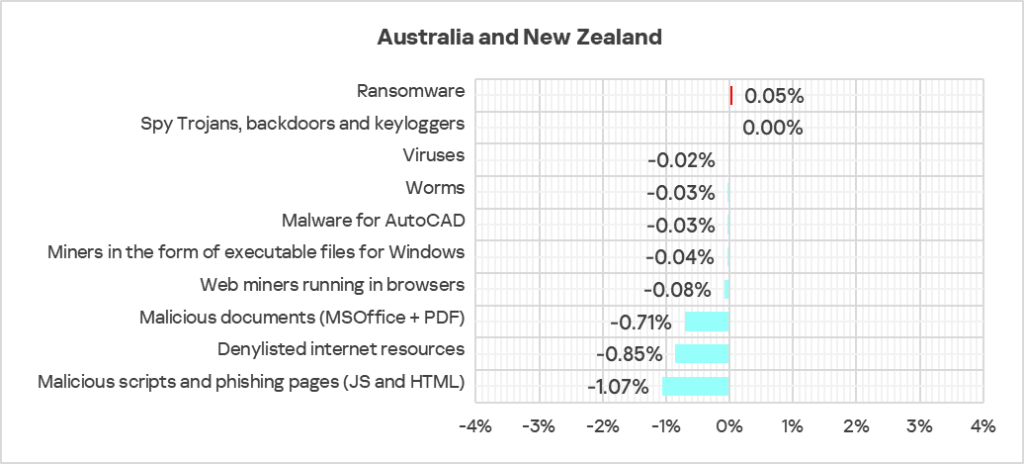
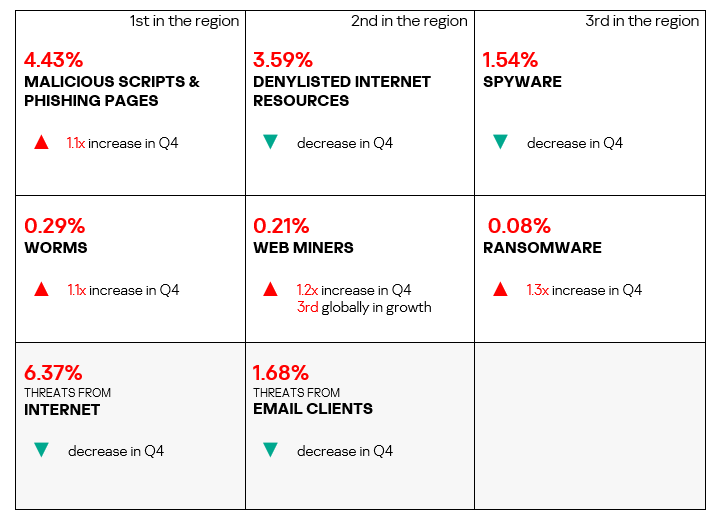
- Compared to the previous quarter, the largest proportional increase was in the percentage of ICS computers on which ransomware was blocked – by 2.3 times. The region ranked first globally in terms of growth of ransomware in Q4 2024.
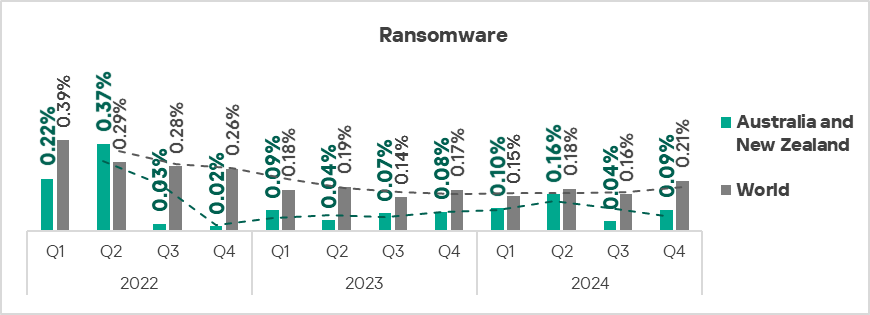
- The heatmap below illustrates changes in the rankings of threat categories in the region since the beginning of 2022. Malicious scripts and phishing pages have been the leading threat category in the region throughout the observed period, while denylisted internet resources have consistently ranked second. In Q4 2024, spyware moved to third place, surpassing malicious documents. Worms moved from sixth to fifth place in the regional rating.
Threat sources
- Threats from all selected sources exhibited a decrease in Q4 2024.
Industries
- The most affected industry in the region, as selected for this report, was building automation.
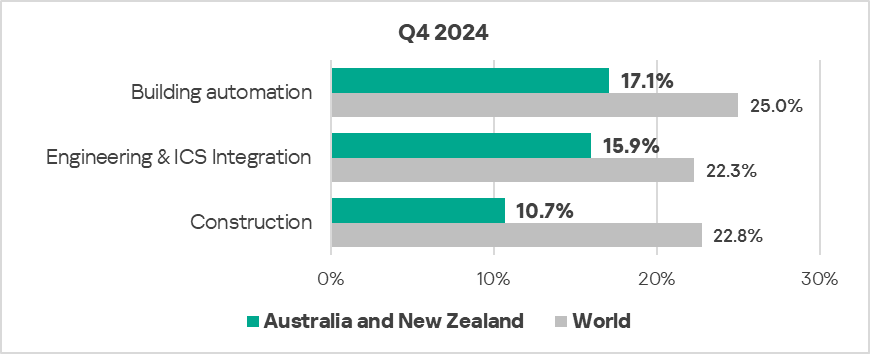
- In Q4 2024, all selected sectors exhibited a decrease in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
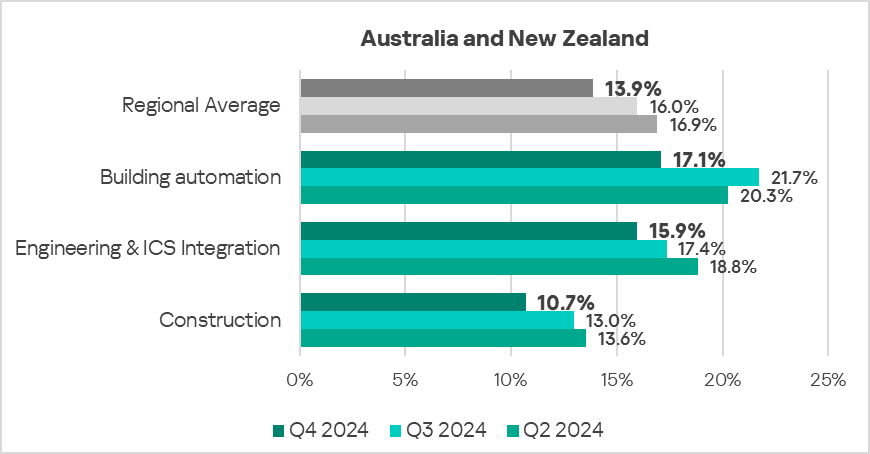
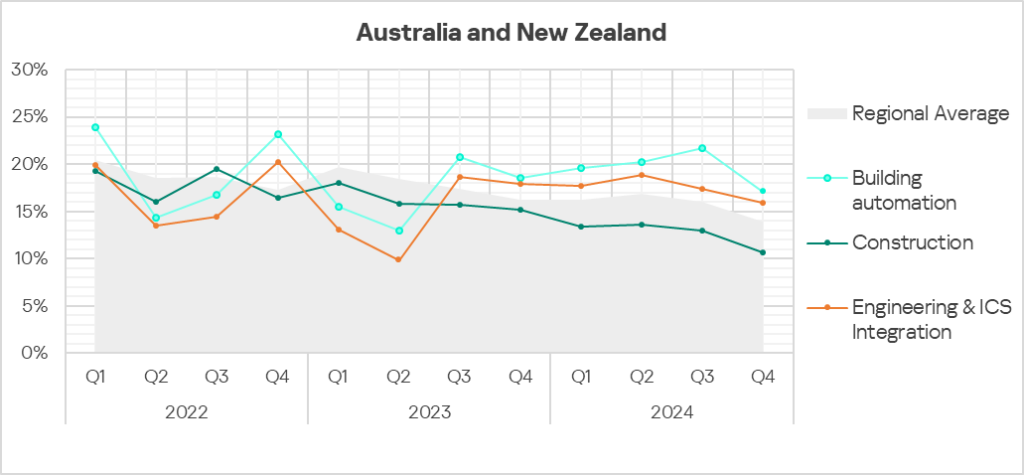
- The building automation and engineering & ICS integration sectors exhibit highly fluctuating trends, oscillating around the regional average until Q3 2023 in terms of the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked. The construction sector continues to show a mostly downward trend, below the regional average.
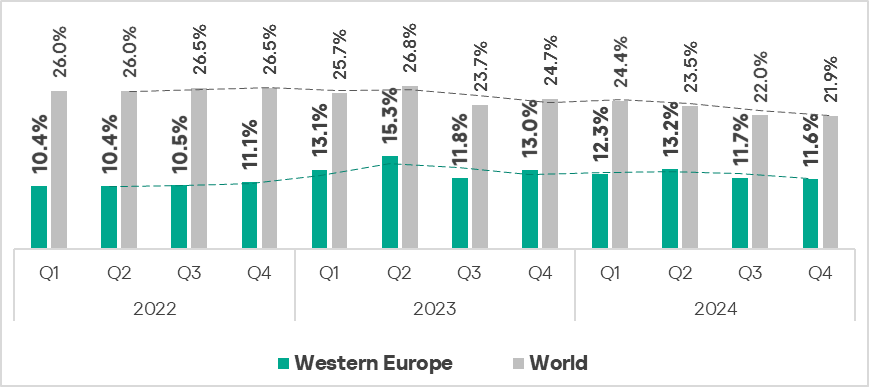
Western Europe
Current threats
Overall
- Eleventh place in the global ranking.
- In general, this region has one of the lowest percentages of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
- In Q4 2024, the region showed a decrease in threats that were blocked on ICS computers.
Comparative analysis
Threat categories
- Compared to the global average, the percentage of ICS computers in the region on which each threat type was blocked was noticeably lower across all threat types.
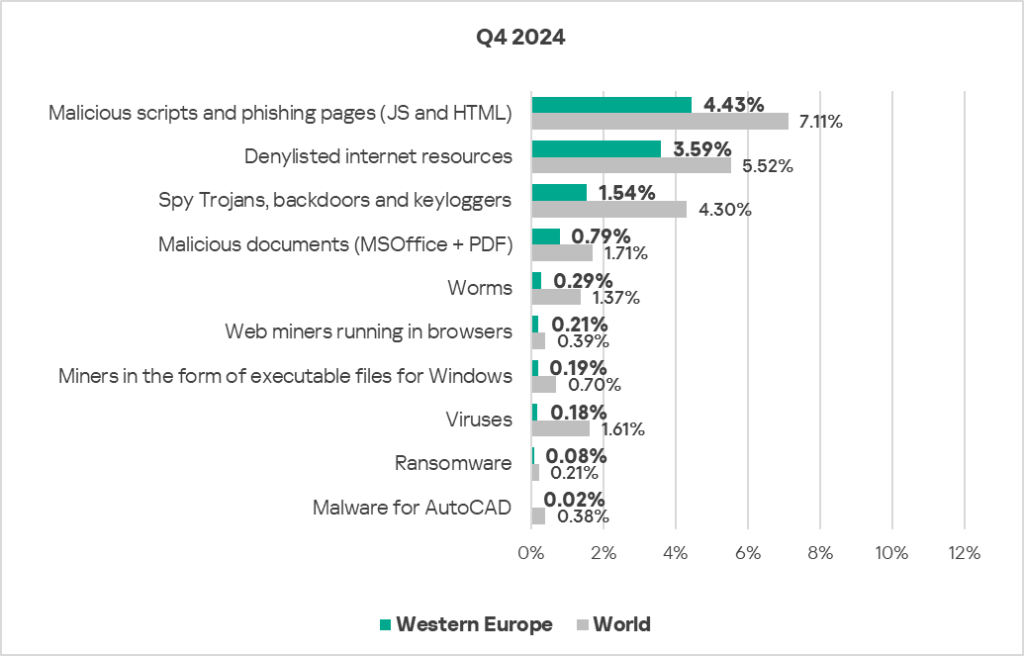
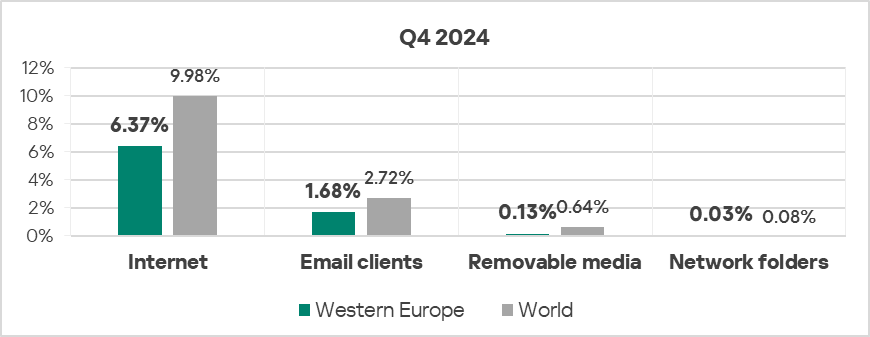
Threat sources
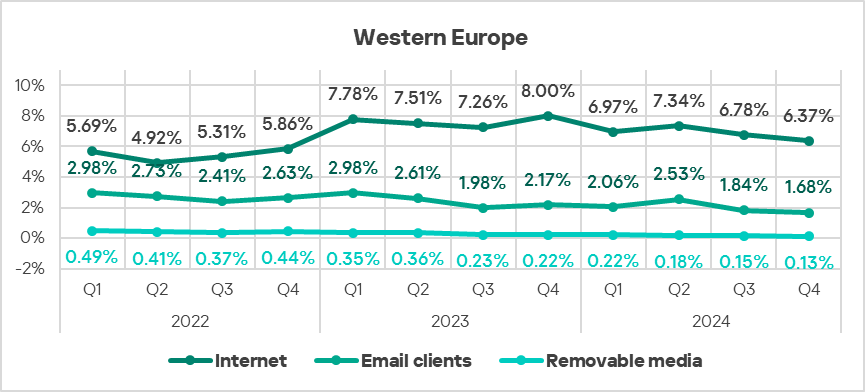
- All threat sources showed values noticeably below their respective global averages.
Quarterly changes and trends
Threat categories
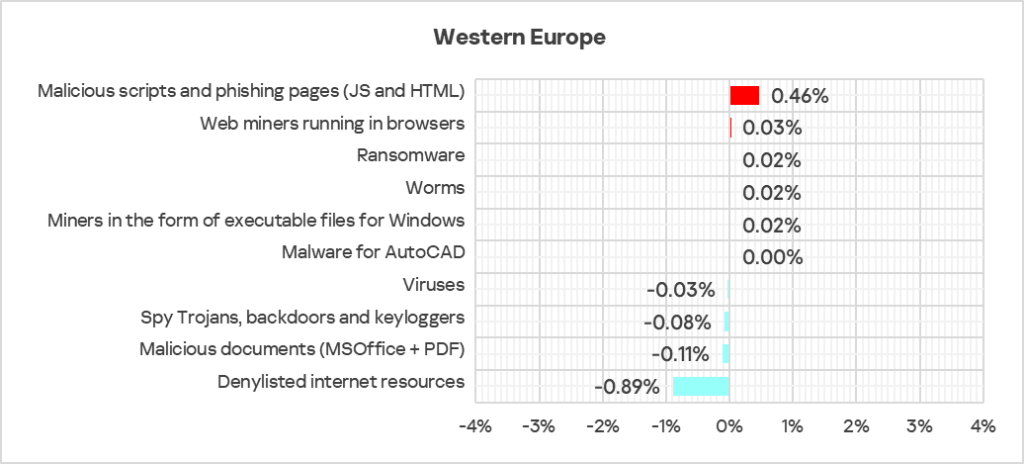
- The largest proportional increase in Q4 2024 was in the percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Ransomware: by 1.3 times.
- Web miners: by 1.2 times, ranked third globally in terms of growth in Q4 2024.
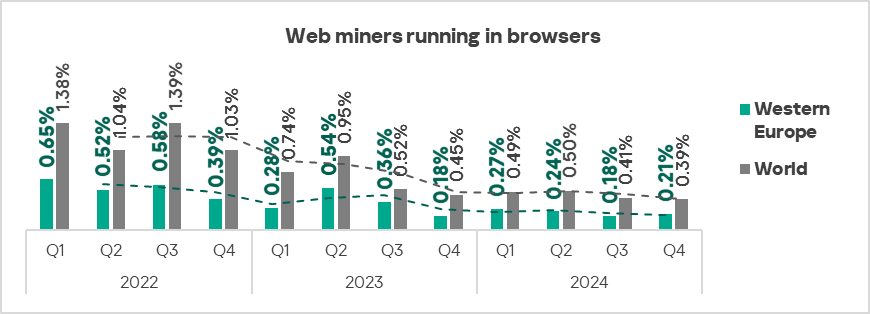
- Executable miners: by 1.1 times.
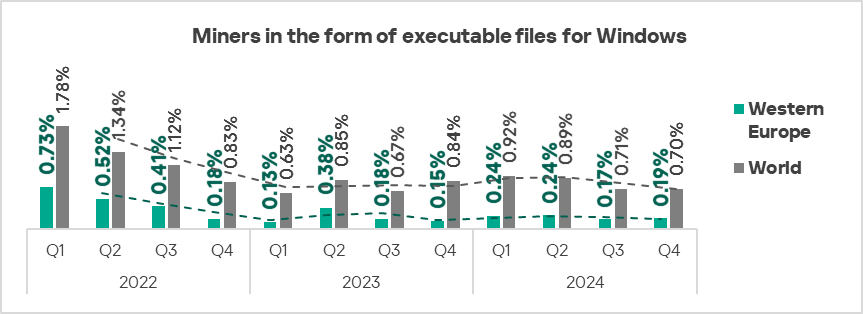
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: by 1.1 times.
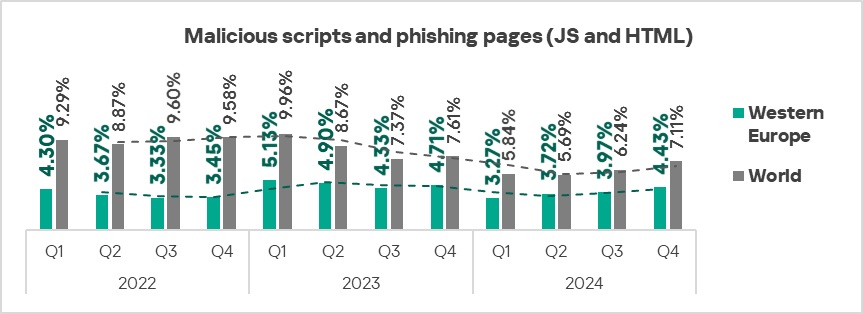
- Worms: by 1.1 times.
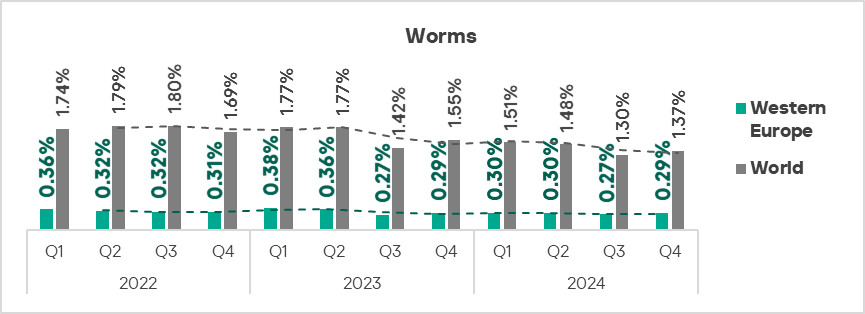
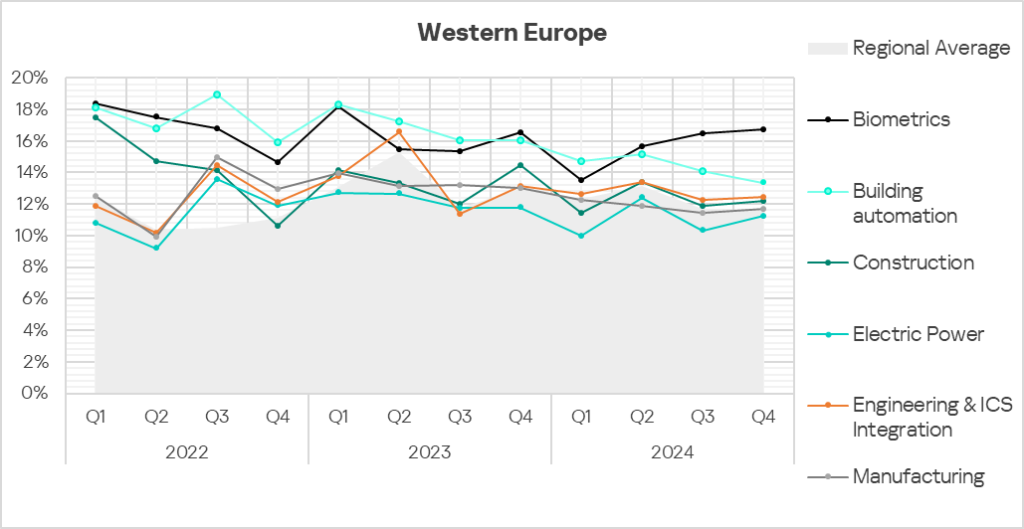
- The heatmap below illustrates changes in the rankings of threat categories in the region since the beginning of 2022. Malicious scripts moved back to first place in Q4 2024. Viruses dropped back to eighth place in the regional threat category ranking.
Threat sources
- Threats from all selected sources exhibited a decrease in Q4 2024.
Industries
- The most affected industry in the region, as featured in this report, was building automation.
- From a global perspective, all sectors in the region remained significantly below the respective global averages.
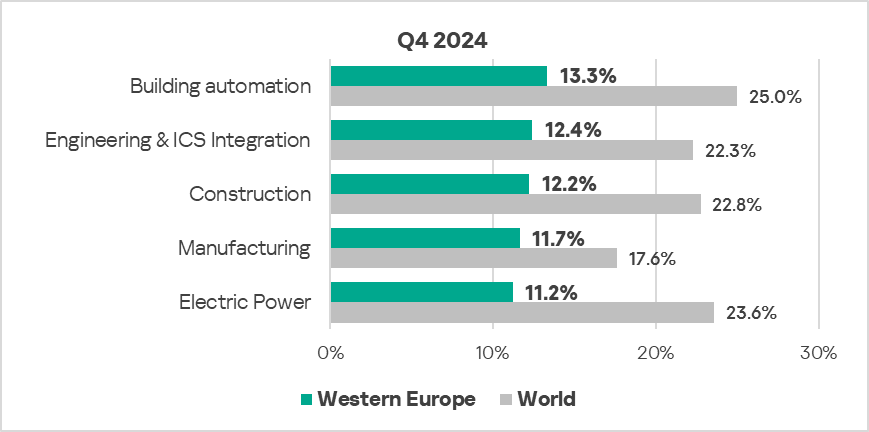
- In Q4 2024, all sectors, except building automation, exhibited an increase in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked. The most notable increase was in the electric power sector – by 1.1 times.
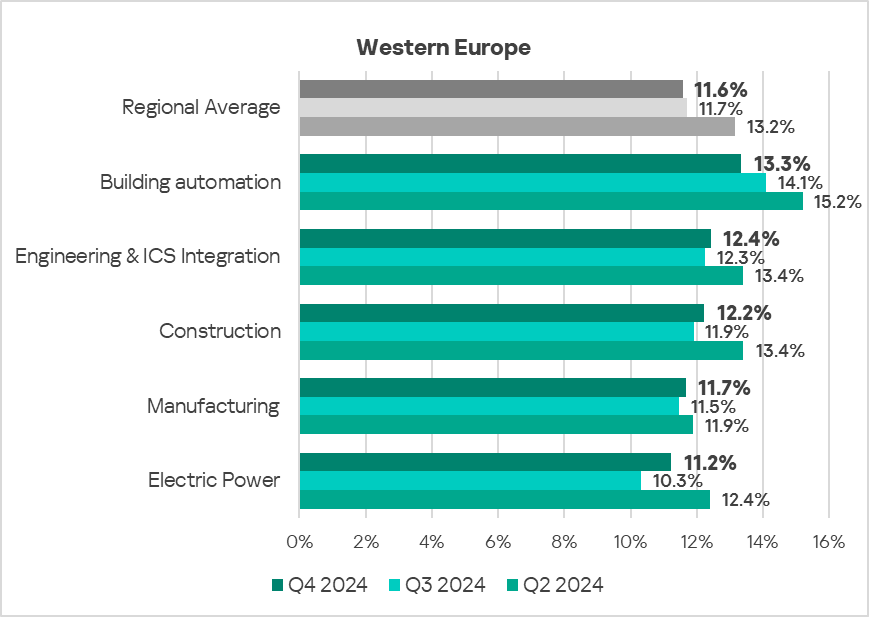
- The long-term trend in the building automation and biometrics sectors remains significantly above the regional average. Biometrics has been demonstrating an upward trend since Q2 2024.
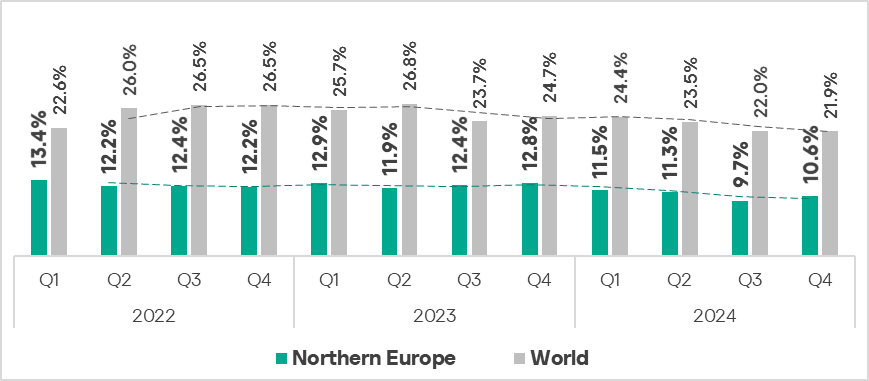
Northern Europe
Current threats
Overall
- Twelfth place in the regional ranking.
- Traditionally the region has the lowest percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
- The percentage is significantly below the global average.
- In Q4 2024, Northern Europe saw an increase in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked – by 1.1 times. The region was third globally in terms of growth.
Comparative analysis
Threat categories
- For all threat types, the percentage of ICS computers in the region on which each was blocked was noticeably lower than the corresponding global average.
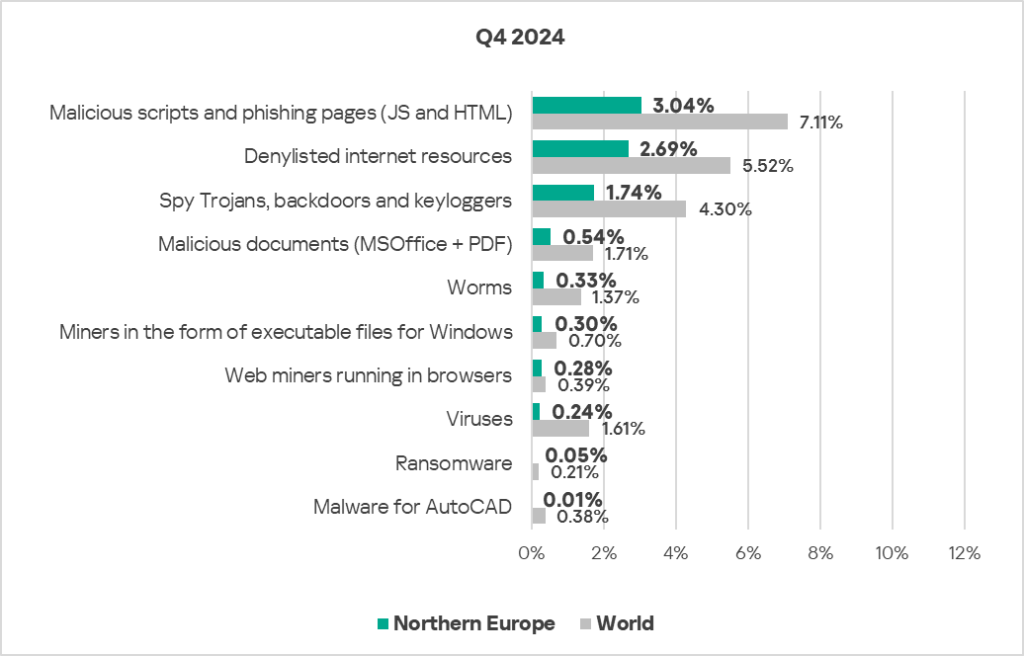
Threat sources
- All threat sources showed values noticeably below their respective global averages.
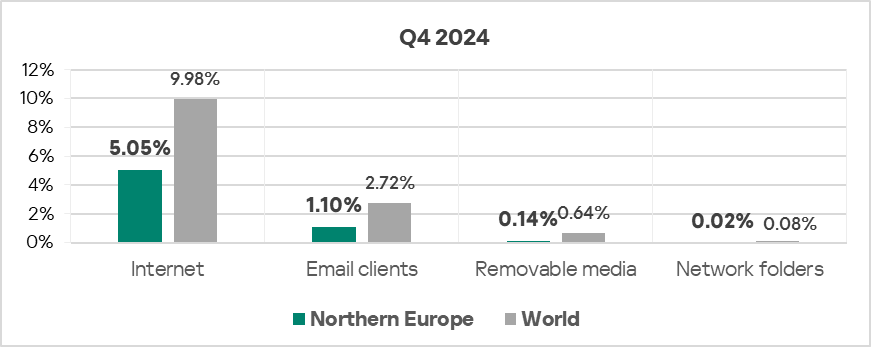
Quarterly changes and trends
Threat categories
- The majority of threat categories exhibited a decrease in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked, compared to the previous quarter.
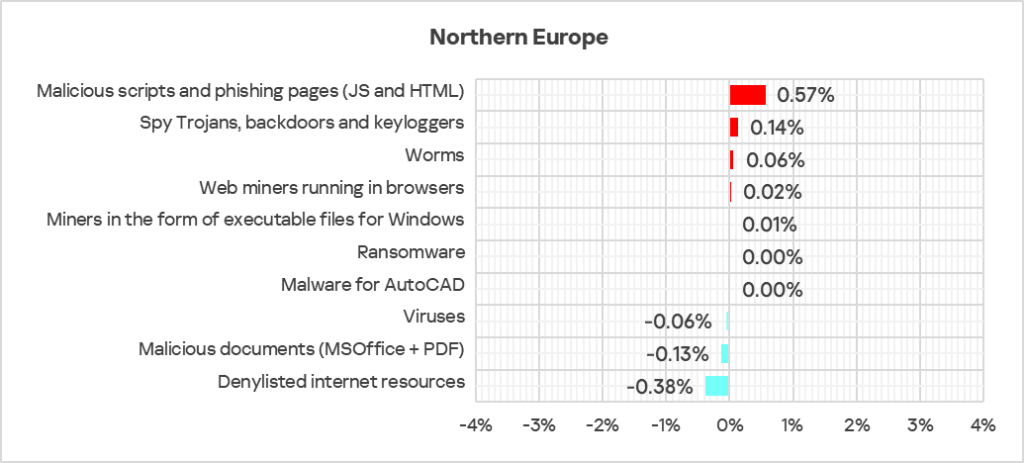
- The largest proportional increase in Q4 2024 was in the percentage of ICS computers on which the following were blocked:
- Malicious scripts and phishing pages: by 1.2 times.
- Worms, by 1.2 times.
- Spyware, by 1.1 times.

- Web miners, by 1.1 times.
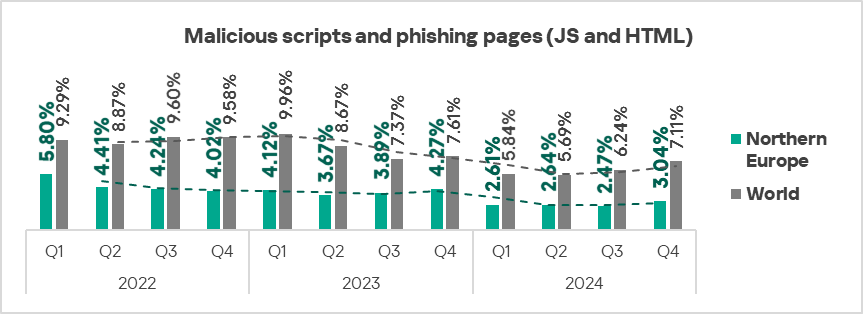
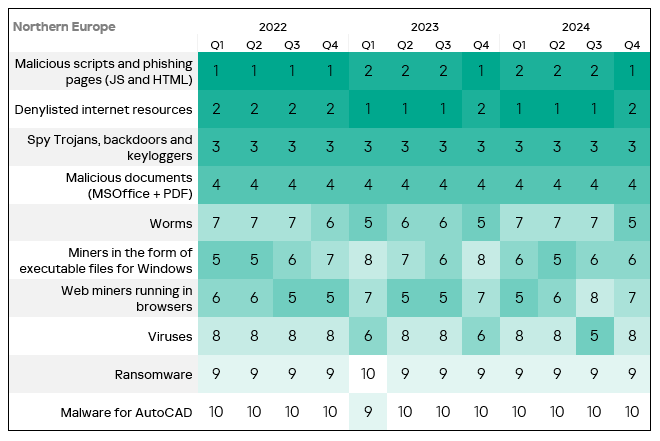
- The heatmap below illustrates changes in the rankings of threat categories in the region since the beginning of 2022. Malicious scripts and phishing pages moved to the top of the ranking in Q4 2024.
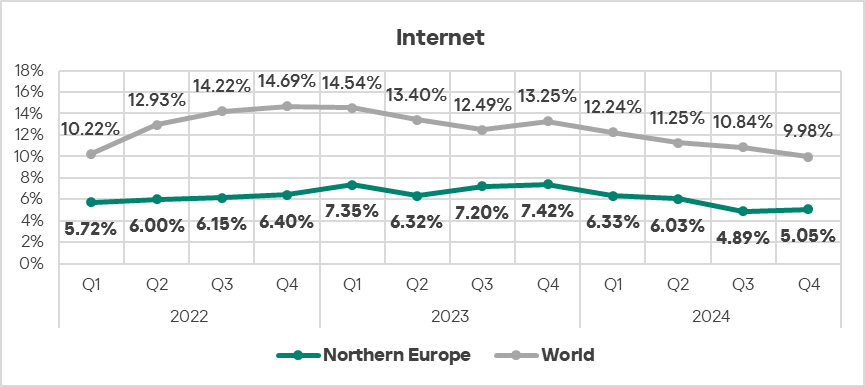
Threat sources
- In Q4 2024, threats from the internet exhibited an increase in the percentage of ICS computers on which such threats were blocked.
Industries
- The most affected industry in the region, as highlighted in this report, was building automation. It ranked fifth in the global ranking of the selected sectors.
- From a global perspective, all sectors under study in the region remained significantly below the respective global averages.
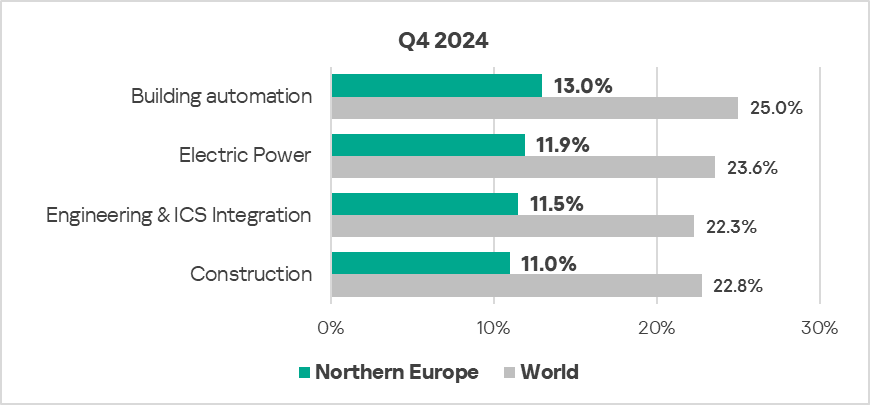
- In Q4 2024, all sectors exhibited an increase in the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
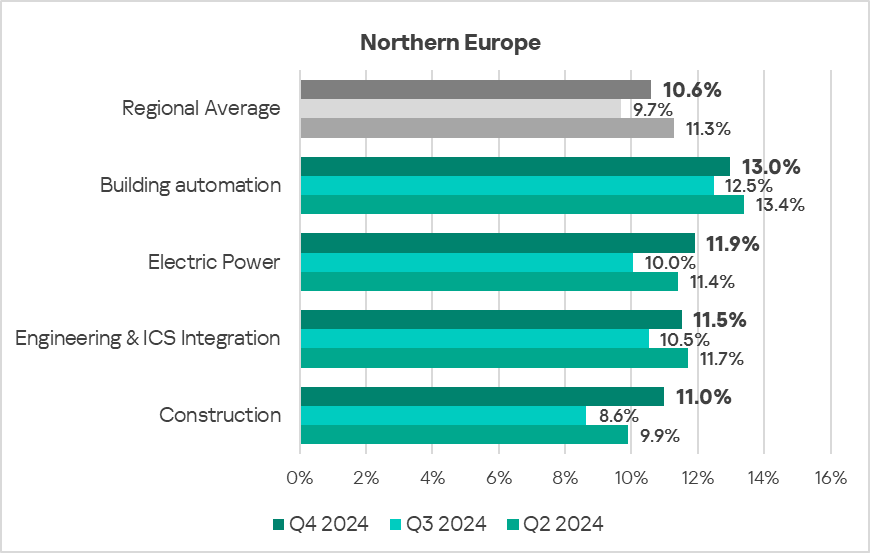
- The most significant proportional increase was in the following sectors:
- Construction: by 1.3 times.
- Electric Power: by 1.2 times.
- Manufacturing: by 1.2 times.
- Engineering and ICS Integration: by 1.1 times.
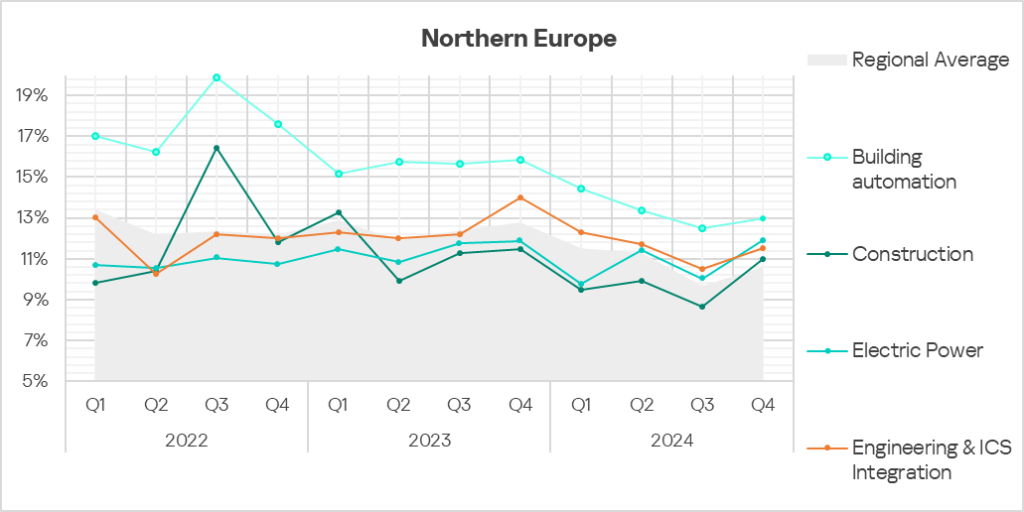
- The building automation trend remains well above the regional average trend, while exhibiting a gradual decline.
Methodology used to prepare statistics
This report presents the results of analyzing statistics obtained with the help of Kaspersky Security Network (KSN). The data was received from KSN users who consented to its anonymous sharing and processing for the purposes described in the KSN Agreement for the Kaspersky product installed on their computer.
The benefits of joining KSN for our customers include faster response to previously unknown threats and a general improvement in the quality of detection by their Kaspersky installation achieved by connecting to a cloud‑based repository of malware data that is not transferable to the customer in its entirety by nature of its size and the amount of resources that it uses.
Data shared by the user contains only the data types and categories described in the appropriate KSN Agreement. This data helps to a significant extent in analyzing the threat landscape and serves as a prerequisite for detecting new threats including targeted attacks and APTs1.
Statistical data presented in the report was obtained from ICS computers that were protected with Kaspersky products and which Kaspersky ICS CERT categorized as enterprise OT infrastructure. This group includes Windows computers that serve one or several of the following purposes:
- Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) servers
- Building automation servers
- Data storage (Historian) servers
- Data gateways (OPC)
- Stationary workstations of engineers and operators
- Mobile workstations of engineers and operators
- Human machine interface (HMI)
- Computers used to manage technological and building automation networks
- Computers of ICS/PLC programmers
Computers that share statistics with us belong to organizations from various industries. The most common are the chemical industry, metallurgy, ICS design and integration, oil and gas, energy, transport and logistics, the food industry, light industry, pharmaceuticals. This also includes systems from engineering and integration firms that work with enterprises in a variety of industries, as well as building management systems, physical security, and biometric data processing.
We consider a computer as attacked if a Kaspersky security solution blocked one or more threats on that computer during the period in review: a month, six months, or a year depending on the context as can be seen in the charts above. To calculate the percentage of machines whose malware infection was prevented, we take the ratio of the number of computers attacked during the period in review to the total number of computers in the selection from which we received anonymized information during the same period.
- We recommend that organizations subject to restrictions on sharing any data outside the corporate perimeter consider using Kaspersky Private Security Network. ↩︎
